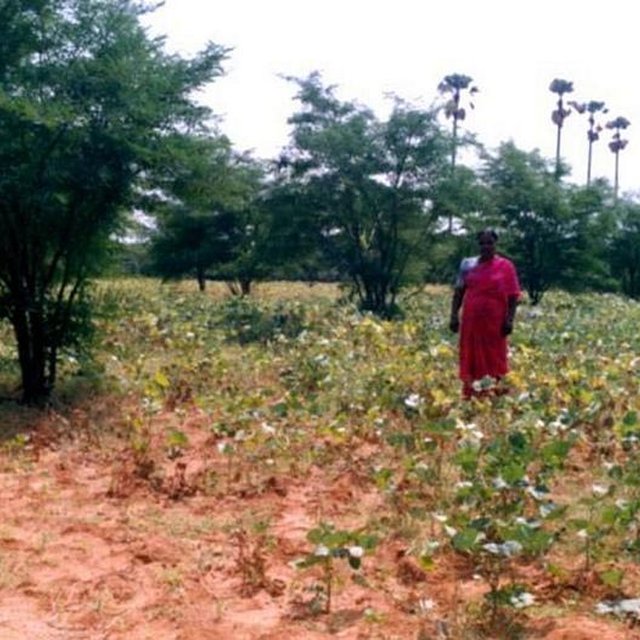
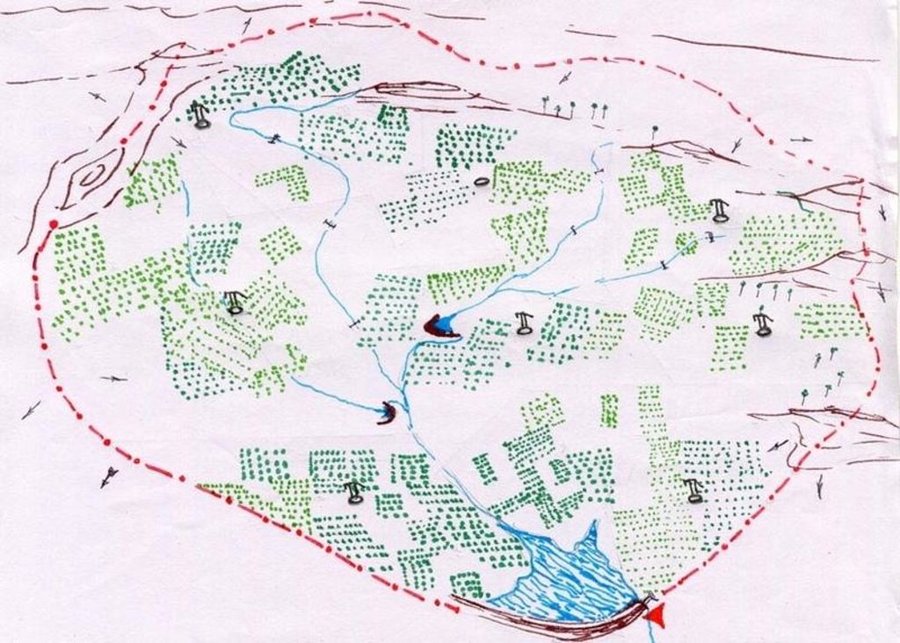
The technology can be described as a combination of tree cultivation ( mainly horticulture species) along with intercrop of pulse crops on degraded private lands, supported by in-situ measures for soil and water conservation. The supportive technology required is provision of water for protective irrigation during establishment phase.
Purpose of the Technology: the technology serves the folowing purposes 1. Short and long term economic benefits to land owners 2. Employment generation leading to reduced migration 3. Conservation of soil and water through vegetative and mechanical measures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: 1. Community organisation, formation of Village Development Association, Identification and training of beneficiaries 2. Delineation of micro-watersheds and plantation blocks. 3. Establishment of farmers's nurseries 4. Land preparation, sinking bore-well, plantation and inter-cropping 5. Watch and ward.
