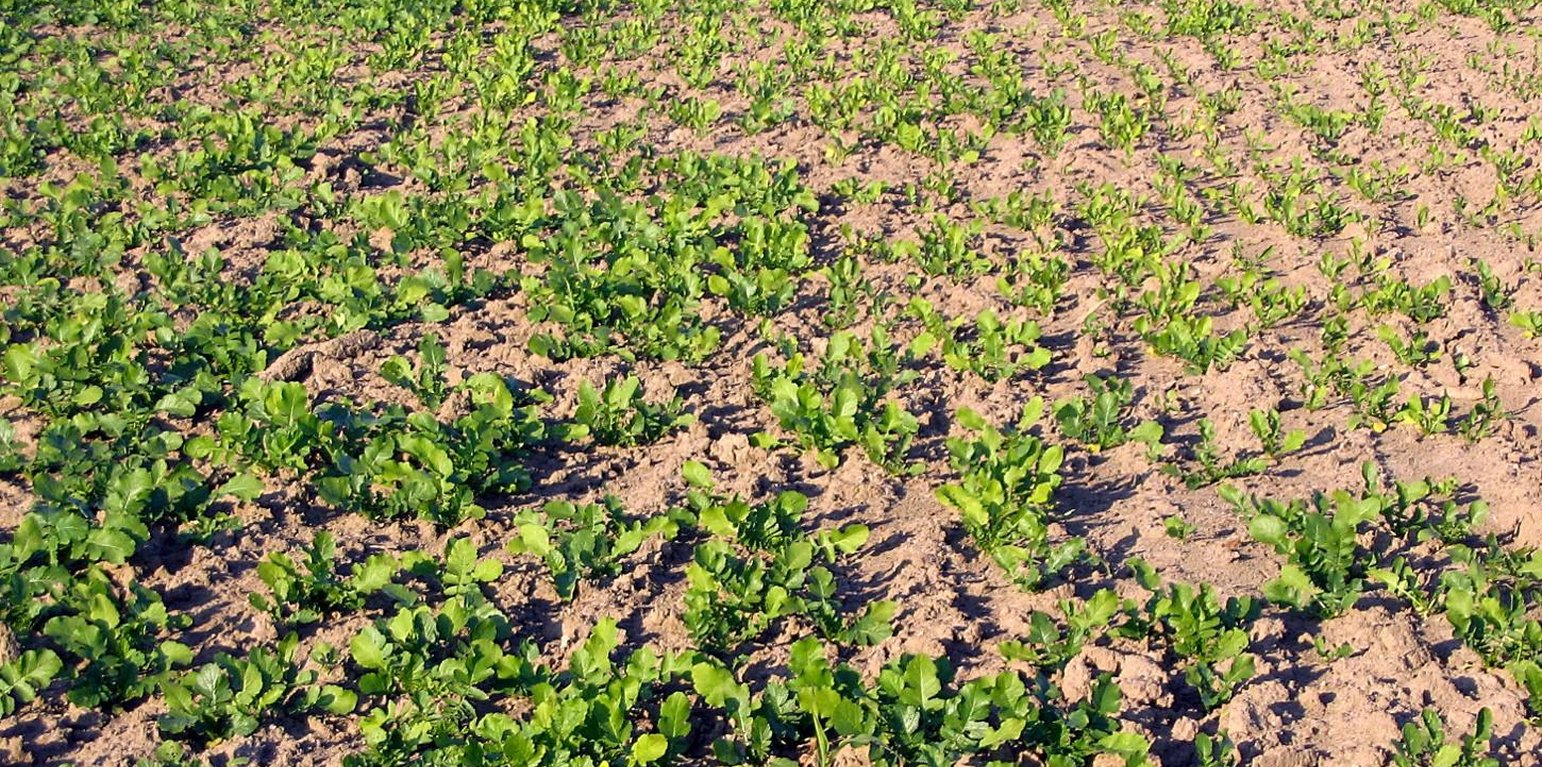




Cover crops will be selected by their capacity to address biomass production towards below-ground tissues. Growing alternative seasonal cover crops between annual crops have the potential to provide multiple benefits in a cropping system.
Purpose of the Technology: Highly developed rooting system will favour the soil quality: from an agronomic point of view, the soil will benefit from natural decompaction and structuring (especially if associated with no-till techniques) due to roots effect. Moreover, root-derived carbon is retained in the soils much more efficiently than are above-ground inputs (e.g. straw, crop residues). As a result, high and deep root productions will increase the more recalcitrant soil organic carbon (SOC) content as well as improve the nutrient cycle. From an environmental point of view, the increase of SOC content due to high root production will favour carbon sequestration within the soil profile and in turn mitigate GHG emisisons.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Following the critera that has already been adopted in the Veneto region for the continuos soil cover on croplands, the application of root-oriented cover crops will involve the alternation of autumn-winter cereals, rapeseed or other herbaceous crops with maize, soybean, sorghum etc. Cover crops that will be sown after the main culture will not be neither fertilized nor treated with pesticides during growing, while at the end of the crop cycle they will be buried as green manure in order to improve SOC, nutrient cycle and finally soil fertility.
地点: Research trial in Veneto region, Italy, 意大利
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播:
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型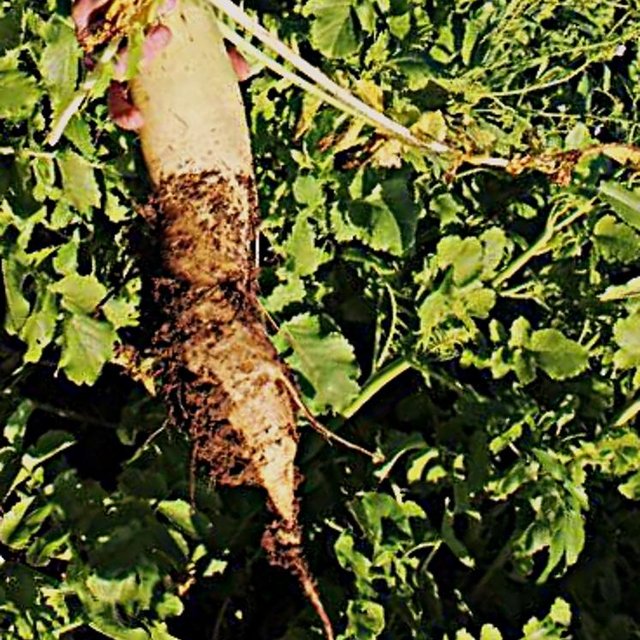







| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (€) | 每项投入的总成本 (€) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 设备 | |||||
| Chopping cover crop | ha | 1.0 | 343.0 | 343.0 | 75.0 |
| Seedbed preparation main crop | ha | 1.0 | 191.0 | 191.0 | 75.0 |
| Harrowing main crop | ha | 1.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 75.0 |
| Weed control main crop | ha | 1.0 | 44.5 | 44.5 | 75.0 |
| Harvesting main crop | ha | 1.0 | 152.0 | 152.0 | 75.0 |
| Sowing main crop: | ha | 1.0 | 121.0 | 121.0 | 75.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seeds main crop | ha | 1.0 | 191.0 | 191.0 | 75.0 |
| Seeds cover crop | ha | 1.0 | 191.0 | 191.0 | 75.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 125.0 | 125.0 | 75.0 |
| Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 254.0 | 254.0 | 81.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1'675.5 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1'861.67 | ||||