Cultivation of Hing (Ferula assa-foetida) in the watershed [Afghanistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Aqila Haidery
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Alexandra Gavilano
Kesht Angoza da abriza
technologies_1306 - Afghanistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
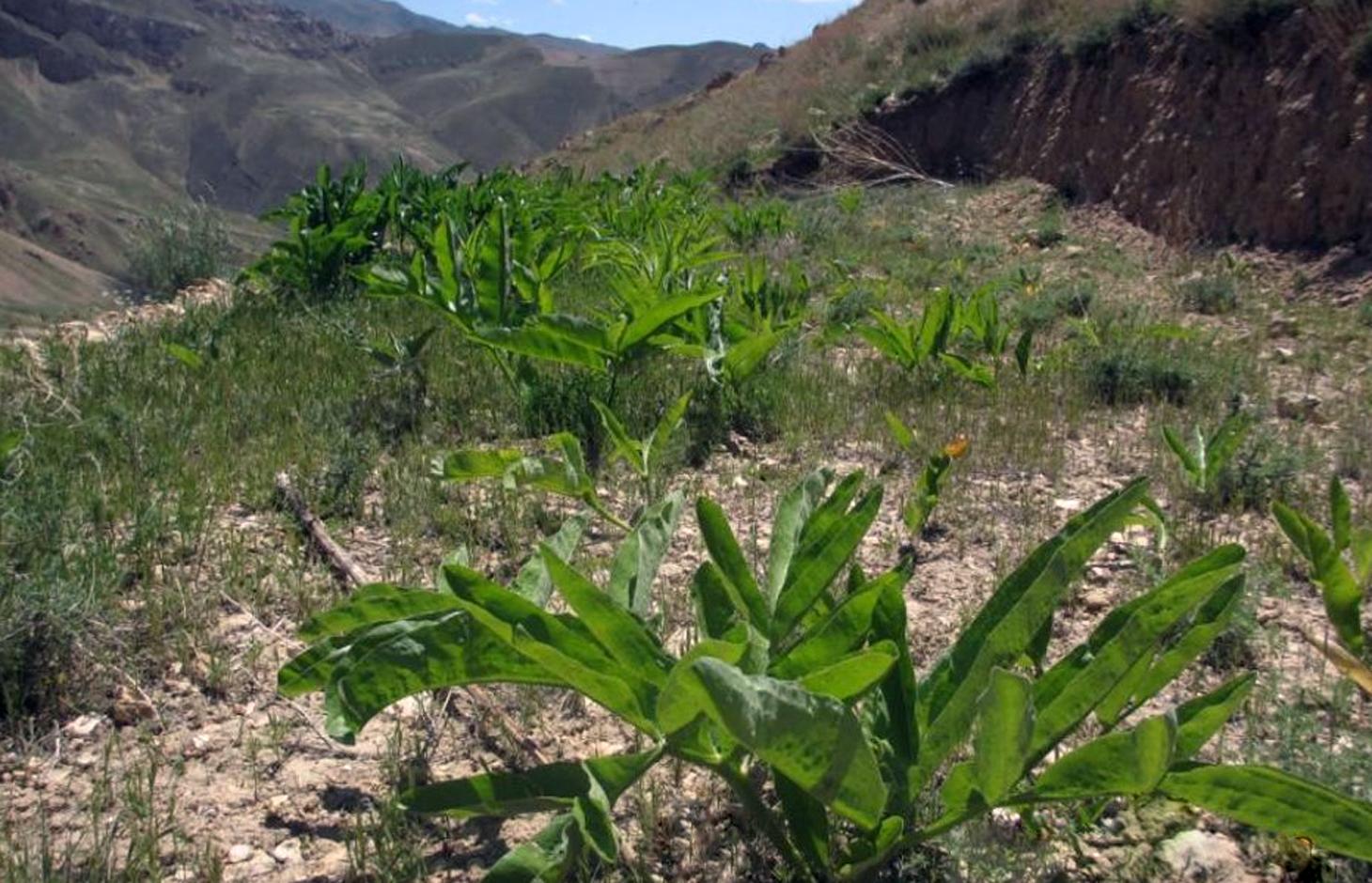
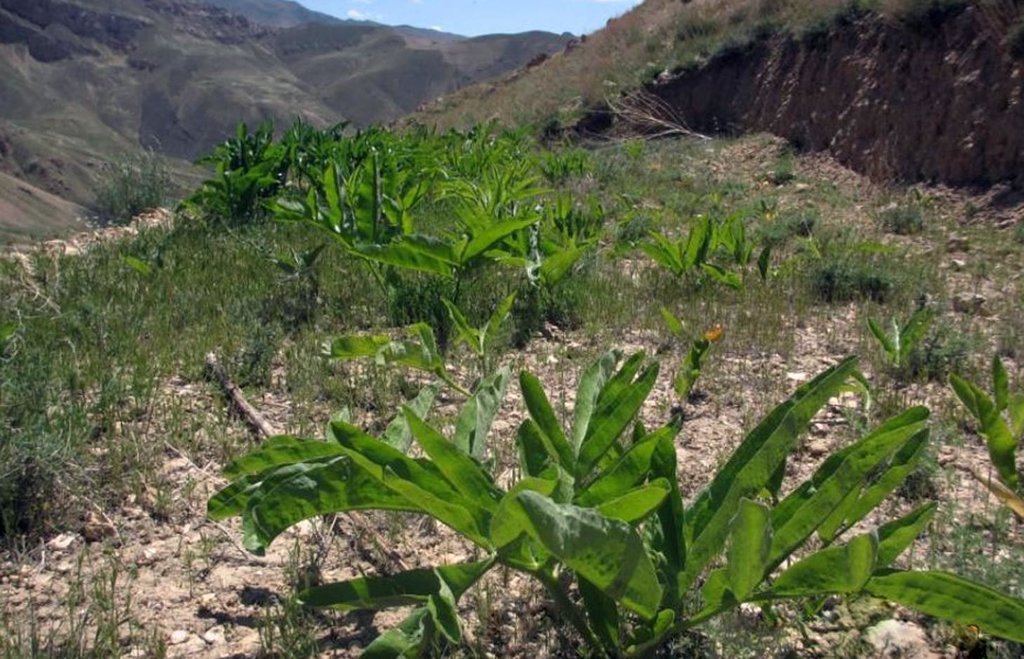
Ferula assa-foetida is an important medicinal plant, a valued cash crop and a native plant of Afghanistan’s range-lands.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Cultivation of hing (Ferula assa-foetida) in watersheds is documented by the Sustainable Land Management Project which is implemented by HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). Ferula assa-foetida, or hing, is a medicinal plant that grows well in shallow sandy and alkaline soils in semi-arid climates and at high altitudes and is a native plant of Afghanistan’s upper catchment areas. Due to the enduring conflict and the consequent breakdown of community-managed grazing in upper catchment areas, most range-lands in Afghanistan are been seriously degraded. Uncontrolled grazing of animals and growing cereal crops on range-lands are the main contributors to the loss of vegetation coverage in upper catchments. One of the negative consequences are flash floods occurring several times a year, damaging agricultural lands, irrigation canals, houses and other infrastructure while often also causing fatalities.
In order to decrease the risk of flash floods, improve pastures and extend cash crop cultivation in upper catchment areas, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation has implemented community-based watershed activities such as structural and agronomic measures to control water runoff.
