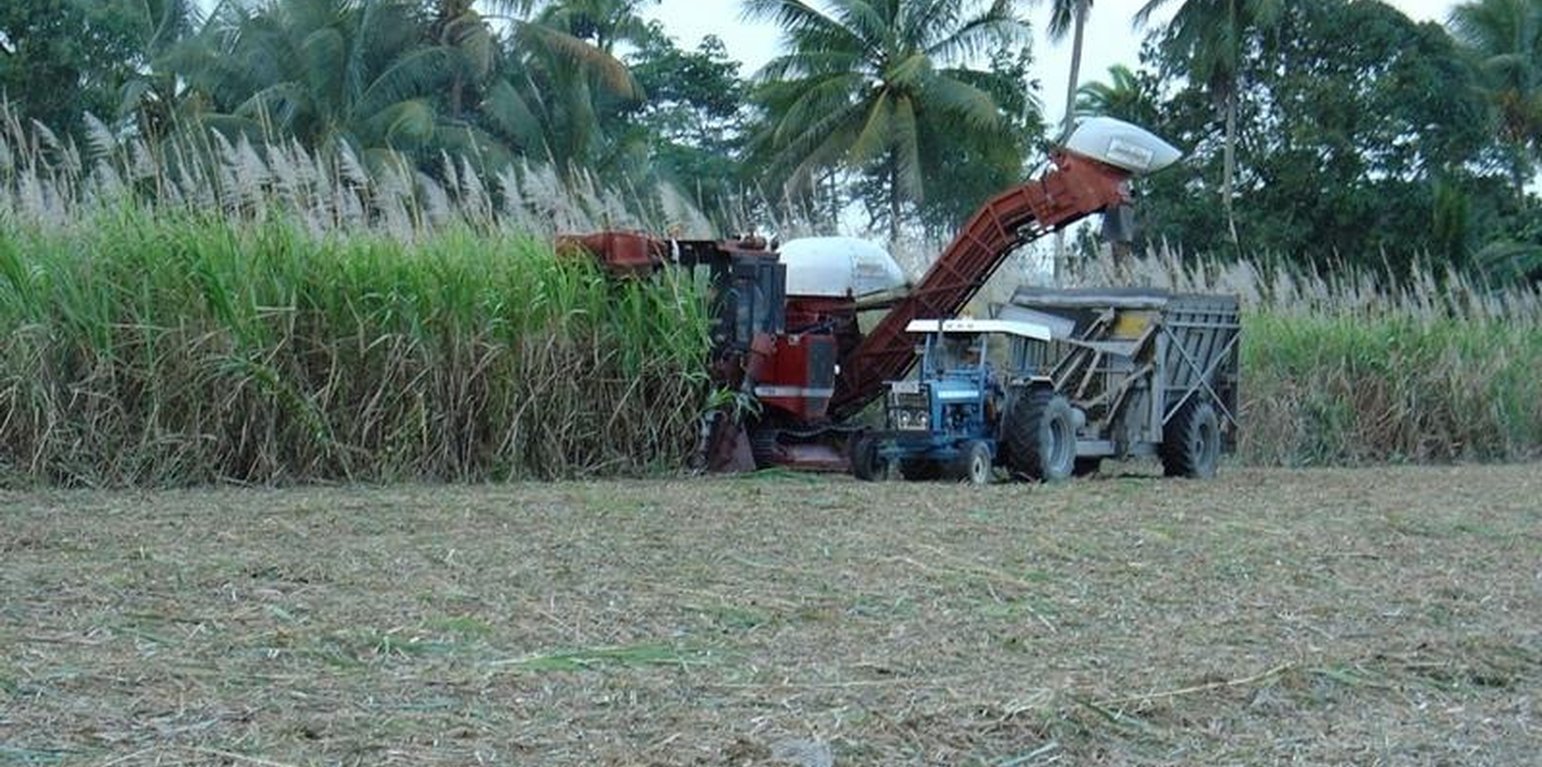




Under conventional production systems, sugar cane is burnt before being harvested. This reduces the volume of trash - comprising green leaves, dead leaves and top growth - making harvesting of the cane simpler, and subsequent cultivation of the soil easier. In the humid tropics of North Queensland, harvesting of cane used to be carried out by hand - as it still is in many parts of the developing tropics. Burning was necessary to make harvesting possible in a dense stand (and to reduce the danger of snakes). However, with the advent of mechanical harvesters in the 1960s, burning continued to be practiced through habit.
