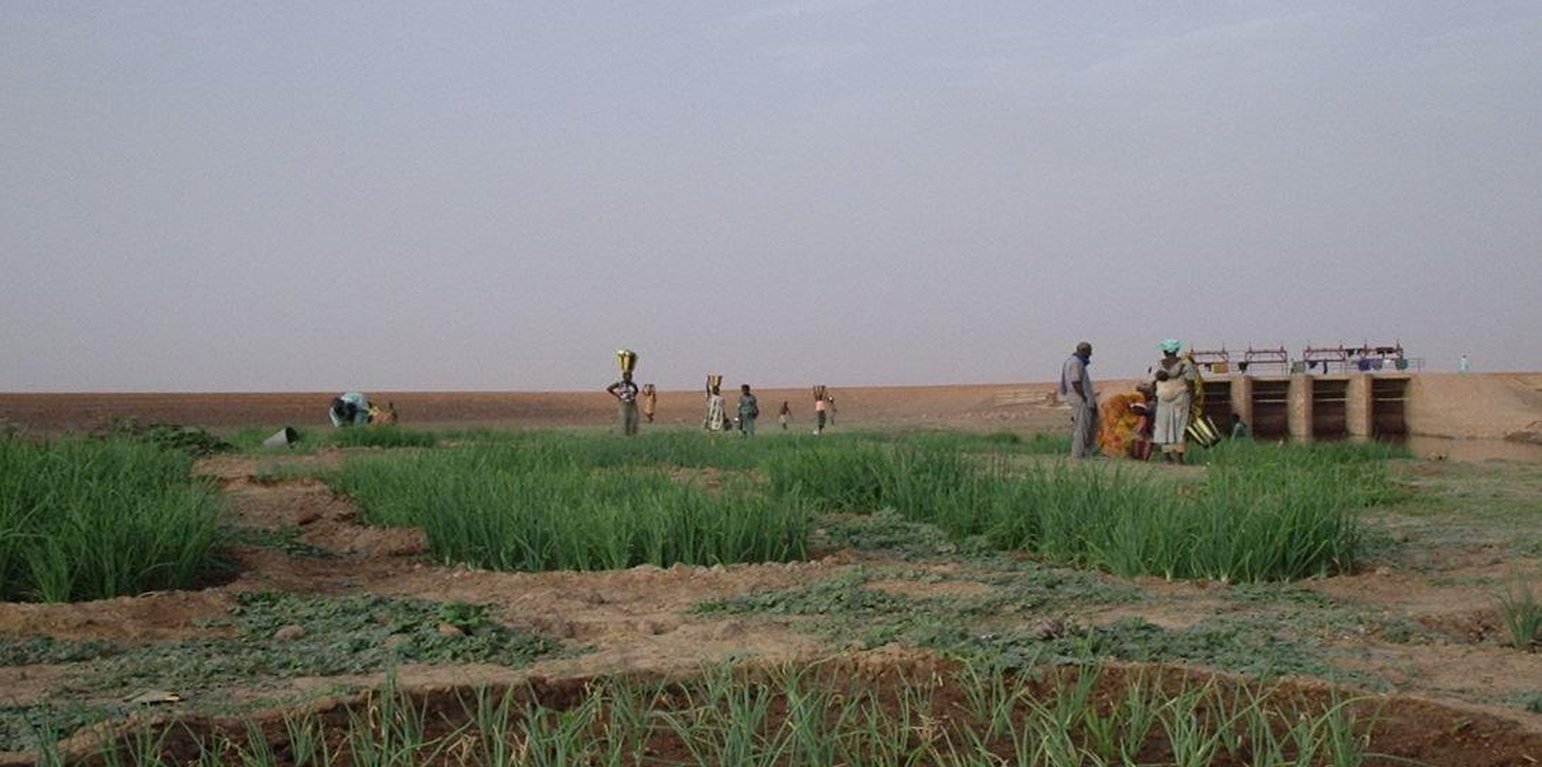




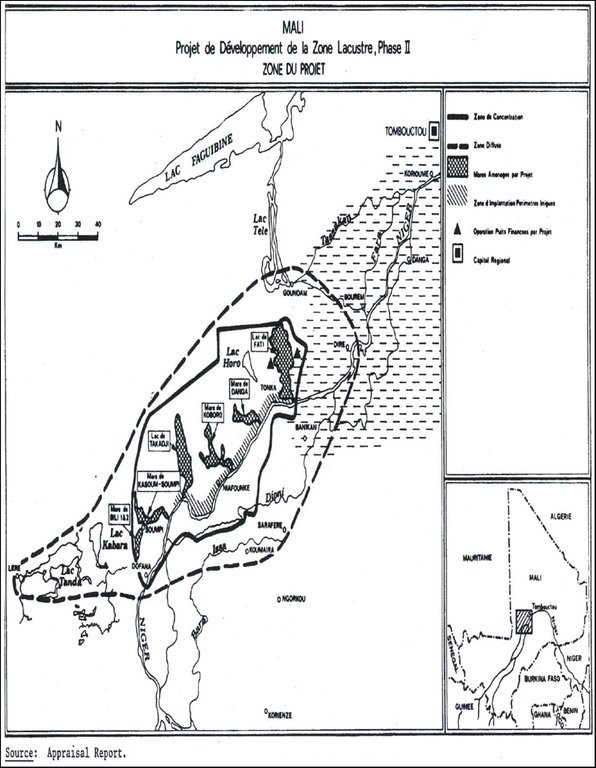
The water for the lakes and ponds in the lakeland area (‘zone lacustre’) alongside the Niger River is supplied when the Niger is in spate by means of a system of natural channels. As the water height of the annual flood wave of the Niger has decreased, some lakes and ponds receive little water. The disadvantages of this natural system are: the loss of harvests due to the flooding of fields before the crops have time to mature, and the rapid retreat of waters that inhibits the capillary effect across large areas.