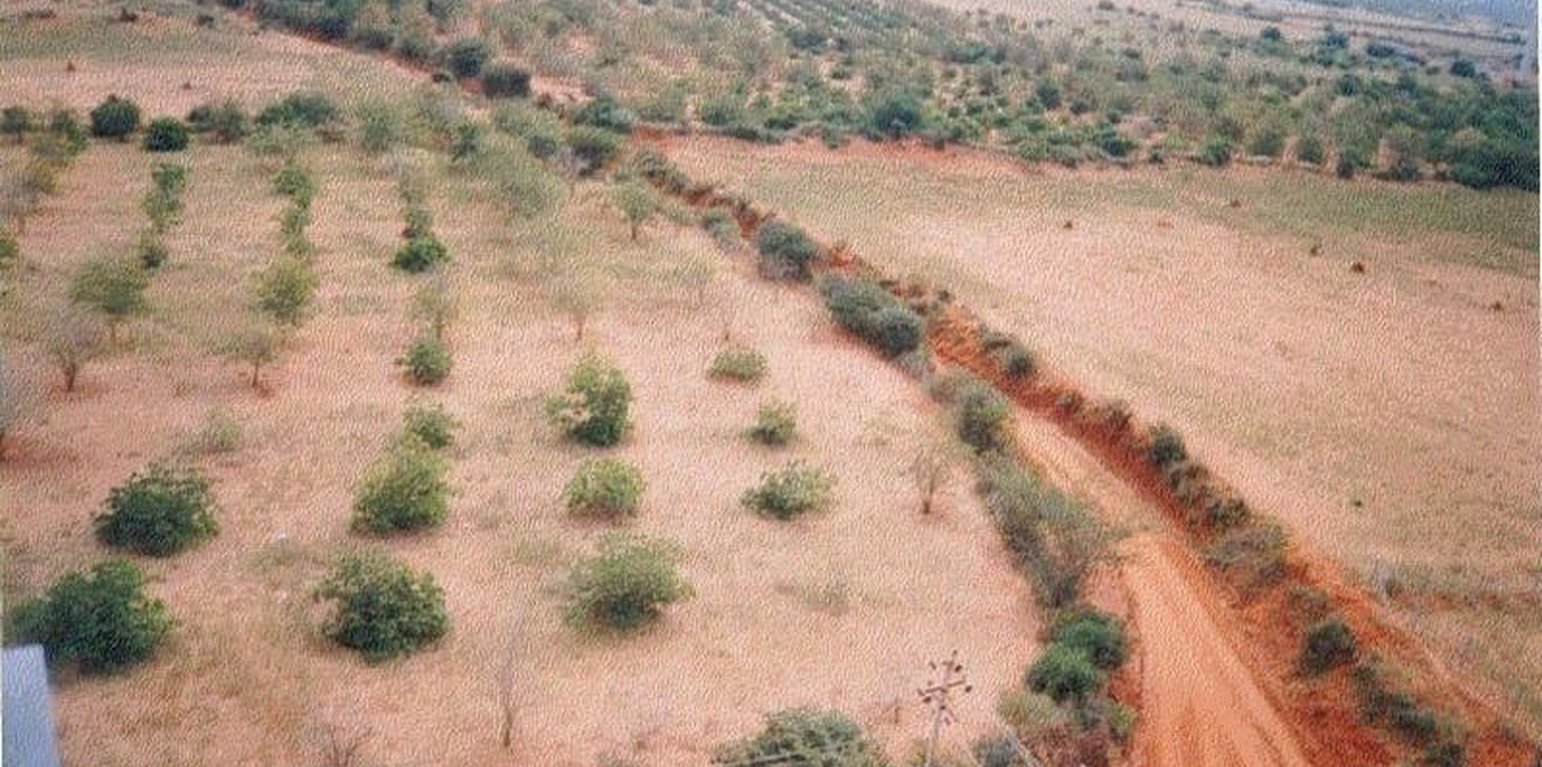
Natural / human environment: The environment is semi-arid, drought prone and subject to wind erosion. Soil depth is good.
地点: Tamilnadu, 印度
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (3.83 km²)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 50多年前(传统)
介绍类型