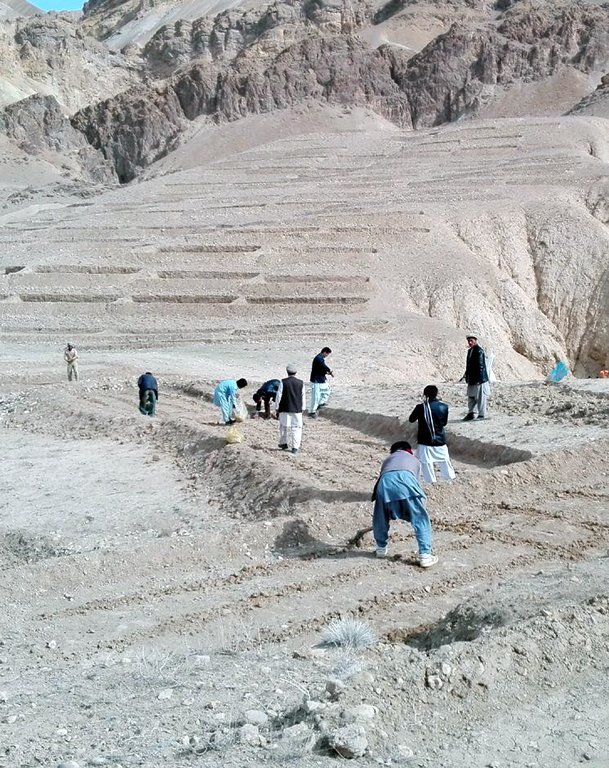
Hing has been identified as a suitable agronomic measure in watershed management in Saighan district. HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and the target communities selected hing as a valuable cash crop and a suitable plant for watershed rehabilitation. Today, hing is cultivated on 1,400,000 m2 (140 ha) in nine watersheds and with the participation of 1500 families. The growing period of hing depends on the local climate but tends to be 5-10 years and culminates in the pants’ flowering. During the first five years hing has grey colored leaves. Later a stem appears and grows more than a meter high. The stem is large and yellow and at the end of the main and subordinate stems are yellow flowers. The width of the hing root varies between 7-15 cm and usually goes as deep as 30-40 cm into the soil. Hing plantations have been established with the involvement of the local communities and are managed by the responsible watershed committee. The harvest of hing is organized by the watershed committee and all households have the right to participate and sell hing for income generation. To maintain watershed activities, such as hing cultivation, a safe box has been created for each community-managed watershed. The watershed committee manages the safe box and collects funds for maintenance, community development and emergency projects, according to the watershed management plan which has been developed by the local communities with support of HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation.
