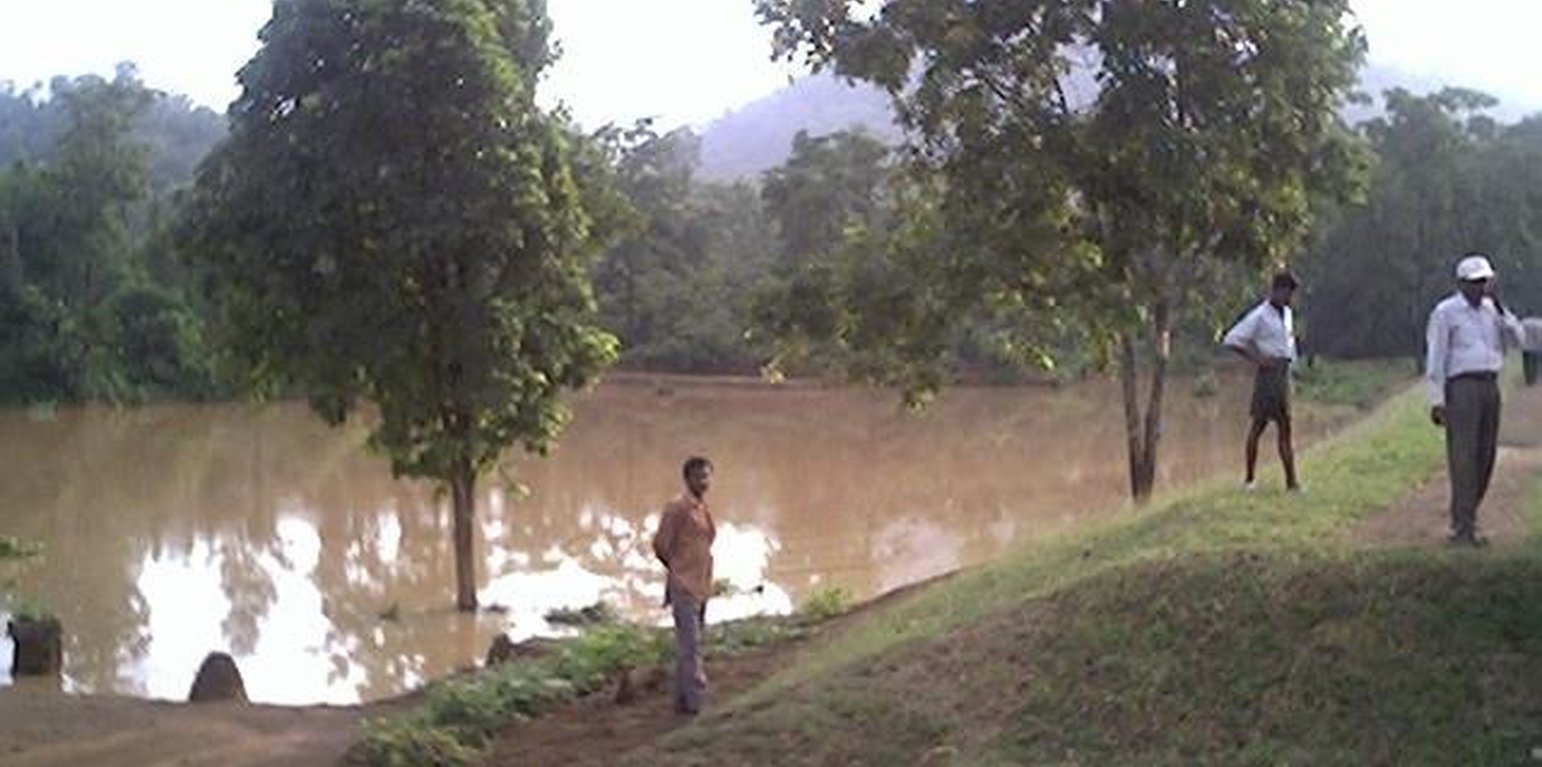




The area is located at the foot-slopes & hill slopes area where run-off is at peaks very often at the time of rainy season. Therefore, sand casting came as a first order priorities by the farmers of this patch. At the outset, a livelihood focused micro-plan had been prepared by the villagers stating the details of the base-line data along with problems & alternative solutions. The patch was identified to be the worst affected, concentraton of poor people (defined by villagers), people of this patch ready to contibute at least 20% of the cost. In the mean time project sent the PIA to BAIF, Bangalore to study the linking of farm ponds & its relevance in this context of our situation. As a demonstration, PIA & other technical team facilitated the villagers. One water harvesting structure was constructed by line deptt of soil conservation just at the down hills to harvest rain water & protect the lands below from sand casting. But there were no alternatives for the land users of that patch about the optimum utilisation recharged water. The surrounding area was totally unbunded with sandy loam soil. Therefore, land users are of opinion to go fo field bunding. Earlier the practice was to dig a trench at upper gadient & put a bund below it out of the excavated soil from trench. But the requirement of land users was to get some water in each farmers land to protect the Kharif & some early rabi crop.(june-dec). By which the lands where, farmers take up only minor millets for their subsistance, that too less production & land So the main purpose of this technology was to convert the land into bunded lands along with to fetch some water at the time of dry spell in between the monsoon period. A four days in field training was conducted by the project to community link workers(SWC), particularly on patch treatment, use of levelling instruments like A-frame, proper planning, design, lay-out of different type of structure in a map & ground. After many rounds of discussion with the land users, one of them ( rich farmers with more land) was ready to do it in his own land. But, the SWC specialist did a detail transact along with land users, although results of first round tansact was mentioned in the micro-plan. The main pupose was to looking at problems & demarkating on the map. After that estimate was prepared & lay-out of key contour was done by SWC specialist with the help of community link workers & land users. The work was implemented by by the labourers with the supervision of the respective User's group leade & monitoring was done by the SWC specialist. The prioty ranking by the land users vegetaive measures like vertiver & Sabai (grass plantation on the bund along the side of the bund. For that, the necessary requirement like nursery, seedling collection was done by agriculture specialist. Training was conducted on the probable alternatives of agronomic measures like taking of crop which is of little longer duration, intercrops & cash crops etc. The vegetaive & structructural measures are subsidised by the project & the agronomic measures was taken up on loan basis. The development fund was also generated out of contribution from the land users which was deposited in a separate account for future maintainance cost.
地点: Khaparakhol, Orissa, 印度
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (0.7 km²)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型






| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Rupee) | 每项投入的总成本 (Rupee) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 20.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 20.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 120.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 2.4 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Rupee) | 每项投入的总成本 (Rupee) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.14 | ||||
Per hac production/economic cost.
Vertiver as fodder on bund.
Vertiver as fodder on bund.
Teak plants has been planted this year. The yeild is yet to come.
Land users believe that some land is wastage due the structure.
Ploughing operation.
Resource rich & resource poor land users accrued double benefit by changing the crop.
Farm employment at lean period. Income through labour
Alternatives to mitigate drought.
Contribution labour from land users because of convincing benefit from the technology. The women also contributed in plantation activities.
Members from other areas of district also learnt the technology through exposure visit.
Some of the land users of other patch of the village decided to take up similar activity.
Land users having land below 1 hac are getting more benefit out this technology.
SLM之前的数量: 50
SLM之后的数量: 10
Earthen hume pipes.
This condition help the land users to take up second crop.
Particularly top-soil.
SLM之前的数量: 30
SLM之后的数量: 20
Production/ Economic benefit becomes double.