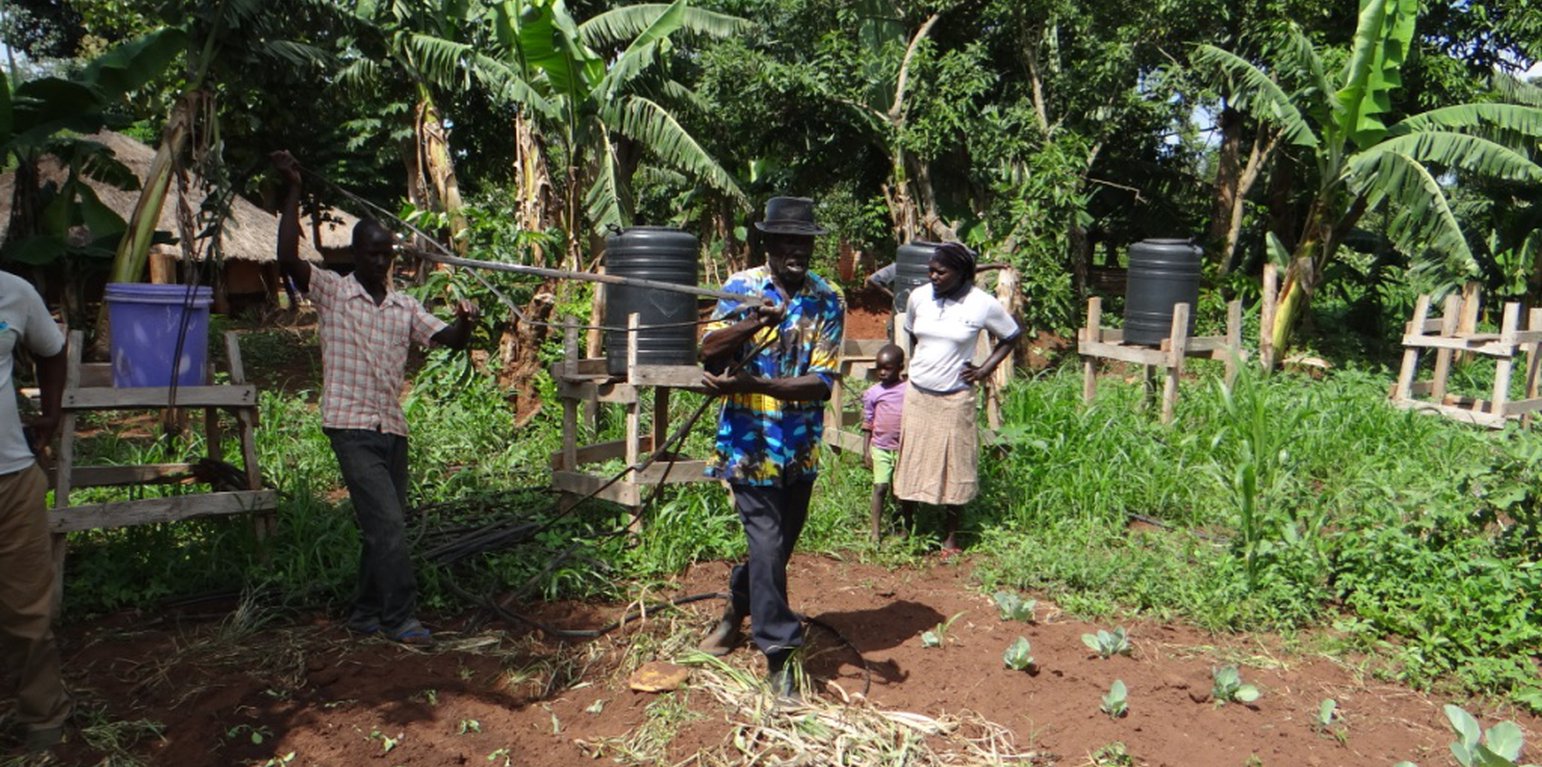




Home garden irrigation is a commonly used practice promoted by farmers in Northern Uganda. It allows involving watering of home gardens during periods of unreliable rainfall. To implement this technology, the land user was first trained by the International Institute for Rural Reconstruction ( IIRR ) which provided the initial training to farmers as part of a campaign to promote adaptation to climate change.
50 to 100 liters tanks with taps were placed on a raised platforms. Perforated plastic tubes allow water to flow and drip irrigate vegetable patches.
A water source is needed in order for the irrigation processes to take place. Hence water is pumped by a tredle pump into the plastic tanks. Perforated plastic tubes help to direct water to the gardens grown within the land users plots. In terms of maintenance, the water tank should be cleaned every month so that only uncontaminated water is used for irrigation purposes. Home gardening can be carried out throughout the year if there is enough water available.
With this technology, the most significant costs occur during the establishment phase for the procurement of water tanks. Important to note with this technology as testified by the land user, is that the high cost of water is the most important factor during the hot and dry season while maintenance costs are low once established in the medium and long term thus making the technology good for scaling.
地点: Town council, Northern Uganda., 乌干达
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
实施日期: 2009
介绍类型



| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (UGX) | 每项投入的总成本 (UGX) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Man days | days | 14.0 | 5000.0 | 70000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Water tanks | pieces | 1.0 | 350000.0 | 350000.0 | 100.0 |
| Taps | pieces | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plastic tube depending on size | pieces | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 580'000.0 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (UGX) | 每项投入的总成本 (UGX) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labourforce | Man day | 30.0 | 5000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Repairs of taps | Repairs | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 210'000.0 | ||||
SLM之前的数量: low
SLM之后的数量: high
Due to constant irrigation
SLM之前的数量: low
SLM之后的数量: high
Due to constant irrigation and monitoring
Water retained in the soil for crop production, thus making land management easier.
SLM之前的数量: low
SLM之后的数量: high
Stored in the water tank
SLM之前的数量: low
SLM之后的数量: high
Due to increased production in the home gardens resulting from irrigation.
SLM之前的数量: low
SLM之后的数量: high
From harvested quality crops.
Watering of home gardens using irrigation technology, no manual carrying water for irrigation required.
SLM之前的数量: low
SLM之后的数量: high
Due to increased harvests resulting from irrigation.
Water stored in tanks as described.
Water stored in tanks as decribed.
Water is collected and retained in the tank and used as required.
Soil is irrigated by dripping causing no run-off.
water harvested and used as required; no excess water run-off to cause floods.