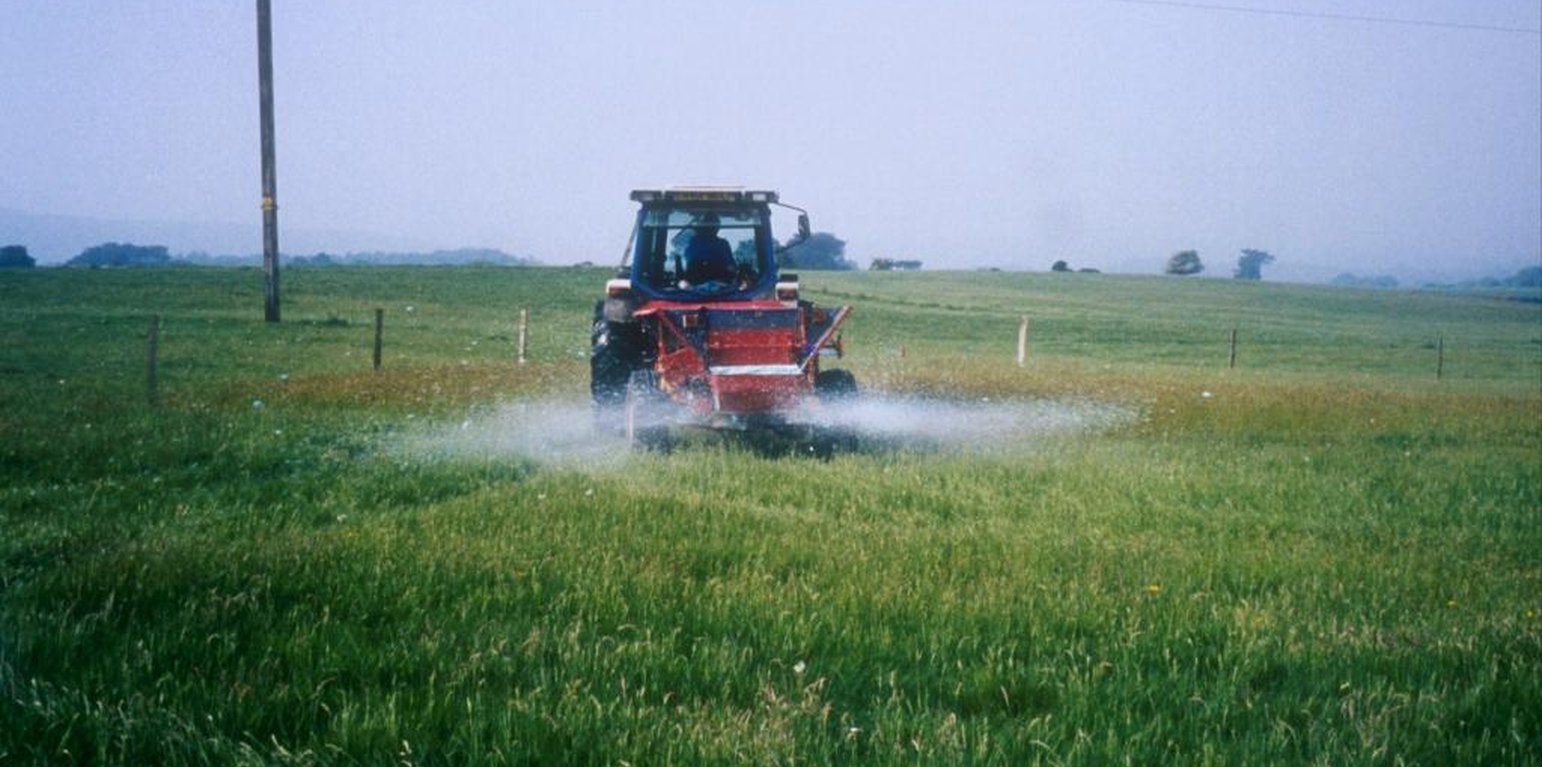




Aims / objectives: To convert the area from intensive pastureland to a semi-natural state with low intensity grazing through alteration of the soil pH. This change in land-use should have a positive effect on both above- and belowground biodiversity.
Methods: Plots were established on two adjacent farms owned by National Trust near Wareham, Dorset (Newlines Farm and Hartland Farm). A control and two sulphur amendments were compared on plots on ten fields (five from each farm) on 50 m x 50 m plots. Elemental sulphur (Brimestone 90TM) or ferrous sulphate (Mistrale “Wet Copperas” 50TM) were applied at equal rates of 2000 kg ha-1 in May 2000 and a second application of 1600 kg ha-1 in March 2001.
Stages of implementation: Treatments were applied in 2000 and 2001. Periodic monitoring has been conducted to monitor changes in plant diversity and soil chemical and biological properties.
Role of stakeholders: Stakesholders played an active role in identifying management options and implementing the technology. When the original plots were established, a charitable organisation was the primary stakeholder. For the intent of the current project, other stakeholders became involved, including parish council, landowners, and conservation organisations.
Other important information: Acidification treatments were applied to plots on the Isle of Purbeck that had previously been used for arable production and then high intensity grazing. The site is located on acidic fluvially-deposited soil and was in lowland heath until the middle of the 20th century at which time the land was tilled and treatments of rock phosphate, marl and chalk were added to increase soil pH and nutrient availability and improve the potential of the land for agricultural production.
地点: Wareham, Dorset, 英国
启动日期: 1999
终止年份: 不适用
方法的类型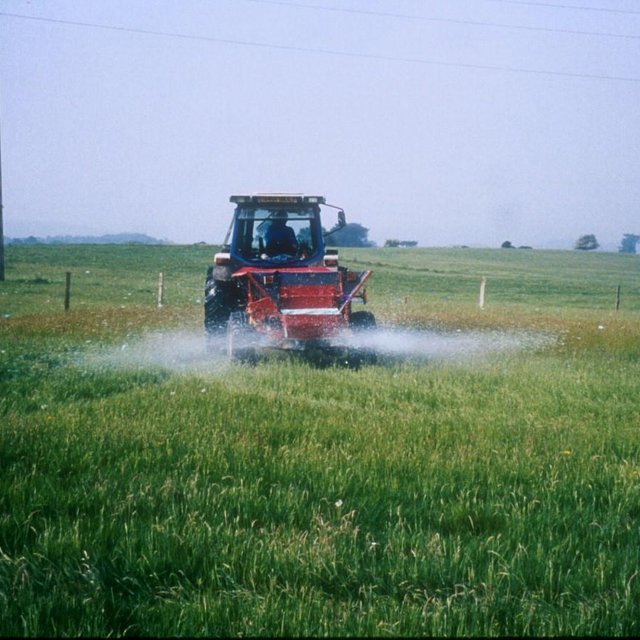

| 该方法涉及哪些利益相关者/执行机构? | 指定利益相关者 | 说明利益相关者的角色 |
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区 | ||
| SLM专家/农业顾问 | ||
| NGO | ||
| 国际组织 |
决策是由......做出的
决策是基于
Research on the approach has been carried out by specialists at Bournemouth University and the University of Reading, UK.
Research was carried out on-farm
土地使用者的劳动力为
Conversion to low input system
Other farms