Water run-off control plan on cultivated land [แอฟริกาใต้]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Ursula Gaemperli
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff
Watercourses and contours
technologies_956 - แอฟริกาใต้
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Kriel Gys
Provincial Department of Agriculture, North West, Potchefstroom
แอฟริกาใต้
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Dept of Agriculture North West Province (Dept of Agriculture North West Province) - แอฟริกาใต้1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

All participant - Law enforcement [แอฟริกาใต้]
Ordering a land user through the act to implement the SWC.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Pieter J. Theron
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
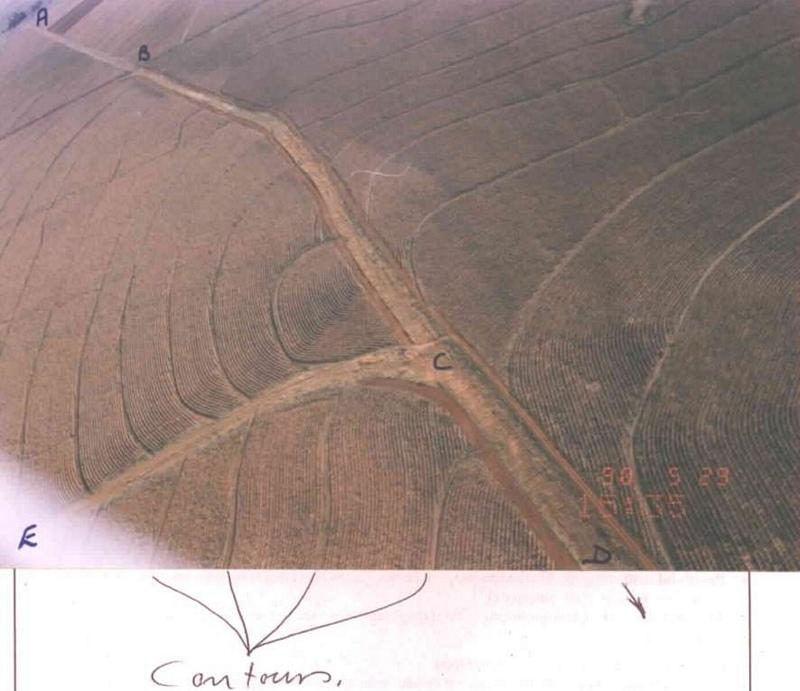
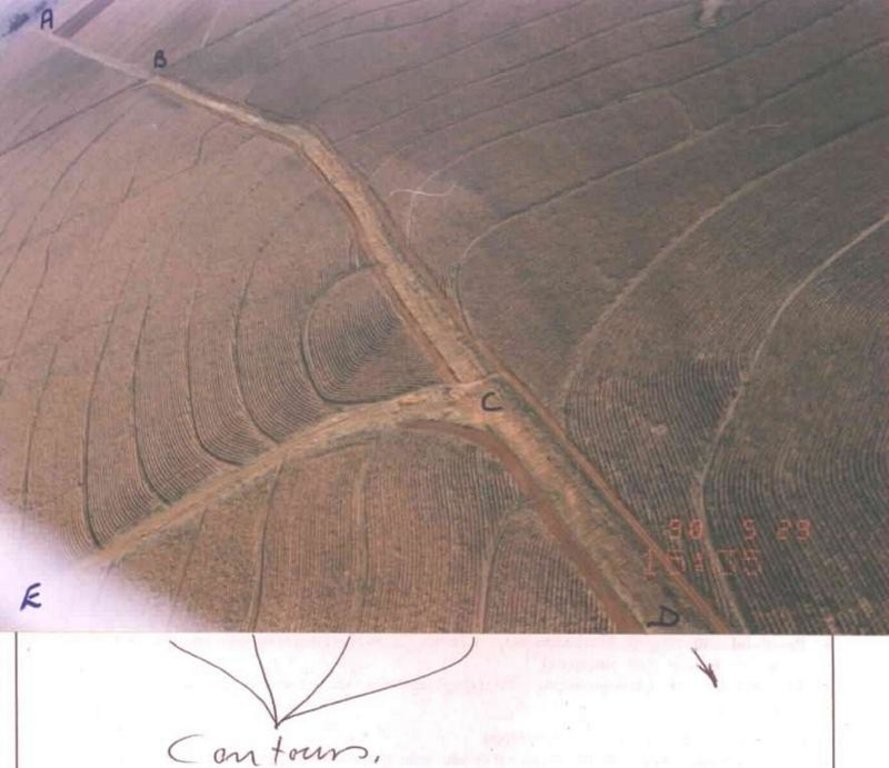
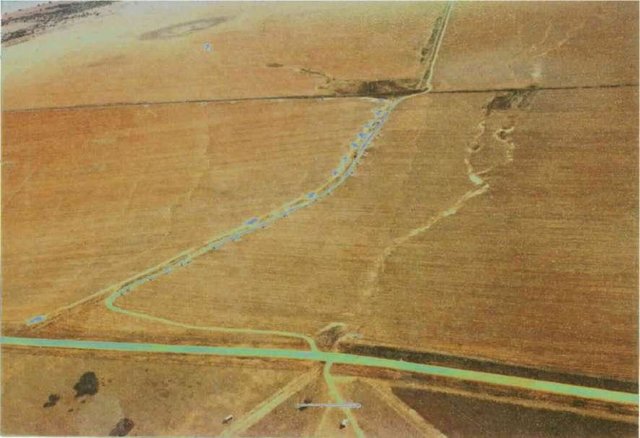
Artificially built watercourses with contour banks with a specific gradient
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Watercourse: According to the topography, one or two watercourses are needed to drain any excess run-off water during high rainfall intensities. A watercourse is built directly downhill. A perennial grass adapted to the specific environment is established in the watercourses. Maintenance requires that the grass must be fertilised according to the climate of the area. Regular (once or twice a year) cutting of the grass is very important to maintain a good grass cover, through which soil erosion in the watercourse can be prevented.
Contour banks: These are built with a gradient to spill the excess water into the watercourse. The purpose of contour banks is to shorten the slope so as to reduce the speed of the water and prevent soil erosion. The maintenance requires keeping the canal in good shape and maintaining the height of the banks.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แอฟริกาใต้
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
North West Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Lichtenburg
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
3.0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 km2.
Although the total extent of the farm is 584 ha, only 250 ha plus 50 ha adjacent land was addressed through this technology.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The contour part came mainly form the USA.
The watercourse part was developed in South Africa.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
major cash crop: Maize
other: Sunflower
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Cultivating lands without the necessary soil conservation works to prevent soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cultivating the lands preventing soil erosion through plant directions
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A7: Others

