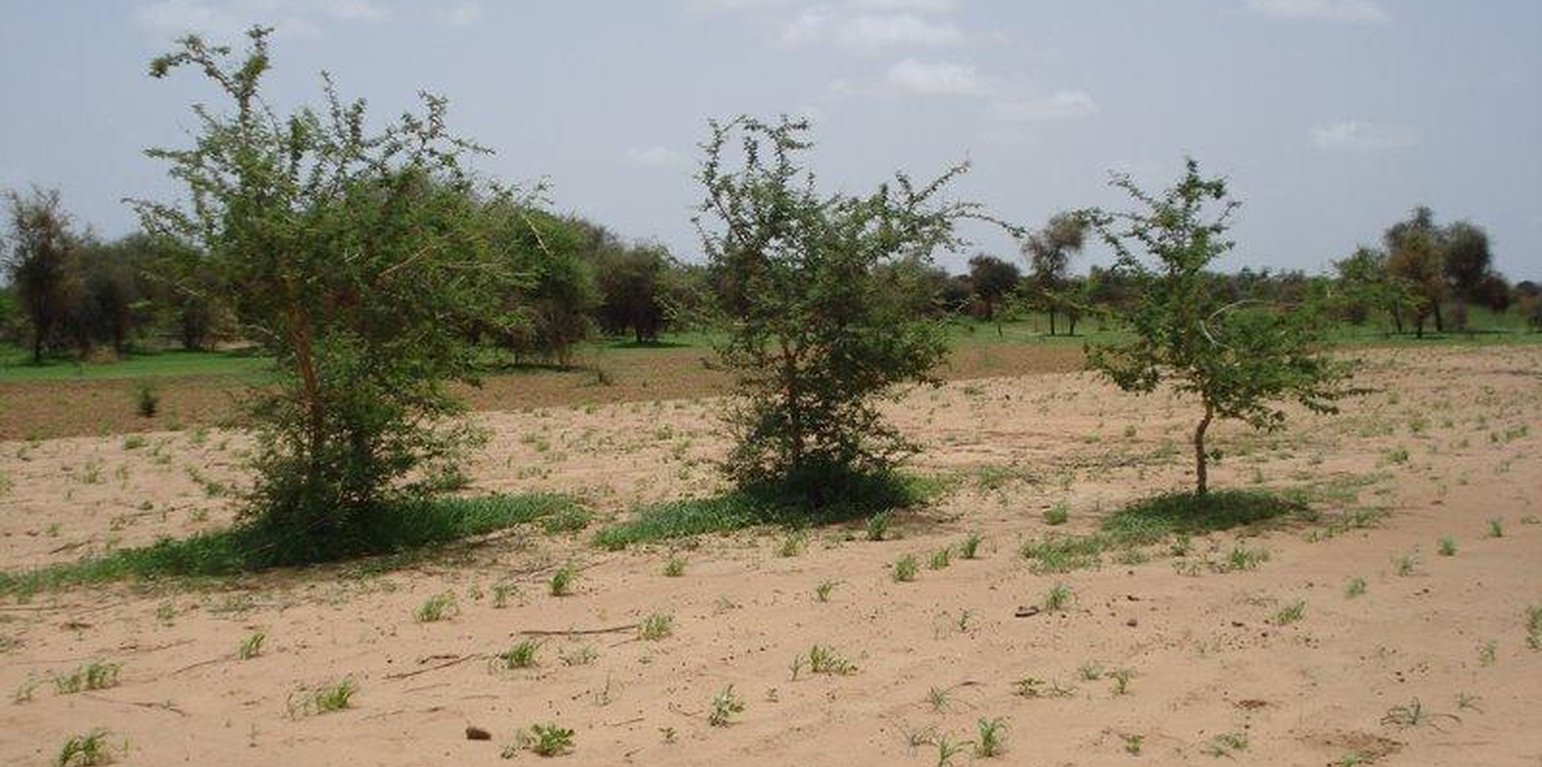




Acacia senegal is the dominating woody species in this agroforestry system. To improve soil properties and crop production, organic manure is applied and a fallow system practiced. One part of the field is being cultivated with either millet (Pennisetum typhoides), cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) or maïz (Zea mais] whereas the other part is left fallow for two years before rotation.
Purpose of the Technology: Initially, the main objective of the land user applying the technology was to improve soil properties and crop production in his fields by maintaining any tree and protecting natural regeneration when preparing his land for cultivation. With the start of exploiting Acacia senegal for the exudates, gum arabic, the potential of revenue increase through gum exploitation became evident and the objective shifted from soil protection to gum exploitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Because of knowledge his father passed on to him, the land user applying this agroforestry practice believes that any tree in his fields is useful and should be protected.Through the technique of assisted natural regeneration, trees naturally growing in the field are protected to reach mature age instead of being cut to clear area for cultivation. The only inputs related to this technology are those for seeds for crop cultivation. During the 3-4 months of gum Arabic exploitation, the land user is obliged to survey his fields day and night, as intruders try to tap the Acacia senegal trees illegally. However, this task is fulfilled by the landuser himself and does not involve expenses for payed manpower.
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology site is located in the sylvopastoral region of the Ferlo in the north of Sénégal. The agro-climatic zone is classified as semi-arid with mean annual precipitation of 300-400 mm. The main land use type in the area is extensive pastoralism followed by rainfed agriculture. Pastoralism is primarily practiced by transhumant Fula (Peulh) herders and further by Mauritanian Moor herders with herds of dromedaries. Vegetation cover in the area has been largely degraded due to cutting for domestic uses and cattle feeding, bushfires and overgrazing. The soil is exposed to wind erosion which carries away nutrients in the topsoil and therefore declines soil fertility. During intense rains in the rainy season, surface runoff is accelerated and leads to the formation of gullies and ravines.
地点: Barkédji, Louga, 塞内加尔
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播:
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 10-50年前
介绍类型








| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (不适用) | 每项投入的总成本 (不适用) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seeds for millet | ha | 1.0 | 1.68 | 1.68 | |
| Seeds for groundnut | ha | 1.0 | 5.25 | 5.25 | |
| Seeds for cowpeas | ha | 1.0 | 7.85 | 7.85 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 14.78 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 14.78 | ||||
As the land user can count on income from gum exploitation he is less vulnerable to crop failure
Applies especially for fallow part, cultivation might be entirely given up
Income from gum arabic exploitation
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible
Biological N-fixation (A.senegal), but amount questionable
Through plant litterfall, application of manure
Mainly applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part only little
Applies for the cultivated part only
Birds building nests in trees on fields
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible