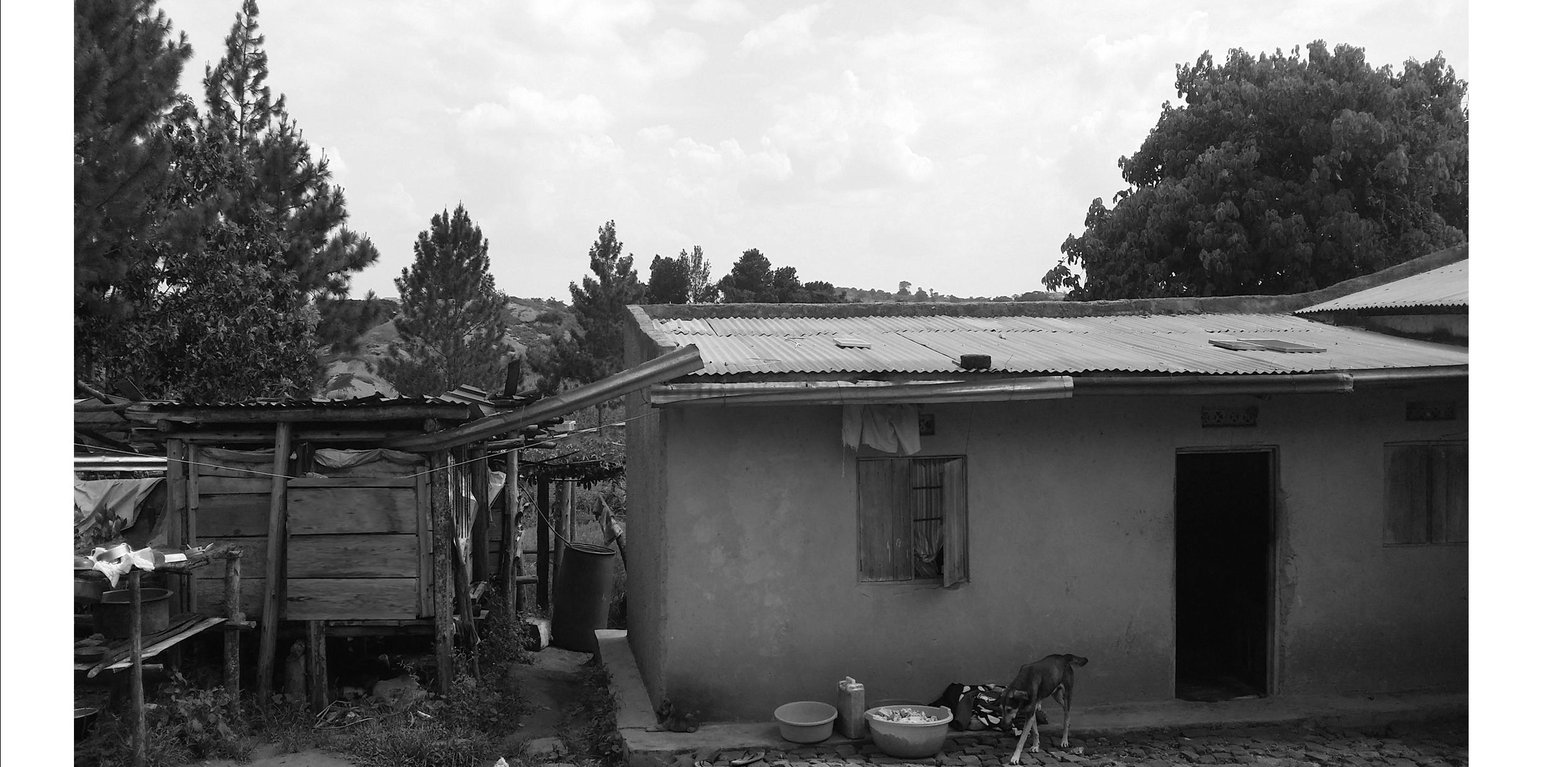




The wooden water reservoir system was introduced to the farmer by staff of the area's local government as a demonstration site to educate others on how to cheaply harvest and store rainwater in a relatively clean form for domestic, livestock and irrigation use. The farmer’s house was fitted with gutters to tap rainwater and direct it into the water reservoir. The water collected is used to buffer the water scarcity during the dry season, which normally stresses livestock and crops in the area. The water can be stored for as long as three months, depending on the size of the water reservoir and the use of the water.