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour tillage
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes - Cultivating land on a step slope without proper conservation practices.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - How to solve the problem)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Topography; concentrating water in valleys causing soil erosion (steep slopes).), Poor conservation ethic
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
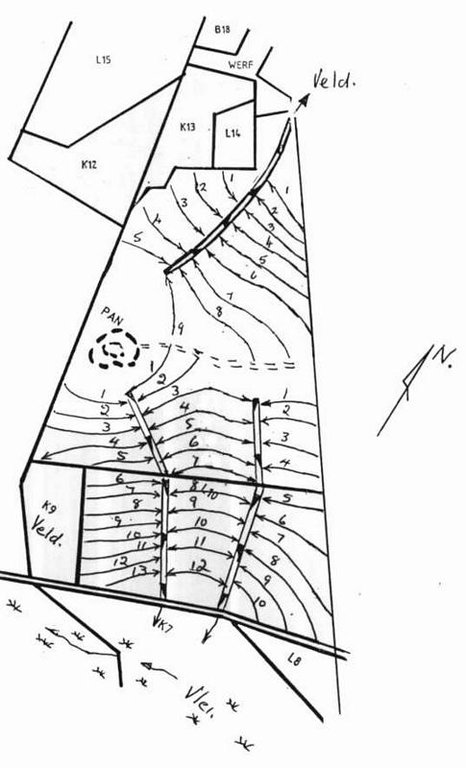
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Water run-off control plan
Location: Lichtenburg. North West
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, Maintain soil fertility as less fertilizer are lost by water run-off
Vegetative measure: watercourses
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): seeds 6-8kg/ha
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Grass species: Digitaria Smuts, Eragrostis curvula, Cynodom dactylon
Structural measure: bunds/banks: contour
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.3-1.75
Spacing between structures (m): 72-33
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Construction material (earth): Construction contour banks with soil form the ditches
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.3%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
ผู้เขียน:
Pieter J. Theron
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
rand
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
6.0
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Established grass in the watercourses | After construction according to design specifications |
| 2. | Surveying | Dry season |
| 3. | Construction of contours | Any time depending on soil moisture |
| 4. | Construction of watercourse | Before growing season |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Construction of contours | ha | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 30.0 |
| แรงงาน | Construction of watercourses | ha | 1.0 | 1660.0 | 1660.0 | 30.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Establish grass | ha | 1.0 | 840.0 | 840.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 4500.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 750.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
50 Contours are constructed on the 250ha Total length of contours = 26.7km In this case the land user received a total amount of R 9042 (1141$) subsidy for the contours.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building contours and watercourses | Any time / Before planting of crops |
| 2. | Building contours and watercourses | Depending on soil moisture / |
| 3. | Maintenance | Before planting of crops / Annually |
| 4. | Cultivation between contours | Depending on the crop / Annually |
| 5. | Maintaining a good grass cover | Rainy season /Once or more times a year depending on the grass |
| 6. | Fertilisation of the grass in the watercourse | Rainy season /Once or twice in the rainy season |
| 7. | Watercourse, cutting the grass | Beginning of rainy season/Annual |
| 8. | Contours repairing flood damage | Dry season/After heavy rains |
| 9. | Contour opening ditches | Before planting of cops/Annual |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor & plough or a grader
Contours per kilometre. NB currant tariff for subsidy. Watercourse construction per volume soil moved and grass establishing per ha above the current tariff for subsidy from April 1998
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Soil moisture and clay contents
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Heavy thunder storms in summer
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Average slope 2-4%
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium - high
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is medium - low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 100% of the land.
90% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (If management is good).
Off-farm income specification: Farmers are dedicated to make a living out of farming, although there are some farmers with an off-farm income such as transport.
Market orientation of production system: Farmers very seldom produce their own food expect for meat.
Level of mechanization: Tractors with modern implement
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
When not possible to work on the contour banks
การจัดการที่ดิน
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
access to roads
input constraints
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Short rows when planting crops as contours are not parallel
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60
หลังจาก SLM:
20
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
25
หลังจาก SLM:
4
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
soil fertility
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
dam siltation
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 11-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
16 percent of all households in the area
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: So little, almost none. The lack in technicians from government promoting this technology and to deliver technical services are the main reasons expect for the poor conservation ethic of the farmers.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Prevent soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good regular maintenance |
| Building up a good layer of topsoil |
| Effective run-off control of excess rainwater |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Effective erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
|
Improve water infiltration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Increase crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Prevent off-site siltation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good maintenance |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Hampers cultivation | Adapt change in cultivation practises |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Cannot think of any |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

All participant - Law enforcement [แอฟริกาใต้]
Ordering a land user through the act to implement the SWC.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Pieter J. Theron
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล