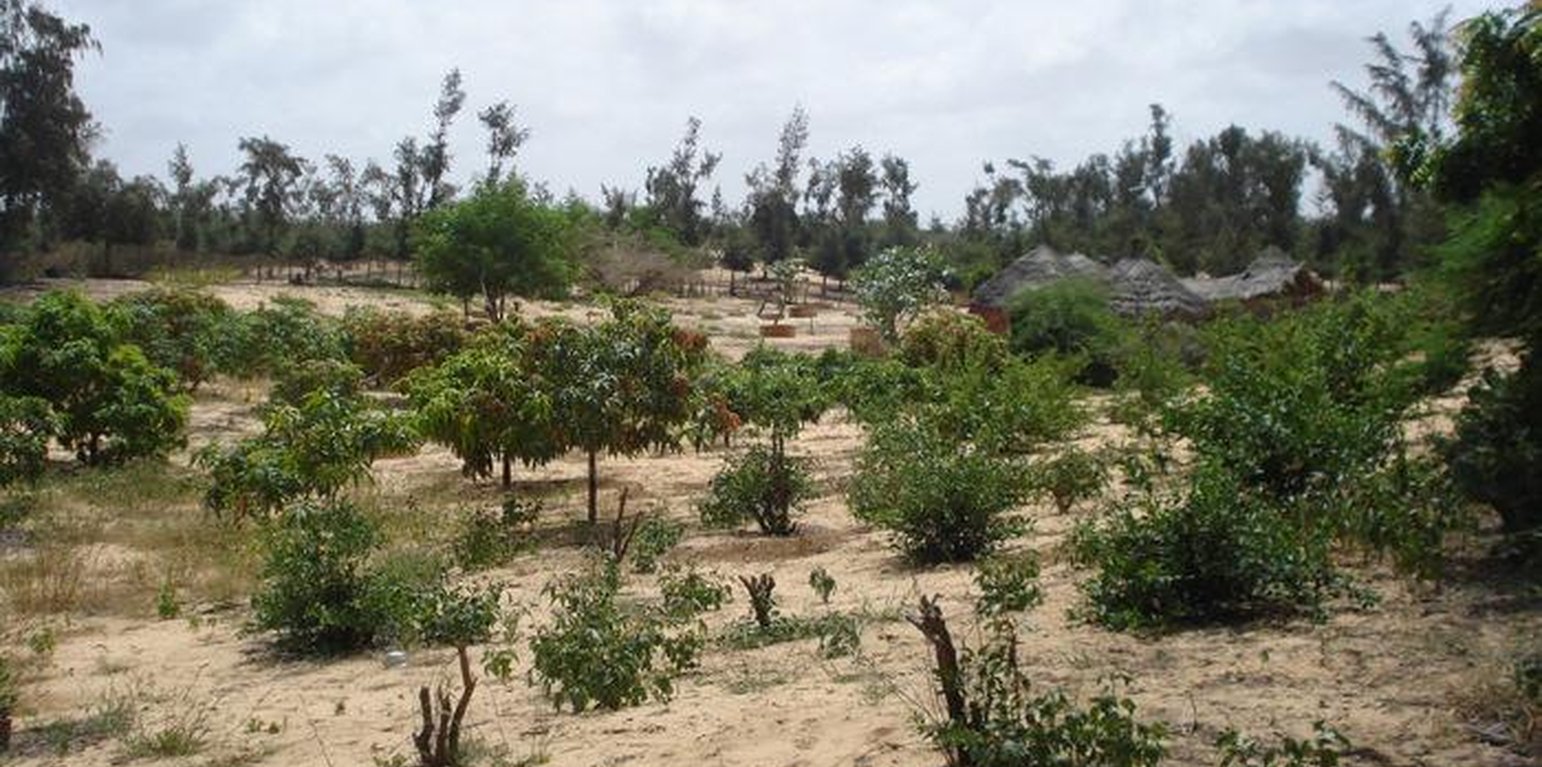




This fruit orchard, mainly containing Mango (Mangifera indica) and Citrus (Citrus lemon) trees, is located in the hamlet of Thioukoun which is part of the village of Lompoul-sur-mer. The surface accounts for about 0.46 ha. Long before the establishment of the orchard, land cover consisted of denuded or sparsely covered white wandering sand dunes threatening agricultural production and villages alike. For some years vegetable production took place on this piece of land and later the orchard was established. Fruits are aimed at sale on the local market but production is insufficient for commercial purposes due to a pest and senescence of fruit trees. Citrus fruits are used by the cultivator and his family for pharmaceutical purposes. Inorganic fertilizers and organic manure are both used in order to improve soil fertility. Irrigation with water from one of the 8-9 m deep wells is practiced for a few Cocos nucifera plants but not for the other species. Labor is done by employees with whom the assigned caretaker of the orchard shares the little revenues from selling fruits on the market. The orchard is protected by a hedge made of dead Balanites aegyptiaca and Acacia raddiana branches and contains a small number of living individuals of other species.
Natural / human environment: The Niayes, located between Dakar and St. Louis, constitute a territory of 5-30 km width covering a surface of 4’200 km2. The region profits from a cool, humid climate, caused by the northern maritime winds (alizés) during the the dry season, while the rest of Senegal experiences the dry and hot Harmattan winds from the East. This results in favorable conditions for vegetable production during the dry season. Sand dunes cover the entire territory being categorized as white or wandering dunes, yellow semi-fixed dunes and as a system of continental fixed red dunes. The continental sand dunes support a shrub savanna which has been used as grazing ground by Fulbe pastoralists for centuries. The near-surface groundwater is the key that allows for cultivation of the zone, however considering the decline in rainfall during the last 60 years, the future of this water source remains uncertain. Lack of rainfall was one of the causes that led to the retreat of natural vegetation which therefore was not sufficient to stabilize the dunes any longer. Migration of sand dunes could now attain up to 10-12 m a year. However, deforestation at the beginning of the 19th century as well as overgrazing were important factors causing gradual desertification in this system.
地点: Thioukun, Department of Kébémer, 塞内加尔
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷))
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型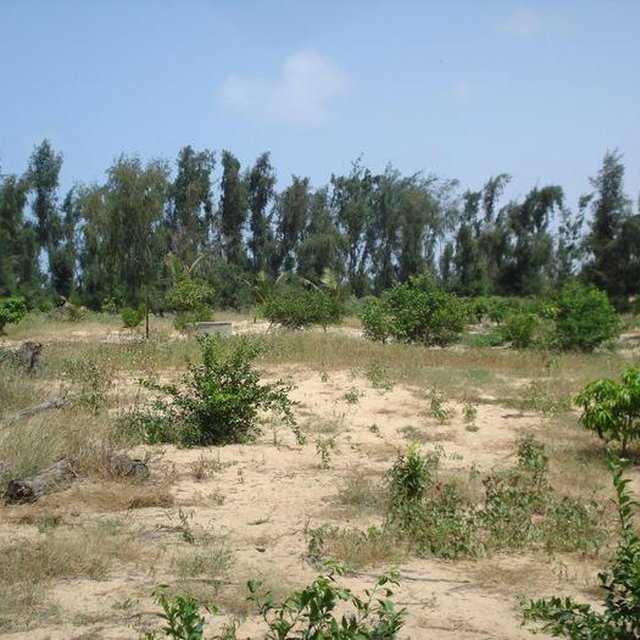




The mango fly