A new system then brought fundamental changes in soil management: The ‘green cane trash blanket’ (GCTB) technology refers to the practice of harvesting non-burnt cane, and trash blown out behind in rows by the sugar cane harvester. This trash forms a more or less complete blanket over the field. The harvested lines of cane re-grow (‘ratoon’) through this surface cover, and the next year the cycle is repeated: the cane is once again harvested and more trash accumulates in the inter-rows. Generally the basic cropping cycle is the same, whether cane is burnt or not. This involves planting of new cane stock (cuttings or ‘billets’) in the first year, harvesting this ‘plant crop’ in the second year, and then in years three, four, five and six taking successive ‘ratoon’ harvests. In year six, after harvest, it is still common, even under the GCTB system, to burn the residual trash so that the old cane stools can be more easily ploughed out, and the ground ‘worked up’ (cultivated) ready for replanting. A minority of planters, however, are doing away with burning altogether, and ploughing in the residual trash before replanting. A further variation is not to plough out and replant after the harvest in year six, but to spray the old cane stock with glyphosat (a broad spectrum non-selective systemic herbicide) to kill it, then to plant a legume (typically soy bean) as a green manure crop, and only replant the subsequent year after ploughing-in the legume. Under this latter system, one year of harvest is lost, but there are added benefits to the structure and nutrient content of the soil.
Whatever variation of GCTB is used, there are advantages in terms of increased organic matter, improved soil structure, more biodiversity (especially below ground) and a marked reduction in surface erosion - from over 50 t/ha to around 5 t/ha on average. Less erosion is good for the growers - but is also of crucial importance off-site, as sediment lost from the coastal sugar cane strip is washed out to sea, and damages the growing coral of the Great Barrier Reef.
地点: Ingham, North Queensland, Australia, 澳大利亚
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (800.0 km²)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期:
介绍类型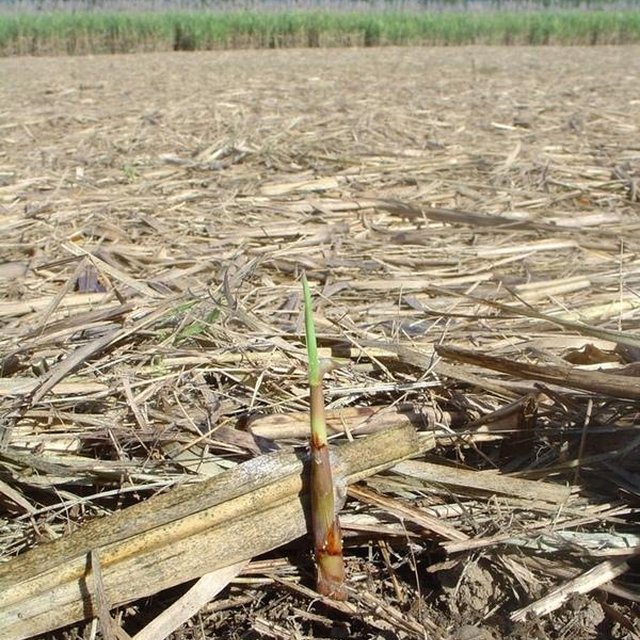





| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Contract harvesting | ha | 1.0 | 390.0 | 390.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| Herbicides | ha | 1.0 | 33.0 | 33.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 543.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 543.0 | ||||
Enhanced reputation of sugar cane growers as 'environmentally friendly'
From >50 t/ha to 5 t/ha; although the location is relatively flat, soil erosion can be high due to high rainfall
Loss of nutrients reduced, inproved soil structure