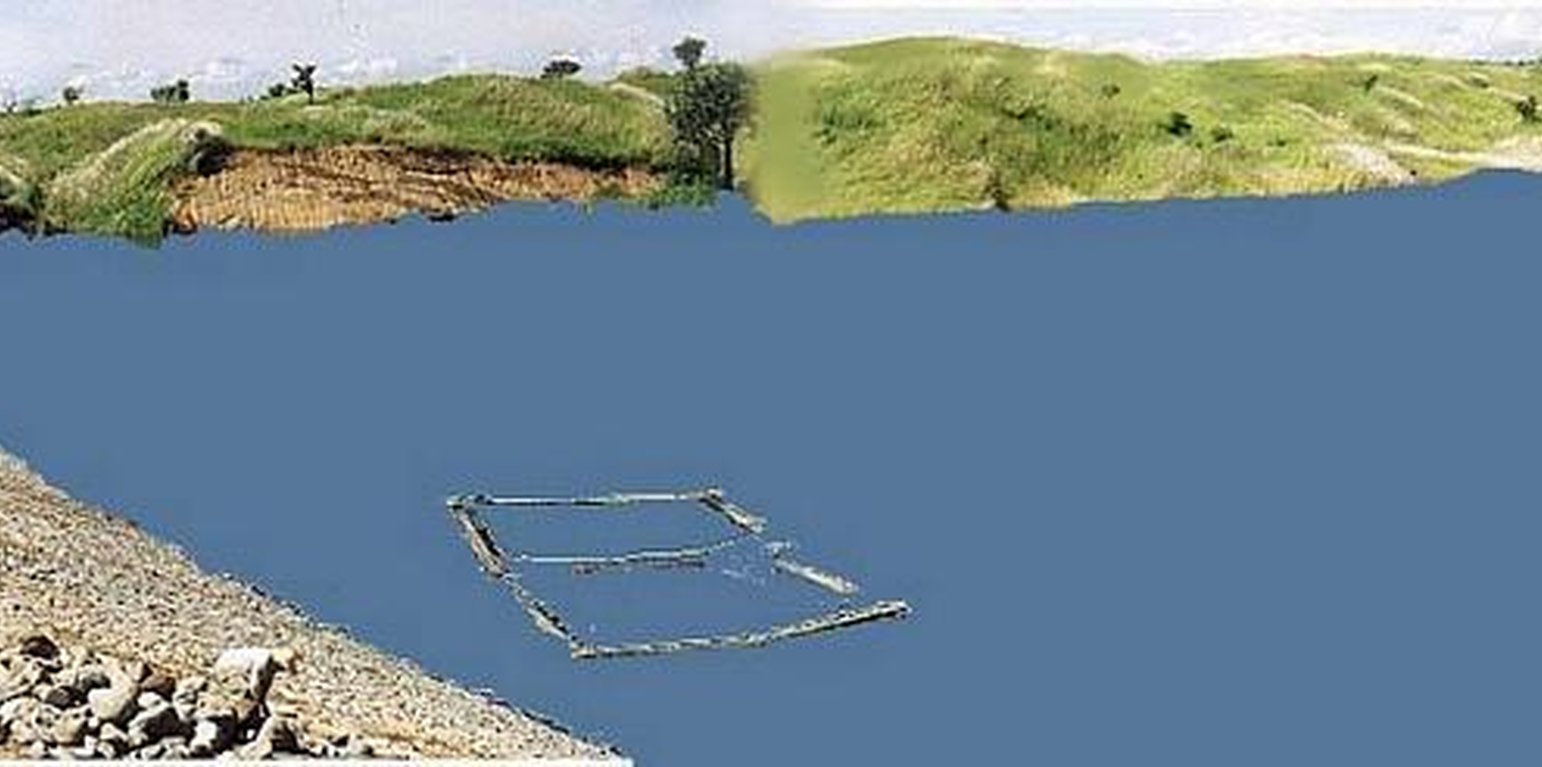




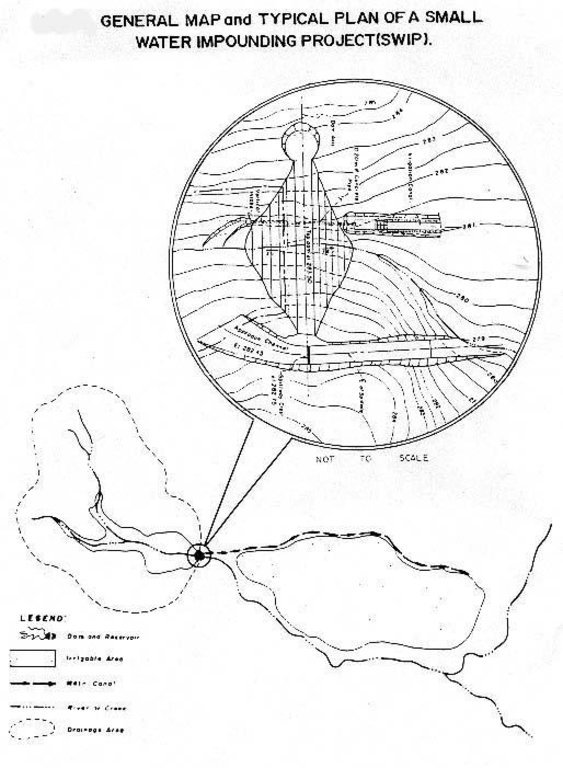
Small Water Impounding Project (SWIP) is a water harvesting and storage structure consisting of an earth embankment spillway, outlet works and canal facilities. It is designed for soil and water conservation and flood control by holding as much water as possible during the rainy season. The reduced volume and force of runoff subsequently reduced their eroding power of water thereby minimizing soil erosion and silting of fertile bottom lands. The reservoir with its stored water is an important supplemental source of water for agriculture and is also used for fisheries. SWIP development involves a holistic approach. The watershed is developed for land use that enhances water infiltration and minimizes soil erosion (for the long life of the reservoir). The most common use of the watershed is agro-forestry. The service area is used for high value crops that minimizes the use of water on a controlled basis. A holistic and integrated approach is done in managing the micro-watershed. The farmer-beneficiaries of the irrigation water and those of the watershed are organized into an association. They maintain the system and protect the watershed by advocating sustainable agriculture.
地点: Nueva Ecija, Nueva Ecija, 菲律宾
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (10.0 km²)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型




| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Phil. Peso) | 每项投入的总成本 (Phil. Peso) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 39000.0 | 39000.0 | |
| 设备 | |||||
| machine use | ha | 1.0 | 55000.0 | 55000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 94'000.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 2'350.0 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Phil. Peso) | 每项投入的总成本 (Phil. Peso) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 900.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 375.0 | 375.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1'275.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 31.88 | ||||
rice production
Fish culture
Picnic grounds
Farmers are organized into an association
Including soil fertility management
During construction
Woodland taking over grassland
reservoir area
Increased groundwater recharge
dry season flow