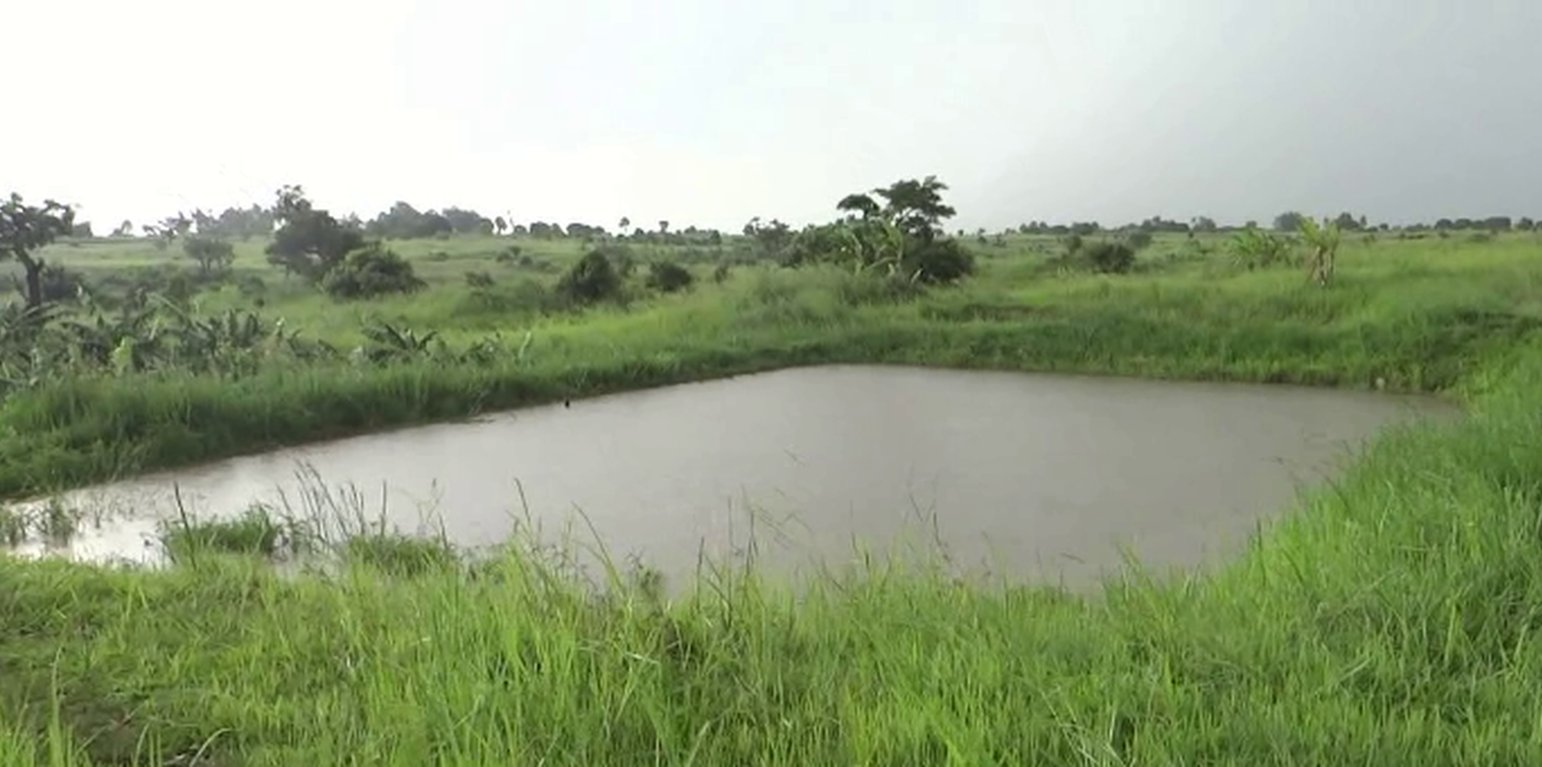




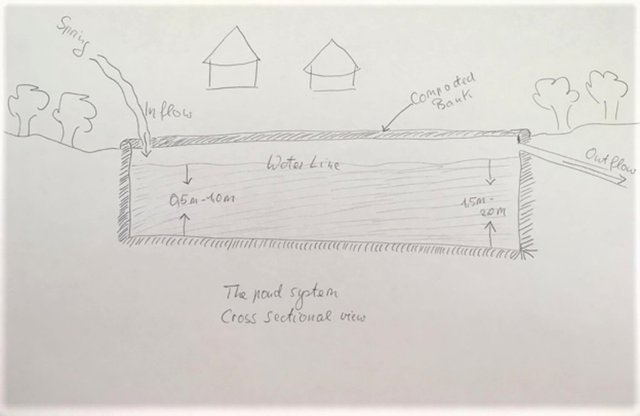
Fish ponds are a common feature in Northern Uganda specifically constructed to raise fish for home consumption and sale to supplement household incomes. Often they are situated on gentle slopes (3-5%) and in wetlands protected with natural vegetation on the levees to act as stabilizers. They are usually recharged from a natural spring.
Establishment of a fish pond requires initial consultation with the extension agents or experts to access knowledge, skills on establishment as well as proper procedures including testing water suitability, presence of reliable water to constantly provide water to the pond, labour, hoes, wheel barrows, spades and slashers.
