

Multistory gardening is an innovative and exciting technology for year round vegetable gardening. Multi-storey farming not only makes efficient use of water but it is also safe from droughts and floods.
Purpose of the Technology: This micro-gardening concept being a low input activity is ideal where labor and other resources are scarce. Multi-storey gardens lead to development of self reliance in vegetables for nutrition and food security in the vulnerable households.
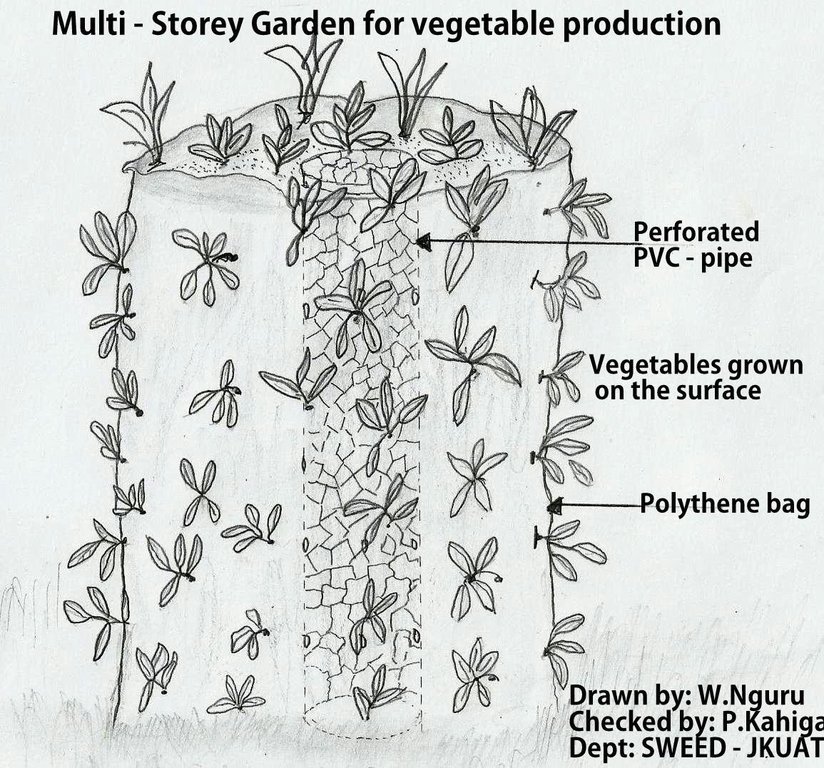
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Materials required for multi-storey gardening include empty cereal bag or animal feed bag, one empty oil can or 6”PVC pipe with holes, 2buckets small stones, 6 buckets soil, 6 buckets manure, seeds, adequate water to irrigate the bag garden and gardening tools. The following procedure is used to set up the garden. 1) Mix the soil and well decomposed manure thoroughly. 2) Cut out the bottom of the oil can and make holes on the sides. 3) Fold back the bag and fill the bottom 15cm with small stones. 4) Place the can on top of the small stones in the center of the bag. 5) Fill the oil can with small stones 6) Fill the area between the oil can and the bag with the soil-manure mixture up to the can level. 7) Pull up the can to the level of the soil compost mixture with a tilting motion. Repeat steps 5, 6 and 7 until the bag is full and a central core of stones is formed leaving the tin at the top of the bag garden. Pour water into the tin through the central core till the soil is soaked.
Natural / human environment: Multistory gardens technology is suitable for urban gardening in Kenya where land for farming has greatly reduced due to urbanization.These bag gardens are also suitable for dry, non fertile areas where soils are not suitable for conventional gardening, areas with water scarcity..
地点: Embu, Eastern Province, 肯尼亚
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷))
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型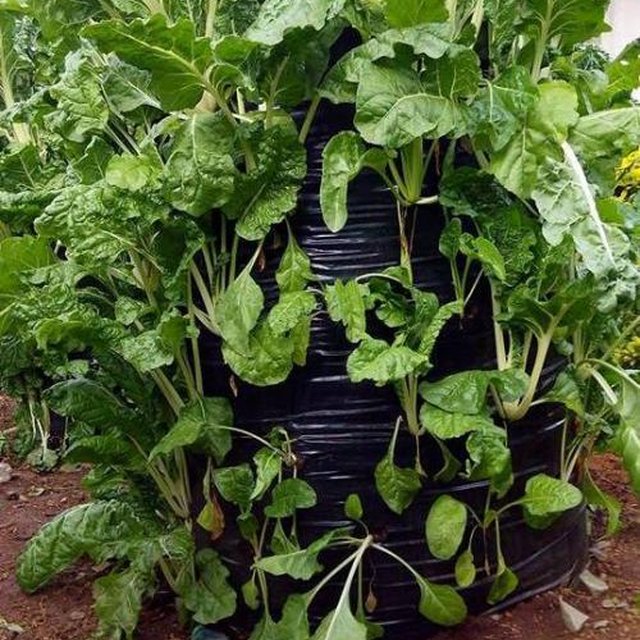




| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Kshs) | 每项投入的总成本 (Kshs) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | Labour per 10 bags | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seedlings | Seedlings | 320.0 | 0.00156 | 0.5 | 92.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| Manure | 20.0 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 100.0 | |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Polythene bag | Bags | 10.0 | 0.25 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 29.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.29 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Kshs) | 每项投入的总成本 (Kshs) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Weeding | Mandyas | 3.0 | 0.8333 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| Harvesting | Mandays | 1.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Tools | Ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.07 | ||||
Improves dietary diversification