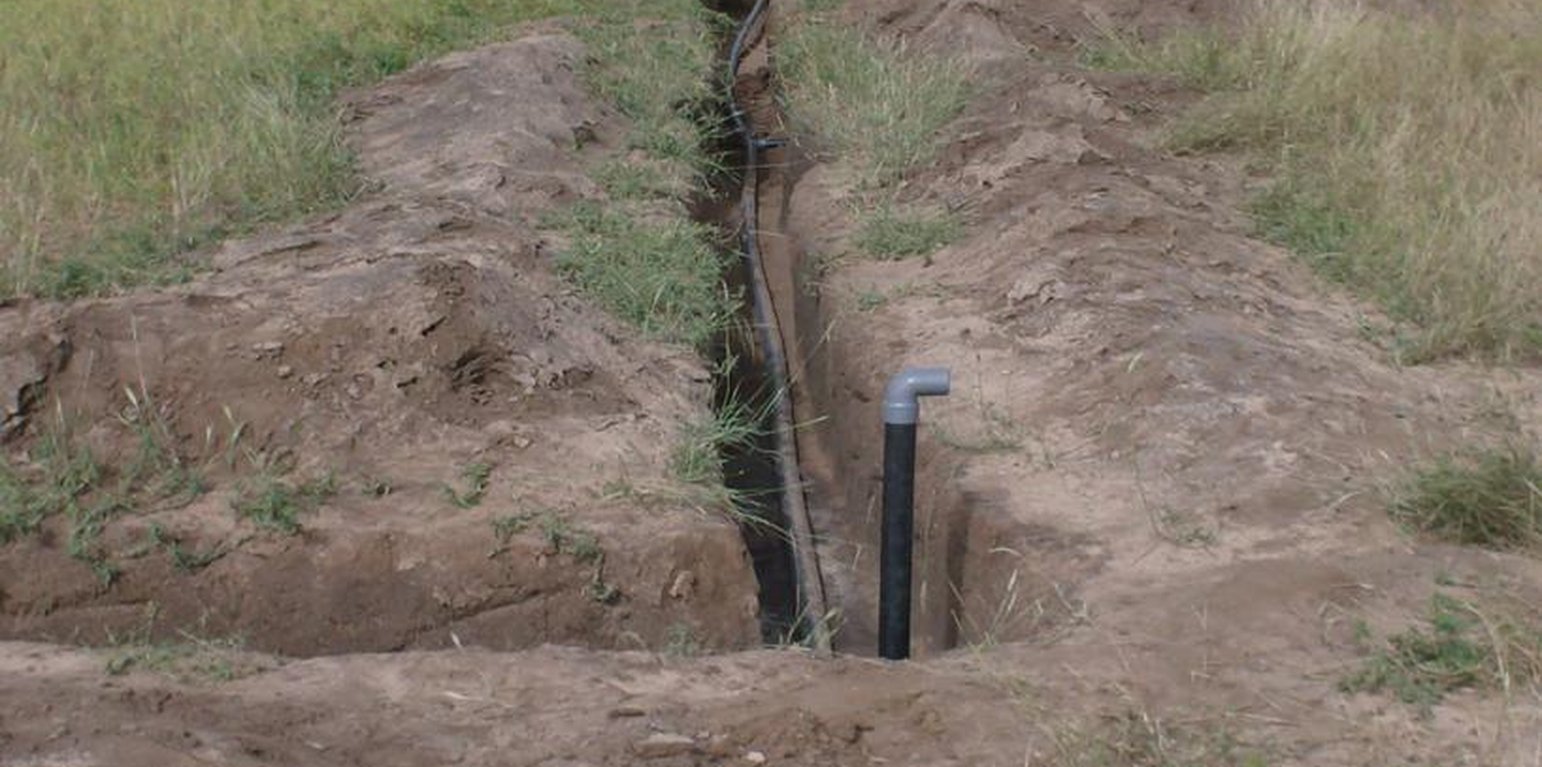




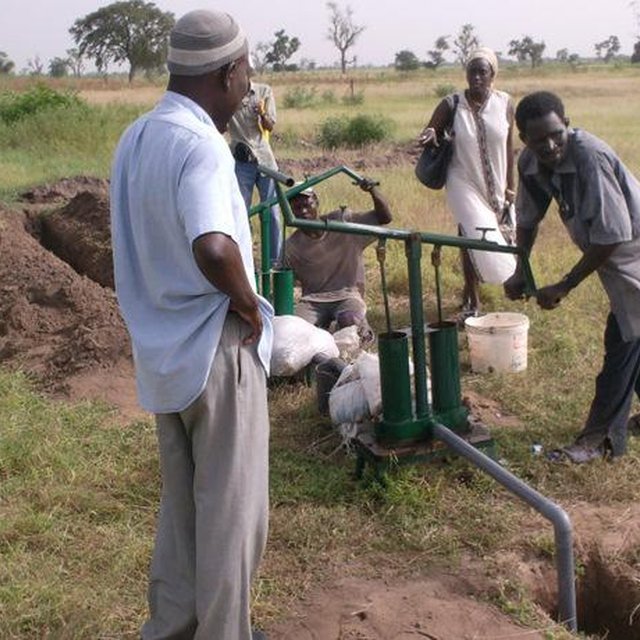
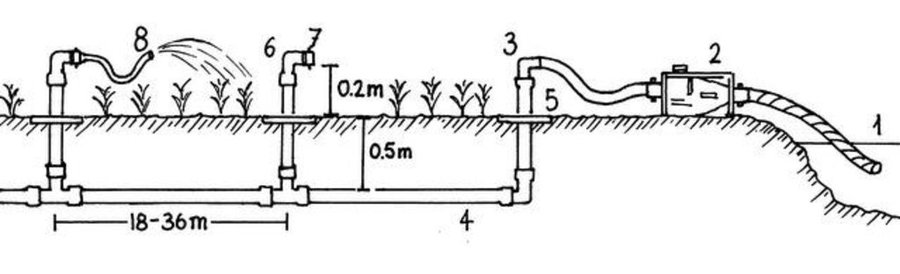
The principle of the Californian system is to convey water to the crops through fixed underground rigid PVC pipes (40–75 mm diameter). The pipe network is buried at 0.50 m depth to avoid deterioration by UV radiation and agricultural practices. Risers with hydrants are fixed to those rigid pipes at regular distance (18-36 m). To each riser a 14 m long flexible hose is attached which can be dragged around to irrigate the individual plots and crops. The installation of the pipe network can be made locally by plumbers. Water is supplied through a pump (manual, pedal or small motor) from a well, a reservoir or a river. From the intake water is conveyed to the highest point of the plot which allows the conveyance to the field’s most distant point (irrespective of topographical conditions - upslope or downslope).
The system is remarkably efficient in sandy or salty soils. It is adapted to small–scale farming especially for vegetable crops, rice and tree crops and is suitable for areas ranging between 0.25 - 1 ha; one riser irrigates an area of 500-1000 m2. The system as such does not require maintenance. In case of deterioration of pipes or fittings, the farmer can easily fix the problem himself or with the assistance of a local plumber. The estimated life expectancy for the Californian system is 6-10 years in West African conditions. Ideal conditions for transfer / adoption of the technology include: (1) Availability of shallow aquifers, and other water sources; (2) Occurrence of sandy soils and sandy clay soils; (3) Clearly defined land legislation and tenure; (4) Access to markets and to microfinance institutions.