In relation to the building of control structures and the deepening of channels supplying water to ponds and lakes, the projects main objectives are to: restore water supplies to the lakes and ponds previously fed by the Niger River; regularise water supplies to the ponds and lakes; increase the area under cultivation; restart the growing of flood recession crops and other activities in the areas around ponds and lakes; restore the environment and biodiversity around ponds and lakes; raise the water table around the ponds and lakes.
The deepening of the channels has made it possible to recharge lake and pond basins. It is the reason why we are now seeing the resumption of farming, market gardening, animal husbandry and fishing around the lakes and ponds. By building control structures and large dykes it is possible to control pond and lake recharge, optimise yields and crop growing, and increase the area under cultivation. There is a diversification of production and incomes through the farming of small family units and market gardening plots in the lake and pond areas. The installation of bridge crossings with causeways running across marshlands have helped to open up the area and, as such, facilitate the transport of farm produce, the provisioning of local communities and the circulation of road traffic. The development of the dual road/ferry scheme (the Saraféré-Niafunké road and 40-tonne motor ferry) has revived an economic and human activity that was dying out due to extremely high levels of male outmigration, which left women running households and highly vulnerable.
The stages of initiating, planning and implementing works and installations are based on the studies (soil, topographical and socio-economic) carried out by a consultancy and private company recruited through a tender process to deliver the works according to a well-defined timetable. An oversight and control office undertakes the monitoring and control of works quality and the meeting of agreed deadlines.
In principle, works are carried out during low-water periods when most of the floodplains are dry. The swampy nature of the area makes any intervention in the rainy season impossible. Furthermore, the planning of activities must respect the constraints imposed by nature. The Dabi installation on Lake Takadji is a good example of the application of technical standards.
The application and modus operandi of this good practice involve the following: the water inlets for the lake and pond basins alongside the Niger River are reopened by deepening the feeder channels; the high waters of the Niger River feed the ponds and lakes; water supply is controlled using a cement structure fitted with gates to prevent: the water flow from reversing when the Niger’s water levels are low, water flowing into the ponds and lakes before harvesting is complete; flood gauges to measure annual high water levels.
Various actors are involved in delivering this practice. Their roles are as follows: Beneficiaries are not required to participate in works delivered by contractors (works involving large pond and lakes), but they take charge of the development of VIS plots with support from the World Food Programme (WFP) in the form of supplies. External support from the project/programme finances the installation of facilities, the pump units and the first season’s inputs. Consultancies undertake feasibility studies, produce project specifications and plans, and carry out the monitoring and oversight of works. Local authorities, as a general rule, are involved in the planning of activities or, alternatively, make provision for activities in the PDESC. They also handle the upkeep and maintenance of installations.
地点: Timbuktu Region; Niafunké, Diré and Goundam circles; communes of Soboundou, Soumpi, Tonka, Tindirma, Mali, 马里
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (332.0 km²)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 10-50年前
介绍类型




| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (CFA Franc) | 每项投入的总成本 (CFA Franc) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 其它 | |||||
| total construction | ha | 1.0 | 580.0 | 580.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 580.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1.12 | ||||
Increases in agro-sylvo-pastoral production, increases in local people’s incomes and standard of living. Rice production on a quarter-hectare VIS can increase family income by around 80% compared to traditional means of production involving 1.5 hectares of floating rice grown on the river. The percentage of households that are vulnerable to food insecurity has dropped from 20.4% in 1997 to 5.8% in 2006.