The establishment of the technology requires a clean roof for collecting rainwater, gutters, poles, iron sheets, tarpaulin, hose pipe, jerry can and nails. Further equipment required include; a hammer, hoe and panga (large knife for weeding and forest works). At the farm in Kyegegwa, the reservoir is constructed 3 meters away from the farmer’s main house located at the top of a gently sloping hill. The establishment process involves: leveling of the site on which the technology is planned and constructing a water reservoir supported by a wooden structure. The support structure is constructed using four poles made in such a way that the two front poles are taller (5m) while the two poles behind are shorter (3m). This will give the roof a slight slope to prevent rainwater from stagnating on the roof. A raised rectangular floor supported by the poles is then established at a height of 0.5m above ground. The rectangular reservoir base dimensions are 1m×4m×2m (h×l×w) and is divided into 4 compartment. Each of these, lined with water-tight tarpaulin, can hold 2000 litres of water. The water so collected in the reservoir can be extracted under gravity through a 1.5cm diameter hose pipe into a jerry can placed below the reservoir.
The cost of establishment and durability of this rainwater harvesting system is mainly dependent on the type of materials and gutters used. In Kyegegwa District, wood for construction of the system is locally available valued at US$ 67.99 for the construction of the reservoir system. The iron sheets, gutters and nails are acquired from Kyegegwa Town where they are valued at US$ 127.28. The labor required is also locally available where it takes four men to establish the structure at a total cost of US$ 17.95 in three days.
The water reservoir is semi-permanent and can last for about 1.5 years depending on the quality of materials used. The maintenance activities include cleaning of the reservoir every month and repairing of the worn out parts at the end of the wet season. The farmer strongly recommends the technology since most of the materials and labour used are relatively cheap and locally available. The reservoir is raised off the ground to reduce contamination and minimize possible accidents with children and livestock. Despite the open space above the water level and the roof, the farmer has observed that the reservoir does not breed obnoxious vectors like mosquitoes. The water collected is relatively clean and the farmer uses it for irrigation of home gardens and for watering of livestock. When properly filtered it is as well used for domestic purposes. The technology can be improved by using treated poles, stronger wood material and tarpaulin of improved quality.
地点: Kyeggegwa, Western, 乌干达
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
实施日期: 2015
介绍类型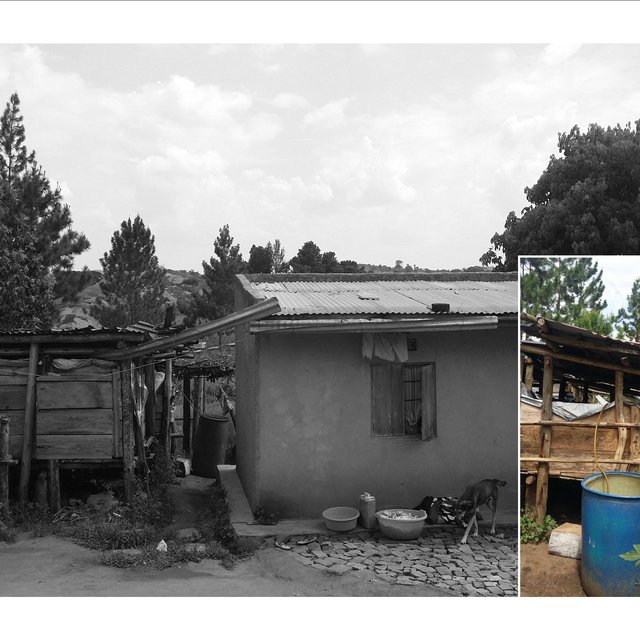



技术规范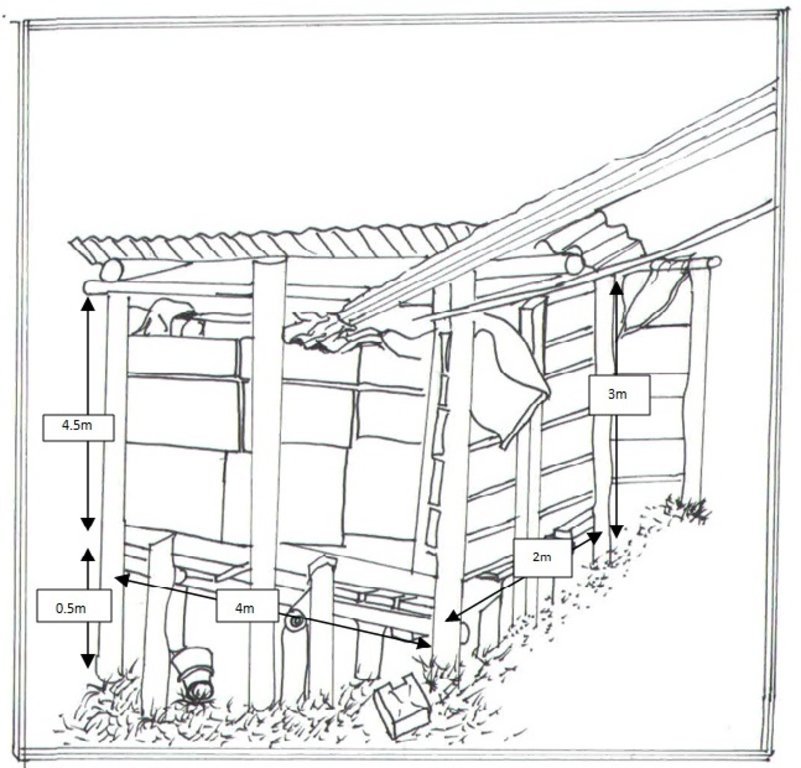
