



In the last 50 years high intensive monoculture practices implied an oversimplification of agro-ecosystems, a decline of biodiversity and a deterioration in the quality of water resources. The need to prevent nonpoint surface water pollution form agricultural practices has recently led to consider wetlands as effective depurative systems. Construction and maintenance of wetlands have been supported by the Veneto region as an agri-environmental measure through the Rural Development Programme (RDP).
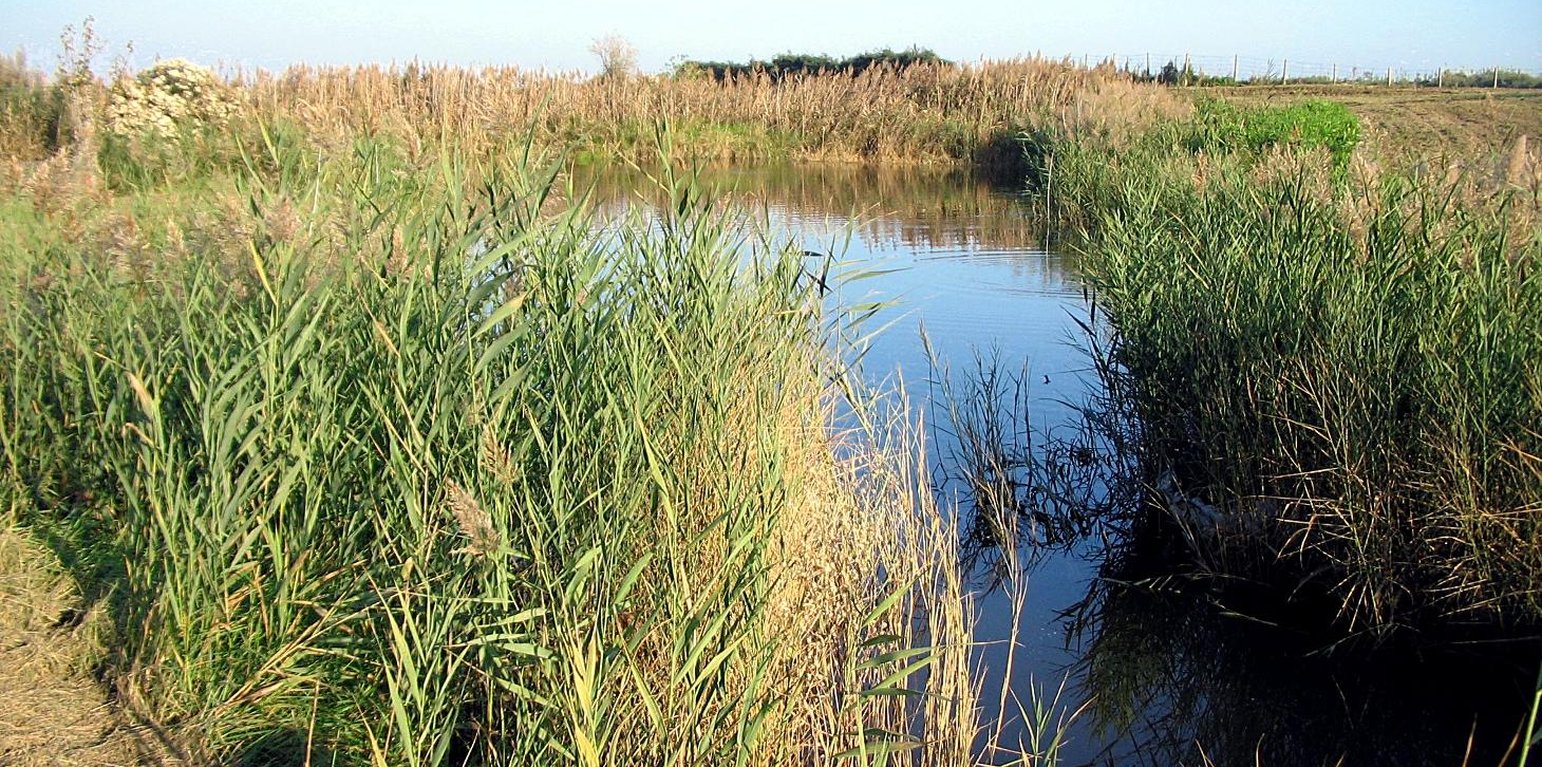
Purpose of the Technology: Wetland systems (WSs) depurate water resources from diffuse pollution, creating a semi-natural environment that promote wildlife and generally biodiversity. WS are characterised by the complete submersion (or for most part of the year) of the soil and a slow water flow that favour environmental and natural functions such as denitrification, flood control, suspended solids sedimentation. Moreover wetlands have been proposed as an alternative land use in reclaimed areas below the sea level which are facing problems of subsidence.