Establishment activities for the fish pond requires at least 3-5 persons for a period of 5 days per week for the following activities: (i) contacting experts or extension agents for guidance (ii) identifying of suitable land for fish pond establishment (iii) training on digging fish ponds (iv) purchasing equipment required (v) hiring labour and negotiating the payment (vi) excavating the pond and, (vii) identifying the right species of the fish and stocking the fish.
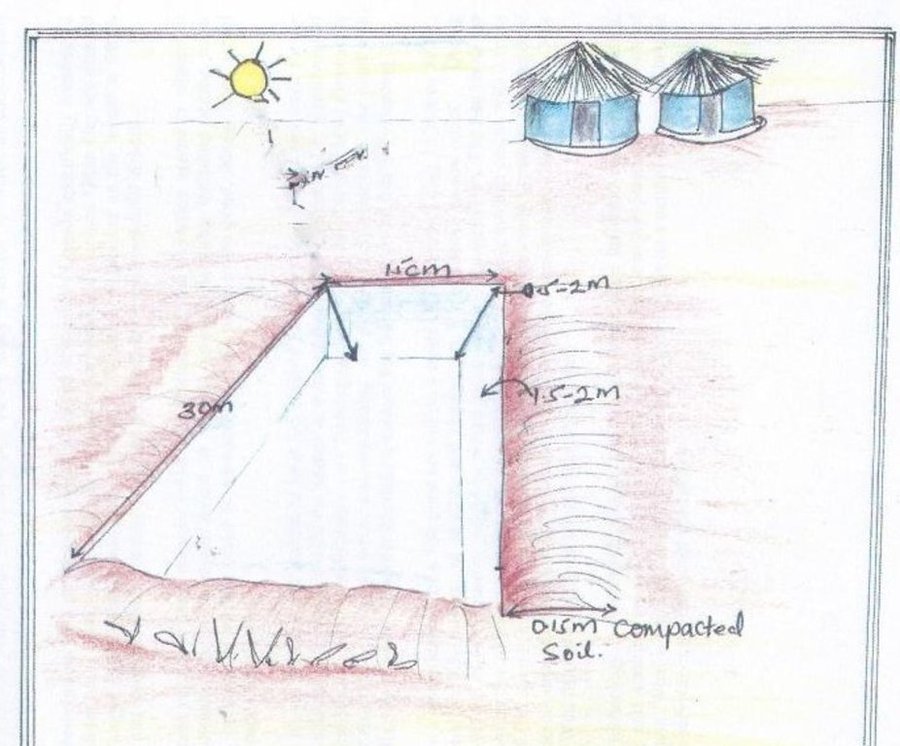
The technical specifications of a fish pond are 30 metres long and 15 metres wide. The depth should be 0.5-1metres at the shallow end and 1.5 -2 metres depth at the pond's outlet. During construction, the soil at the bottom of the planned pond needs to be well compacted. The bottom of the pond should be free of stumps or debris so to avoid leakage through cracks. The banks of the pond consists of compacted earthen rims of approx. 0.15m height and the 0.20 m width.
There shoud be 2 types or more of fish species kept in the fish pond. Sunlight can generally penetrate the pond waters to a depth of about 30-80 cm depending on the water level. The fish species mostly kept include Tilapia, Nile Perch and wild fish.
Once the technology is established the pond system requires only maintenance costs for removing weeds, feeding, restocking and slashing around the pond.
What is not liked about this technology is that it relies on a natural spring. In case of drought survival of the fish is not guaranteed.
地点: Omolo District, Northern Region,Uganda, 乌干达
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
实施日期: 2007
介绍类型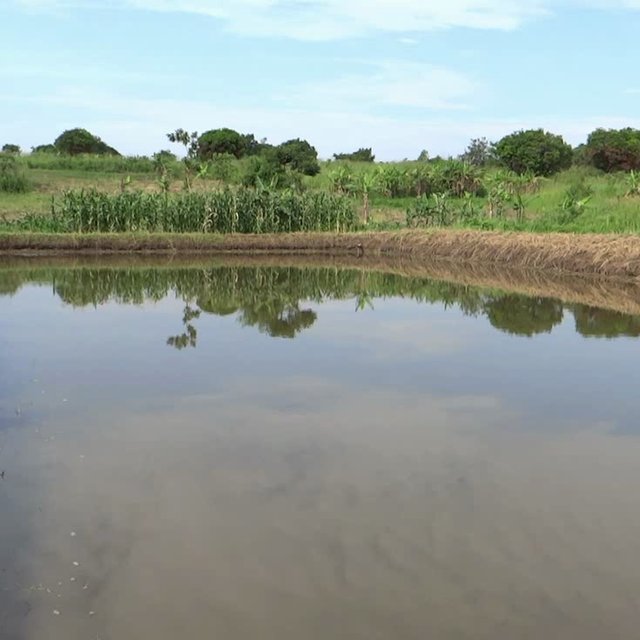





| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Uganda Shillings) | 每项投入的总成本 (Uganda Shillings) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour on monthly basis | persons | 5.0 | 150000.0 | 750000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Spades | Pieces | 5.0 | 10000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Slasher | Pieces | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| Wheel barrow | Pieces | 1.0 | 180000.0 | 180000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | |||||
| Fish fry | Pieces | 50.0 | 500.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Feeds per week | Kilograms | 5.0 | 10000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fish nets | Pieces | 7.0 | 50000.0 | 350000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1'415'000.0 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Uganda Shillings) | 每项投入的总成本 (Uganda Shillings) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour on monthly basis | persons | 1.0 | 150000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 150'000.0 | ||||