



Conservation agriculture (CA) in the Veneto region is characterised by management systems including no-tillage, permanent soil cover and crop rotation. CA has been promoted as an agri-environmental measure of the Rural Development Programme (RDP) by the Veneto region to extend sustainable land management. In spite of being provided by the regional government with subsidies, so far the adoption of CA by the farmers has been very limited since its introduction, amounting less than 1% (ca. 2000 ha) of the total regional cropland area (mainly concentrated in the low Venetian plain).
Purpose of the Technology: CA has been proposed to the farmers with the aim of reducing environmental impacts as well as economic and energetic inputs to the agricultural system. Compared with conventional practices such as soil ploughing, CA is convenient due to the saving of labour and fuel costs, with a direct effect in reducing CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. Limiting the soil disturbance and guaranteeing the continuous soil cover involve both a reduction of water runoff and surface erosion and an increase of soil biodiversity and fertility.
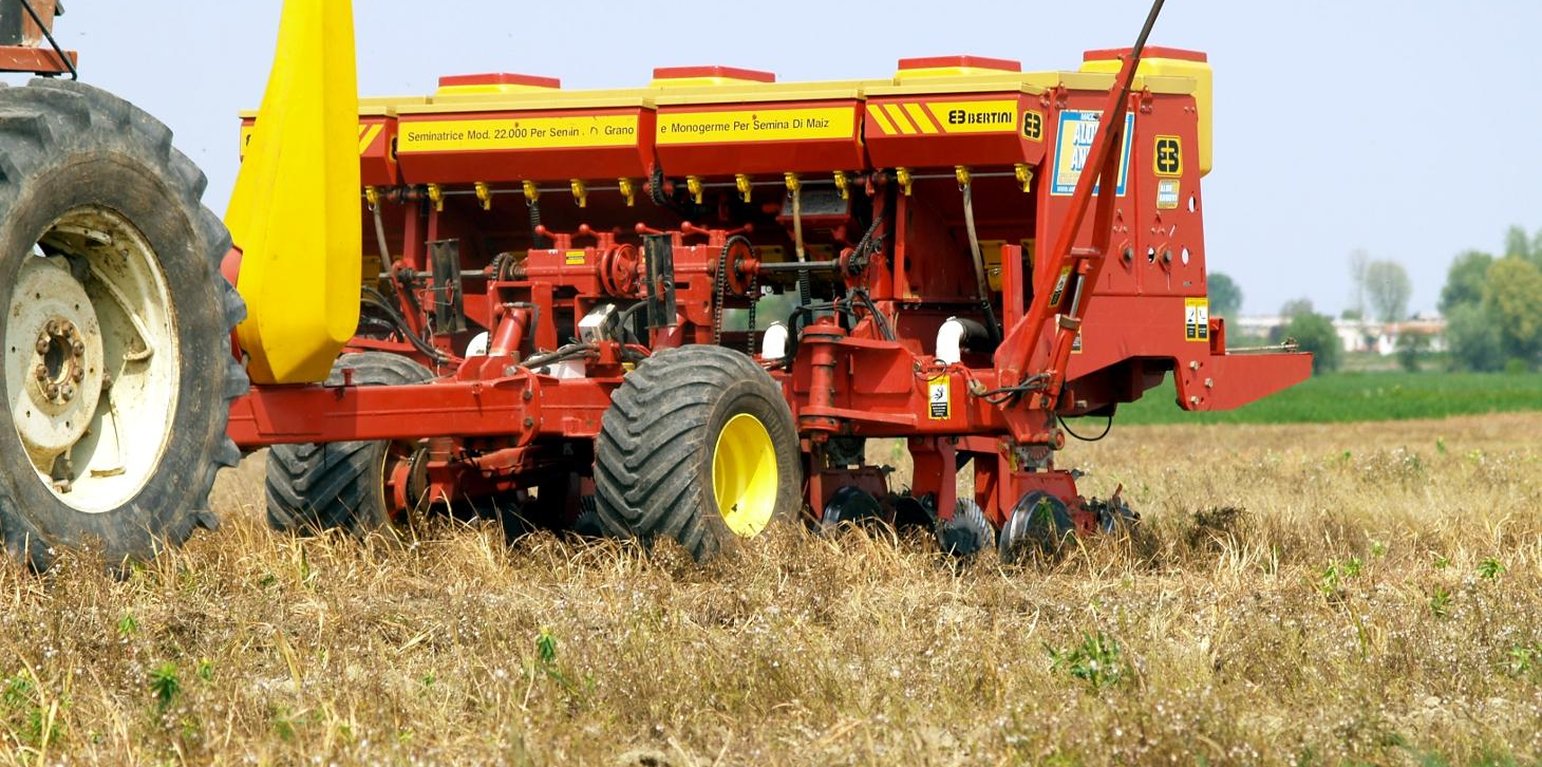
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main winter crops usually cultivated in the low Venetian plain are wheat, rapeseed and barley, while summer season crops are maize, soybean, sorghum. Generally CA consists of direct sowing on untilled soil using a double-disk opener planter for seed deposition, while after harvesting crop residues are chopped and dispersed to the surface in order to guarantee a mulching effect and a rapid incorporation into the soil. Since application of CA practices consider the permanent soil cover, the main crop is followed by cover crops that are usually graminaceae or brassicaceae. Cover crops are neither fertilized nor treated with pesticides during growing, while their final devitalisation is achieved with non-specific herbicides (e.g. Glyphosate, Glufosinate Ammonium).
Natural / human environment: Advantages of adopting conservation agriculture have been widely demonstrated worldwide and can be classified in economic, agronomic and environmental benefits. From an environmental point of view, the soil system preserves its structure and biodiversity thanks to minimum soil disturbance to the root zone, microorganisms, fungi and macroinvertebrates. Greenhouse gas emissions under conservation agriculture compared to traditional cultivation systems are lower and might offset the gains obtained to mitigate global warming. Due to the recent introduction of the technology in the Veneto region (since mid-2000s), conservation agriculture has shown contrasting results in terms of crop yield since still in a transition period between conventional and conservation agriculture practices.
地点: Low Venetian plain of Veneto region, Italy, 意大利
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. 10-100 平方千米)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 10-50年前
介绍类型






| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Euro €) | 每项投入的总成本 (Euro €) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Weed control and cover crops devitalisation | L/ha | 1.0 | 130.0 | 130.0 | |
| Cover crops: sowing | ha | 1.0 | 254.0 | 254.0 | |
| 设备 | |||||
| Weed control and cover crops devitalisation | ha | 1.0 | 44.5 | 44.5 | |
| Main crop: direct sowing on untilled soil | ha | 1.0 | 63.5 | 63.5 | |
| Main crop: combined harvesting and chopping of straw | ha | 1.0 | 190.5 | 190.5 | |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 190.5 | 190.5 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| Fertilisation | ha | 1.0 | 287.0 | 287.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1'160.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1'450.0 | ||||
In the early years
Increased reliance on herbicides