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities for this technology are the following: 1. Layout of pipe network by putting stakes along the line to indicate the orientation of the canal to be dug. 2. Excavate network of canals (0.2 m wide, 0.5 m deep; straight and regular). In sandy soil the interval between risers is 30m x 18m or 36m x 18m (intervals are multiples of 6 m = PVC pipe unit length). Density of risers is 10 -15 risers / ha.
3. Install the pipes into the open canals, fittings are assembled by sticking. 4.Install hydrants composed by a 0.2 m high riser, a PVC elbow and a locally made flow control device (plug); the risers are anchored in the soil through a small concrete slab.
5. Put the pipe under flow condition to verify the water tightness of the system. 6. Bury the canals. 7. Protect risers from sun. Regarding maintenance of the system the following is important: 1.Before starting to pump it is recommended to let open one of the hydrants in order to avoid excessive pressure and blasting of pipes. 2. In case of deterioration of the pipes or fittings, land users can easily fx the problem themselves or request the intervention of a local plumber.
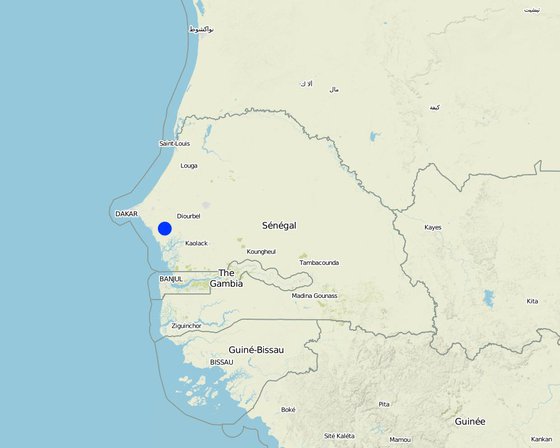
地点: Diourbel, Baba garage village, Diourbel, 塞内加尔
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播:
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型




| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (不适用) | 每项投入的总成本 (不适用) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| PVC | ha | 1.0 | 1333.0 | 1333.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1'383.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1'383.0 | ||||
SLM之前的数量: 0.1
SLM之后的数量: 2
ha per farmer group
SLM之前的数量: < 10
SLM之后的数量: 20
l / person-days
pilgrimage to Mecca, marriages et.
group management of irrigation facilities