Natural / human environment: Bamyan is a remote province of Afghanistan with a high poverty rate. It has a semi-arid climate with cold winters and hot and dry summers. During winter, temperatures can drop below -22 degrees. Summer temperatures can reach to 34 degrees in the month of July. The average annual rainfall in the area is about 230 mm and some years can be very dry. 90% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture for their livelihoods and off-farm activities are marginal. The growing season in Saighan district is relatively short from April to October and farmers can produce only one crop per year. Farmers with access to irrigation water cultivate cash crops, for example potato and vegetables, in addition to staple (wheat) and fodder crops. Those without access to irrigation water cultivate wheat and fodder crops only. Water scarcity from May to September may result in a lack of high value crops.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Afghanistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Bamyan
Further specification of location:
Saighan
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
1.4
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
- Re-introduction
Comments (type of project, etc.):
The technology was introduced since 2012
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- medicinal, aromatic, pesticidal plants - perennial

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Semi-nomadic pastoralism
Intensive grazing/ fodder production:
- Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of management in upper catchment area over the last decades resulted in a severe loss of vegetation and in the loss of biodiversity. Uncontrolled grazing of animals during the spring season prevented seed production of domestic plants. Hot temperature in summer burnt the remaining parts of domestic plants. Each year, the soil is washed away by heavy rainfalls creating gulleys which further reduced the vegetation cover.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The users of watershed areas cut shrubs for fuel and graze their animals. The lack of alternatives left them to overuse resources in upper catchment areas during war and conflict.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: March to July
Livestock density: 10-25 LU /km2
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
No

Grazing land
- Extensive grazing
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cultivation of medical plants
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
Comments:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, cover cropping
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
Comments:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (The upper catchment area have broken to agricultural lands), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Domestic shrubs have been cut and have been used for fuel energy), overgrazing (Without management people grazed their animals in spring season and prevented from the plant seed production.), war and conflicts (3 decades internal wars in Afghanistan)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Continiuosly 3 drought years also had a rule for burning plants in upper catchment areas), poverty / wealth (During internal wars, people were not able to go in other provinces and only they had access to agriculture land and livestock for their livelihood)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
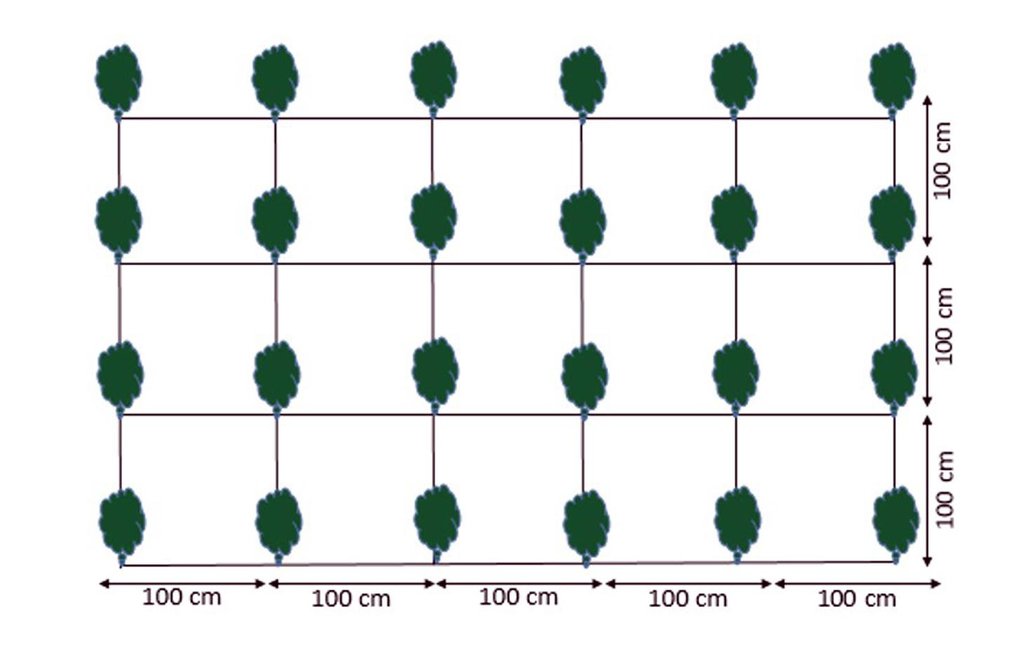
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Cultivation plan of Ferula assa-foetida:
Plant to plant distance 100 cm.
Line to line distance 100 cm.
Seed depth 1-1.5 cm with;
3-6 seeds in one spot.
Location: Saighan watersheds. Bamyan
Date: 18/04/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase of infiltration, Increase vegetation cover through cash crop
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida
Quantity/ density: 4 plant/m2
Remarks: plant to plant and line to line 100 cm
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida and other domestic plants
Quantity/ density: 1 m2
Remarks: Growing domestic plants between Ferula assa-foetida plants
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida and other plants cover the naked area
Author:
Shabir Shahem, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation, Afghanistan