作者:Aine Amon
The support structure is constructed using four poles made in such a way that the two front poles are taller (5 m) while the two poles behind are shorter (3 m), giving the roof a slight slope to prevent rainwater from stagnating on the roof. A raised rectangular floor supported by the poles is then established at a height of 0.5 m above ground. A cuboid reservoir of dimensions 1 m×4 m×2 m (h×l×w) is constructed with wooden panels; divided into four compartments and placed on the rectangular floor. Each compartment, to hold 2,000 liter of water, is lined with water-tight tarpaulin. Water from the reservoir can be extracted under gravity through a 1.5 cm diameter hose pipe into a jerry can placed below the reservoir.
|
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Uganda shillings) | 每项投入的总成本 (Uganda shillings) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Builders | Man day | 8.0 | 22500.0 | 180000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Hammer | pieces | 30000.0 | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Panga | pieces | 9000.0 | 1.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 |
| Dibber | pieces | 15000.0 | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Hoe | pieces | 10000.0 | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Spade | pieces | 15000.0 | |||
| Poles | pieces | 12.0 | 3000.0 | 36000.0 | 100.0 |
| Timber | pieces | 12.0 | 10000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| Wood | pieces | 8.0 | 1500.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Tarpaulin | peices | 1.0 | 45000.0 | 45000.0 | |
| Iron sheet | peices | 6.0 | 25000.0 | 150000.0 | |
| Nails | Kg | 4.0 | 6000.0 | 24000.0 | |
| Hose pipe | Meters | 3.0 | 3000.0 | 9000.0 | |
| Wood and poles | Pieces | 50.0 | 4900.0 | 245000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 885'000.0 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Uganda shillings) | 每项投入的总成本 (Uganda shillings) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Men | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 设备 | |||||
| Hose pipe | meters | 3.0 | 2000.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| Jerrycans | 20litres | 2.0 | 9000.0 | 18000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Poles | pieces | 6.0 | 3000.0 | 18000.0 | 100.0 |
| Timber | pieces | 6.0 | 10000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Wood | pieces | 5.0 | 1500.0 | 7500.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 149'500.0 | ||||
SLM之前的数量: None
SLM之后的数量: 80000 litres in storage by end of the wet season
The water stored in the tank is relatively clean compared to that harvested previously using the run off harvest system.
Costs on irrigation and income from extended growing seasons
Improved nutrition since the irrigation water supports growth of vegetables
Through irrigation in the dry season
The water facilitates dissolution of nutrients