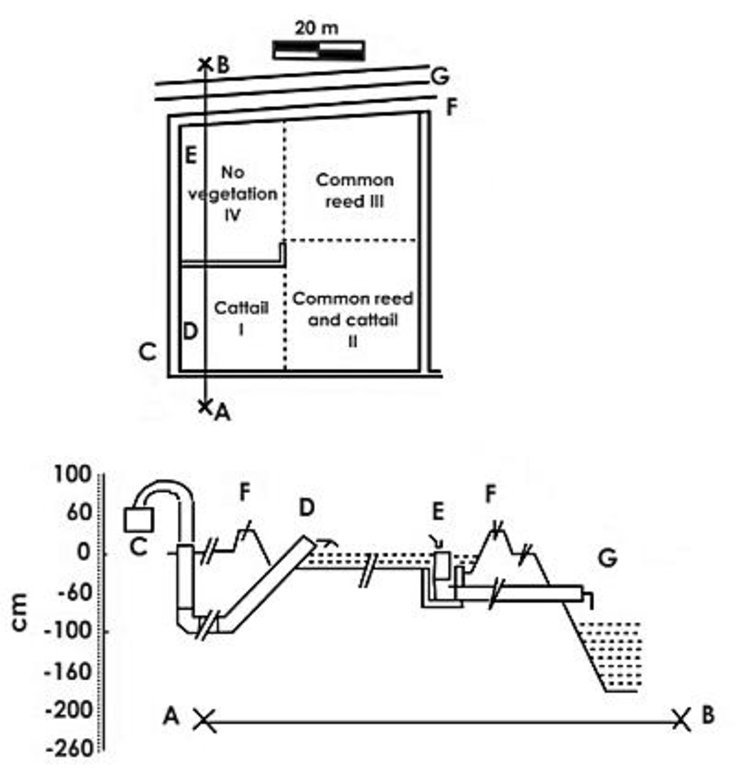
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Thanks to their effectiveness on the improvement of agri-ecosystems, the maintenance and creation of wetland systems have been supported by the regional government in order to reduce the environmental impacts of conventional agriculture practices. The area invested to create a wetland depends on the input pollutants, the size of the area that is considered and the availability of space. The creation of a wetland system provides the establishment of emergent and submerged aquatic macrophytes on a water basin ca. 50 cm depth. The efficacy of water depuration is strictly related to the water residence time.
Natural / human environment: Adopting wetland systems allows to achieve several environmental benefits. Generally, the ecosystem is positively affected by the introduction of a water basin as it provides food, nesting cover and shaded areas to wildlife species. Sediment deposition, anaerobic denitrification conditions and the purifying effect of aquatic plants reduce eutrophication and improve the water quality. Due to their semi-natural structure and high differentiation of plant species, WSs enhance the quality of life through the improvement of agricultural landscape and the creation of recreational areas.
地点: Veneto region, Italy, 意大利
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播:
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 10-50年前
介绍类型





| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Euro €) | 每项投入的总成本 (Euro €) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 其它 | |||||
| Capital costs. System implementation | ha | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 30.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2'500.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 3'125.0 | ||||
Increased awareness on biodiversity
Agro-tourism in improved natural areas
Improved agricultural landscape, biodiversity, agro-ecology and generally natural spaces, even for recreational activities. Moreover reduced water pollution.