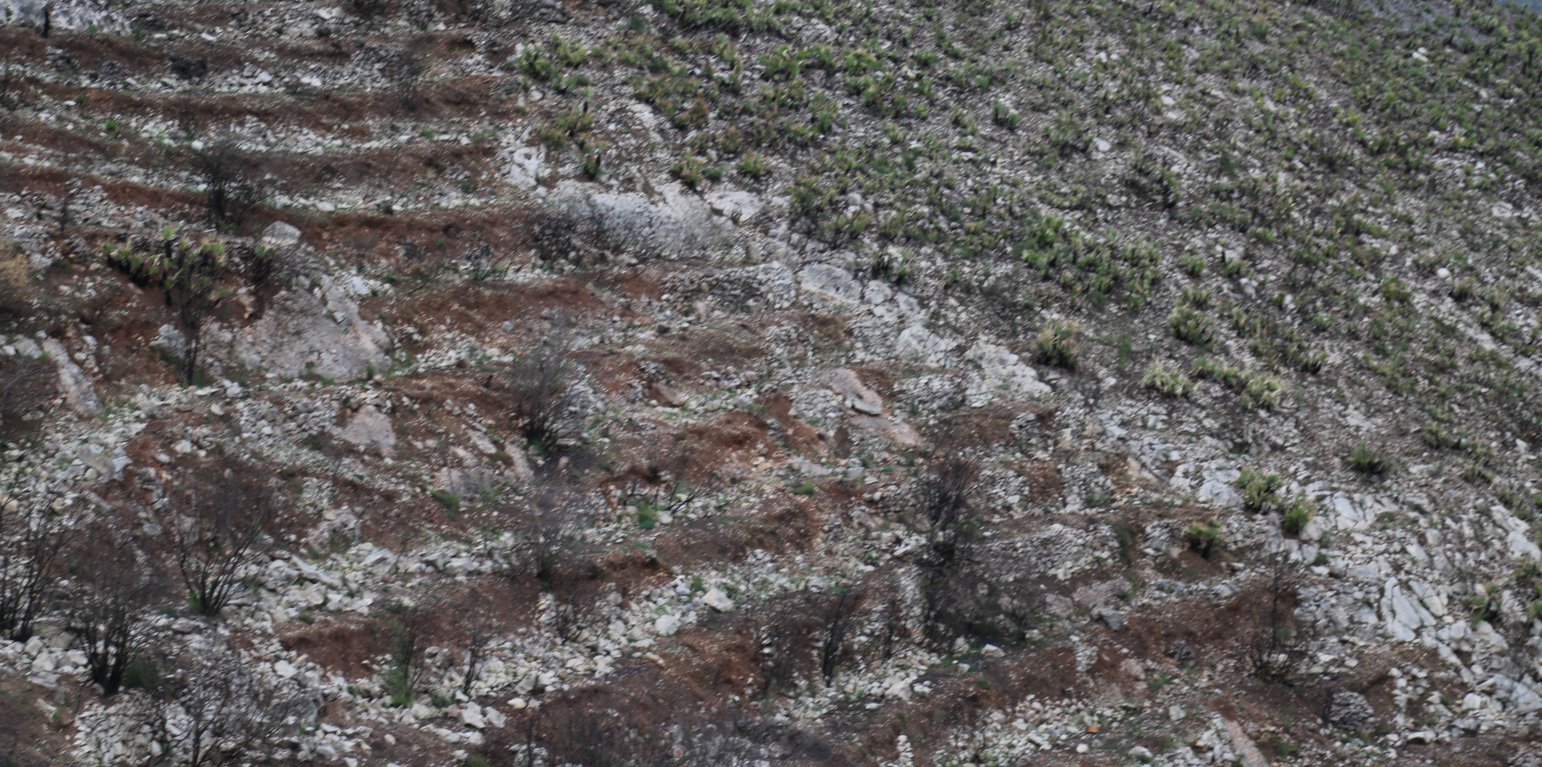




A wildfire is expected for summer 2015 in the Caroig mountain range. The area was afforested with Aleppo pines during the 20th century and nowadays the landscape is composed by mature Aleppo pines at different stages of development with shrub vegetation in the understorey.
Purpose of the Technology: The post-fire area is expected to be reforested with local shrubs species and Aleppo pines.
Perturbation by machinery when reforesting is expected to increase soil erosion.
The research team of the University of Valencia will implement an experiment based on the sediment fences technique to capture and measure post-fire soil losses in a reforested burned landscape.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Maintenance activity deals with the plantation scheme which includes man-power, machinery, access to remote areas and cost of plants, as main expenses.
Natural / human environment: The Aleppo pine trees in the region are typically planted as monoculture for wood production. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-) natural and man-made agricultural (terraces) and afforested lands. Since the 1970´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
地点: Valencia, Spain, 西班牙
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. 10-100 平方千米)
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型






技术规范
作者:ARtemi Cerdà
Bench terraces construction promotes water and sediment deposition and reduces slope lenght.
Location: Valencia. Spain Date: 02-02-2014 Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length Aligned: -graded strips Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs Trees/ shrubs species: Aleppo pine, quercus ilex, quercus coccifera, pistacia lentiscus, rosmarinus officinalis Grass species: brachypodium retusum Bund/ bank: graded Vertical interval between structures (m): 10 Spacing between structures (m): 3 Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5 Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1 Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50 Construction material (earth): ripped soil surface by specialized machinery |
|||||||||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| abandonment | Person days | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| visits to the field | € | 1.0 | |||