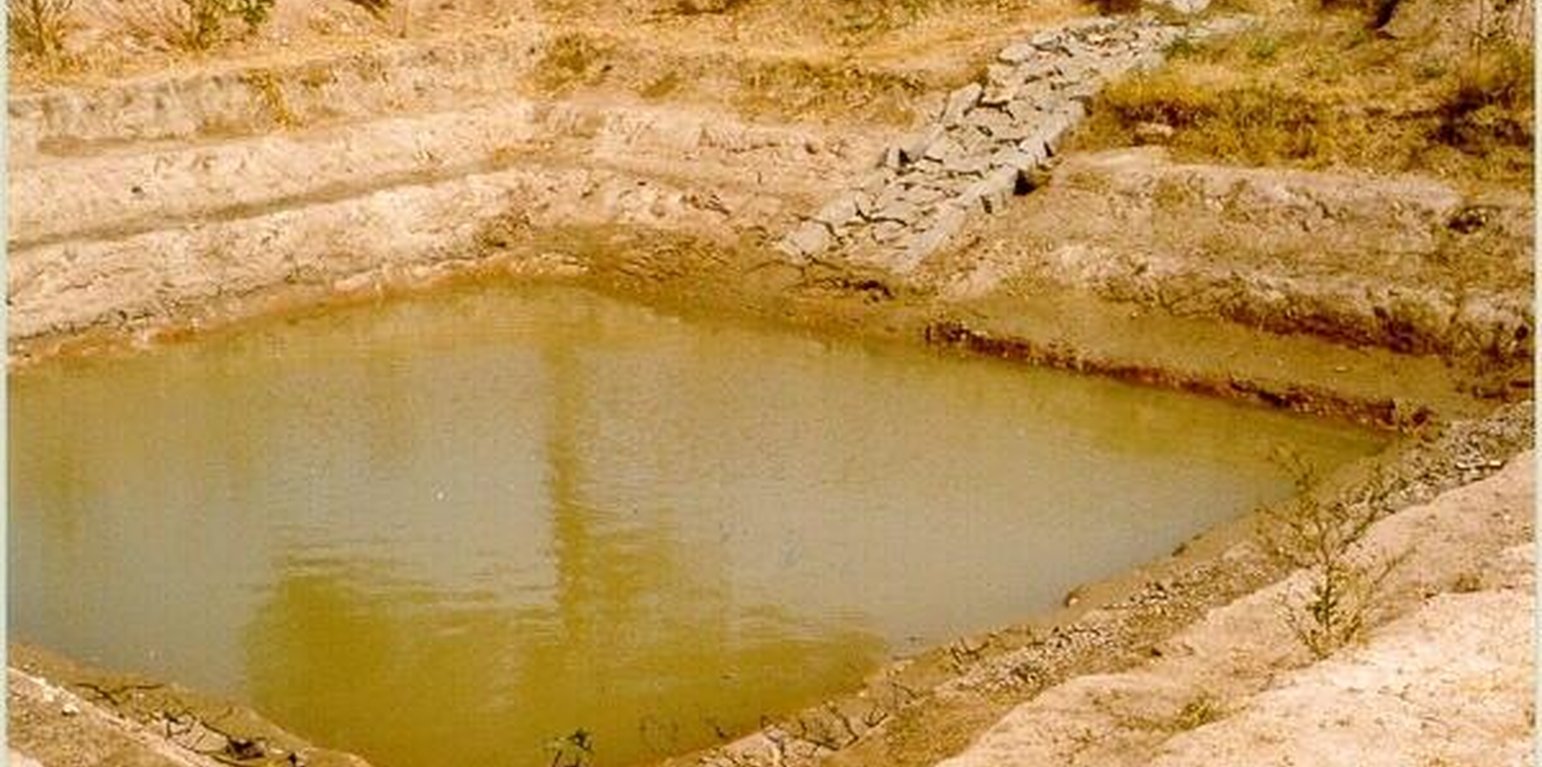




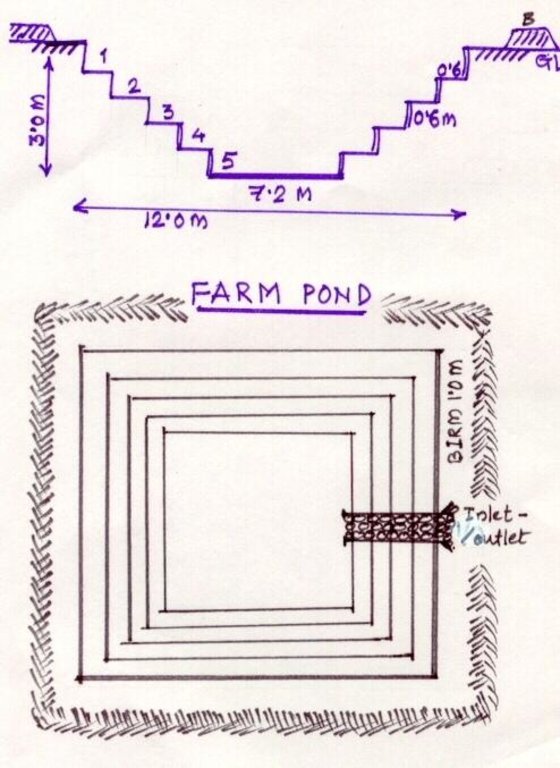
A farm pond comprises of excavated portions of 12 x 12 x 3 m with the steps at 0.6m depth each. The excavated earth is deposited all around the structure as a bund, with a burm space of 1m. An inlet cum outlet provided in the course of flow of rain water to collect and dispose the excess runoff.
Purpose of the Technology: (1). For storage of exess runoff. (2) to increase percolation for ground water recharge, (3). To use for protective irrigation during dry period, (4). To stop further deepening of watercourse in arable lands
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Selection of beneficiary is by the community and site selection, Design/ layout and excavation by the project staff with participation of the beneficiary. Desilting of the structure is by the beneficiary
Natural / human environment: surrounding lands are more slopy and with exposed rocks, most of the surrounding area is left for grazing
地点: Bijapur district, Hadalsang village, Karnataka, 印度
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (0.028 km²)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型


| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Ruppes) | 每项投入的总成本 (Ruppes) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 360.0 | 360.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Stone | ha | 1.0 | 109.43 | 109.43 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 469.43 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 10.21 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Ruppes) | 每项投入的总成本 (Ruppes) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7.3 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.16 | ||||
Second crop also taken
From trees
From trees
Difference in the crop like on bunds and in the patches of crops.
15m x 15m land loss average land holding is very less, thus small & marginal farmers face reduction in the production area with this SWC
After implementing SWC less area is left for very small and marginal land holding.
Subsistance agriculture
To bring new area into cultivation
Water storage in farm pond