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Afghani
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
67.69
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
5.17
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | labour | ha | 1.0 | 12.92 | 12.92 | 25.0 |
| Plant material | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 115.0 | 115.0 | 25.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 127.92 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1.89 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hiring guard for protection of watershed from uncontrolled grazing |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
In 2015, the government of Tajikistan did not limit the export of seeds to Afghanistan.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Good quality seeds are available in Tajikistan. If the government of Tajikistan limits exporting seeds to Afghanistan, seed costs may increase.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are rich.
35% of the land users are average wealthy.
45% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The importance of off-farm income is marginal. However, hing cultivation in the watershed presents a viable opportunity to generate income off-farm for the involved communities. Hing can contribute up to >50% of off-farm income.
The watershed belongs to the communities and all households have the same rights.
The income is saved in a communal safe box and is spent for community development and emergency issues.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Income and costs
farm income
Socio-cultural impacts
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
Watershed committee manage the income of Ferula assa-foetida productions through safe box investment
contribution to human well-being
Comments/ specify:
Improve the economic opportunities of the community to generate income
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
5
Quantity after SLM:
25
Comments/ specify:
Vegetation coverage
Soil
soil moisture
Quantity before SLM:
10
Quantity after SLM:
30
Comments/ specify:
When the plants grow more, cover area and infilterate runoff
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
5
Quantity after SLM:
50
Comments/ specify:
Vegetation coverage
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
beneficial species
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
Comments/ specify:
Vegetation coverage
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
Reduction of flash flood protect lower part resources
damage on public/ private infrastructure
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
| local windstorm | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | not known |
Comments:
Should be cultivated away from flood stream area.
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
Comments:
The estabIishment costs are high because hing yields only after five years. However, the investments and maintenance costs are quickly returned once hing can be harvested.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
750 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
In this calculation, the total number of families in 13 villages are considered.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The establishment costs are too high.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Increase in production of the valuable plants in the upland areas. |
| Protection of the lower lands from the risk of flash floods. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Introduction and increase in valuable cash crop cultivation in unproductive lands. |
| New income opportunity and increase in income of the community members. |
| Reducing flash flood through increasing vegetation coverage |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| The watershed area is common land. | Need active watershed committee members to manage well (good governance). |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| People lack alternatives and have therefore no stake to protect the upland areas. | Negotiation with herders to reduce the number of their livestock because of introduction of as new alternative source of income. |
| Tangible benefits are only visible after five years. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
17/04/2016
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules