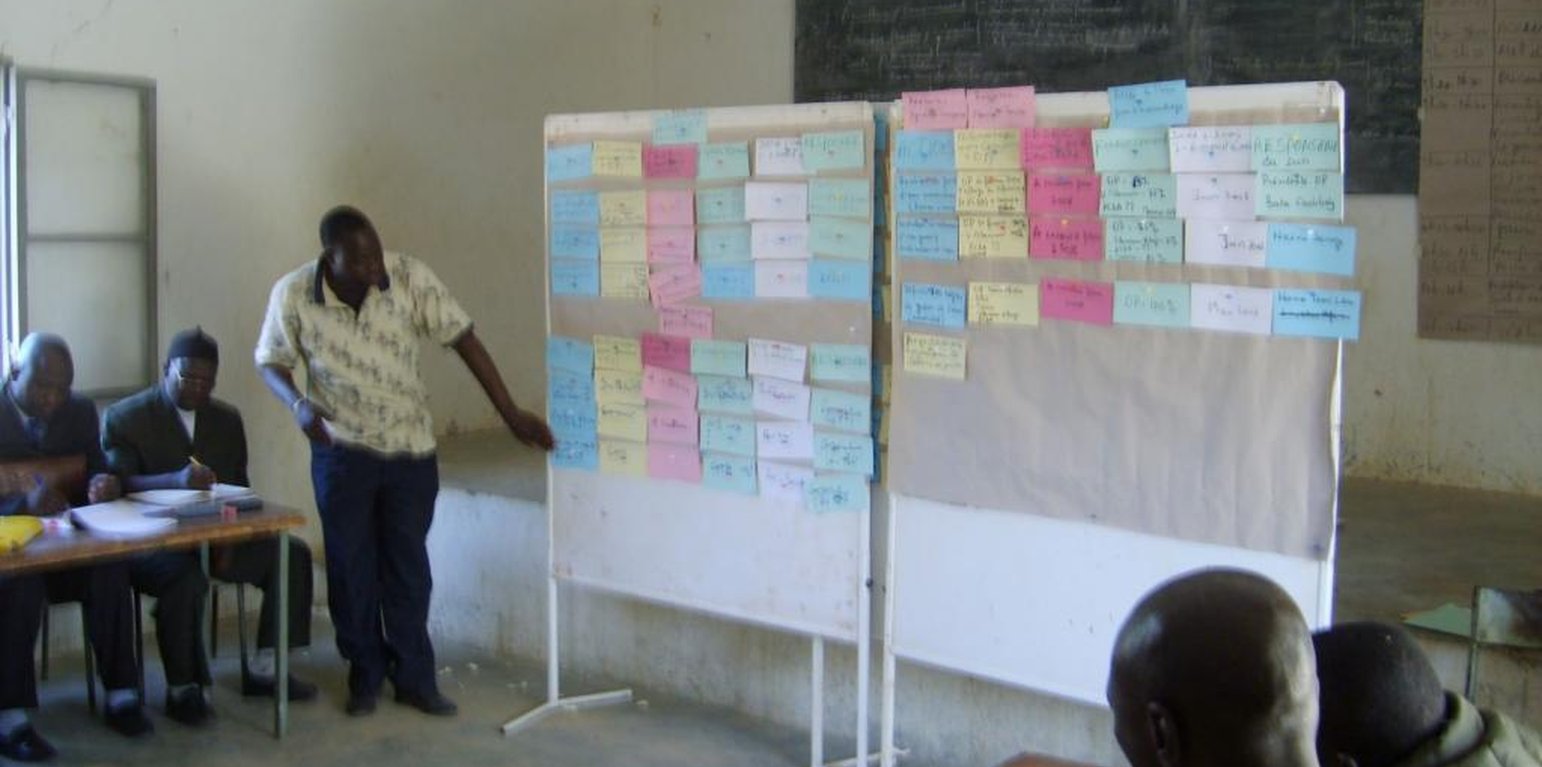




Consultation frameworks aim to facilitate dialogue between commune representatives and sector players in order to direct investments and commune services towards the real needs of professionals in the sectors in question.
The approach involves instituting a consultation framework for local authority actors and professionals from economic sectors in order to identify these economic actors’ needs vis-à-vis community investments, to factor these needs into local and regional authority planning, and to promote trust and collaboration between actors.
The commune identifies two or three high-growth sectors that are a priority for the commune and also identifies the actors (groups, cooperatives, associations) operating in these sectors. It then puts a consultation framework in place that brings together the municipality, sector actors, local technical services, representatives from technical and funding partners, and NGOs appropriate to or operating in the sectors in question. The decision to establish a framework is made on the back of commune council deliberations. Prior to the first consultation framework meeting, sector professionals identify their needs in terms of investments and measures to improve the business environment. During these periodic meetings, attendees negotiate and agree on priority actions and write these up in a very short-term (three-month) action plan. The consultation framework group then moves to install an inclusive monitoring committee to oversee the implementation of the action plan. The committee’s mandate is defined and evolves in accordance with the results that are achieved over time and with new needs arising. The successive nature of the consultation framework meetings means that progress can be measured, required adjustments made and new activities programmed to move the sectors forward.
PACT provides technical support (methods and tools for work, moderation and training) and contributes financially to consultation workshops. The commune formalises the framework, organises the logistics of meetings (invites, meeting rooms, chair hire, accommodation), contributes to implementing the action plan (registering its designated actions with PDESC, financing), provides incentives (supporting the training of cooperatives; land access; linking up actors; acting as intermediary in negotiations among cooperatives, technical and financial partners and NGOs). Professional organisations mobilise and train their members, cover the costs of their designated activities (radio reports, member travel arrangements, opening accounts, etc.), identify and negotiate within each individual profession the required actions for inclusion in the action plan, and contribute to the cost of building infrastructure. Technical services provide technical support to the two main parties (municipality and professional organisations). The monitoring committee helps ensure the action plan is implemented on schedule, identifies obstacles to implementation and communicates these to consultation framework actors so they can find solutions and move forward with a new action plan.
地点: regions of Ségou and Koulikoro , Mali , 马里
启动日期: 2007
终止年份: 不适用
方法的类型
| 该方法涉及哪些利益相关者/执行机构? | 指定利益相关者 | 说明利益相关者的角色 |
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区 | ||
| SLM专家/农业顾问 | ||
| 地方政府 | ||
| 国家政府(规划者、决策者) | ||
| 国际组织 |
决策是由......做出的
决策是基于
土地使用者的劳动力为
consultation framework brings together the municipality, sector actors, local technical services, representatives from technical and funding partners, and NGOs; Commune water-use planning that takes into account commercial (e.g., small-scale irrigation schemes) as well as drinking water purposes
Ségou Region: Ségou Circle (communes of Dioro, Sansanding, Togou, Markala and Farakou Massa) and Macina Circle (communes of Boky-Wèrè, Kokry, Souleye, Saloba and Kolongo) Implementation locations: Koulikoro Region: Koulikoro Circle (communes of Sirakorala, Koula Togouni, Nyamina and Doumba) and Kati Circle (communes of Ouélessébougou, Dialakoroba, Sanankoroba, Dio-Gare and Yélékébougou). The approach has been applied in 20 communes in two regions and four circles. On average, each commune has two cooperatives, which are professional organisations representing between 60 and 120 members.