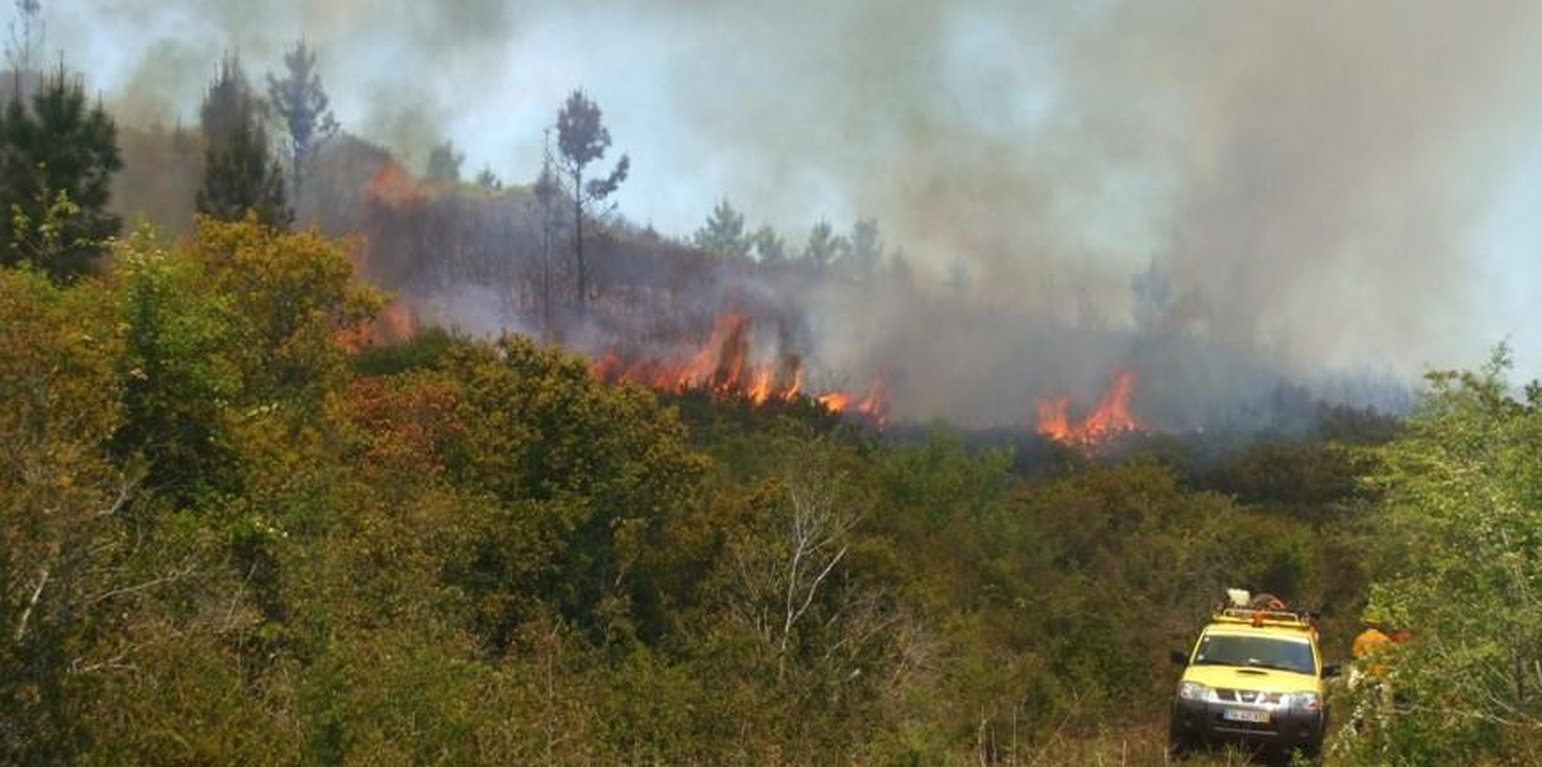
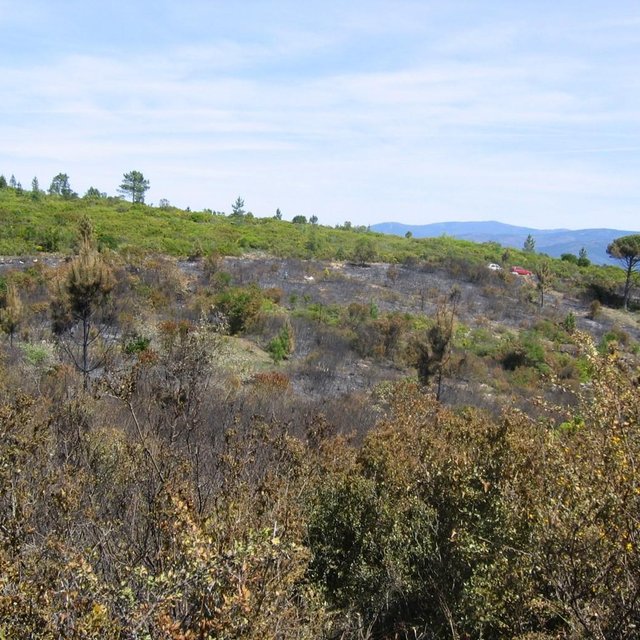
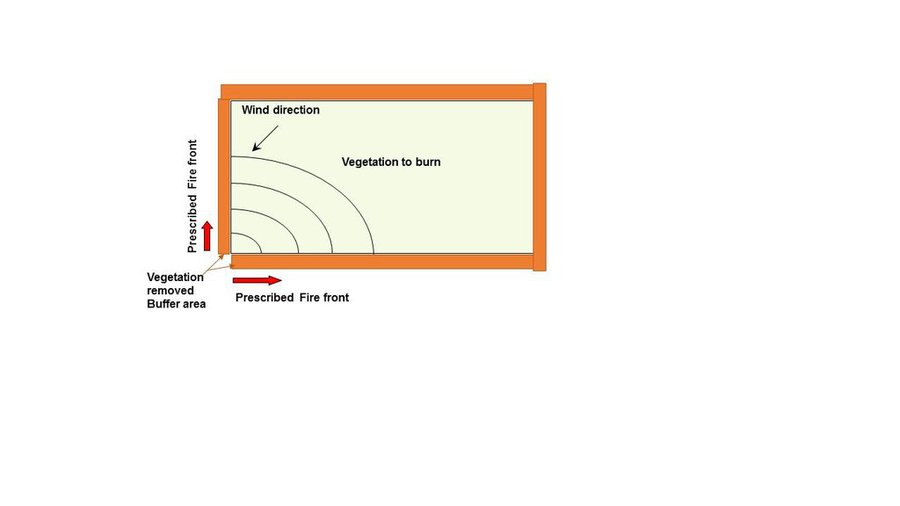
Prescribed fires as a management tool is planned to be set up in shrubland areas of the Caroig mountain range, Valencia.
Purpose of the Technology: Main purpose is reduce fuel load that increases fire risk hazard in the area.
The research team of the University of Valencia will implement an experiment based on the sediment fences technique to capture and measure post-fire soil losses in a landscape burned by the prescribed fire technique.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Climate (less than 30 meter/second wind speed, less than 30 Celsius degree, and air moisture higher than 30%) and vegetation conditions must to be reached for the prescribed fire application.
The delimitation and removing vegetation around the burned area must be achieved in order to reduce fire spread.
Natural / human environment: The Aleppo pine trees in the region are typically planted as monoculture for wood production. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-) natural and man-made agricultural (terraces), shrublands and afforested lands. Since the 1970´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
地点: Valencia, Spain, 西班牙
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷))
实施日期:
介绍类型