



Farmers in northeast parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina traditionally applied the technology to address shallow landslides, surface erosion or loss of top soil due to sheet or interrill erosion. Movements of the upper layers of the soil appears due to unfavorable properties of the soil layers (clays, pseudoclays), set on impermeable geological substrates, all under conditions of intense and long-term rainfall. During the last decades, it has been frequently applied in the area of Kladanj municipality, whose administrative services for agriculture and forestry technically specified and promoted the technology. Landslides are one of the major problems in the hilly areas of Bosnia and Herzegovina, threatening particularly the agricultural lands. The technology is being applied by farmers on their own properties, but it is also part of public interventions, e.g. for the protection of roads or other infrastructure from landslides or in the context of roads recovery programs damaged by landslides. The technology aims to reduce the impact of the shallow (up to 2 - 3 m in depth) landslides of relatively small surface, by preventing further movement of the soil. So far, it is sporadically applied on around 20 – 30 locations in Kladanj Municipality, whose territory is around 355 sq. kilometers.
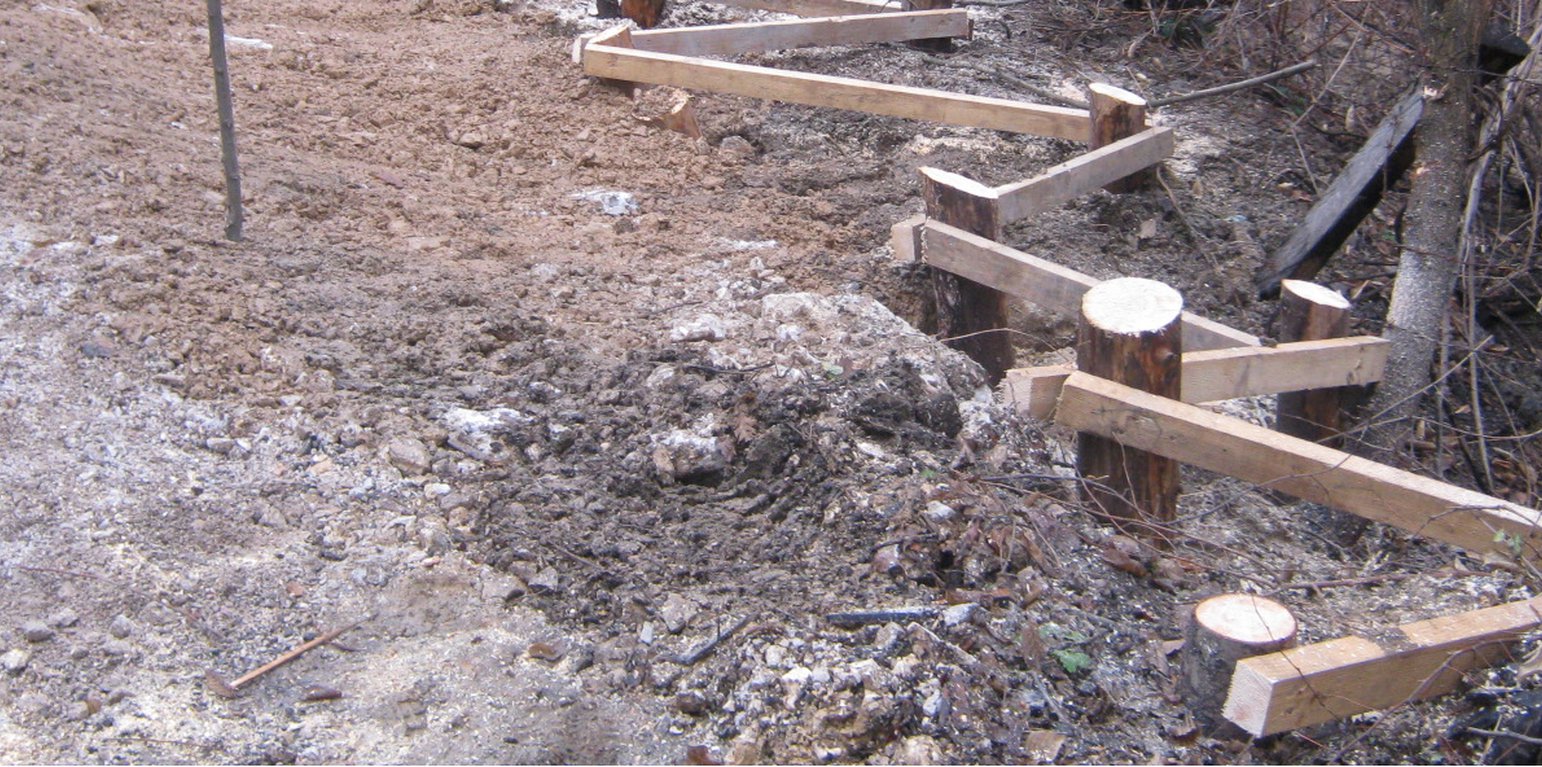
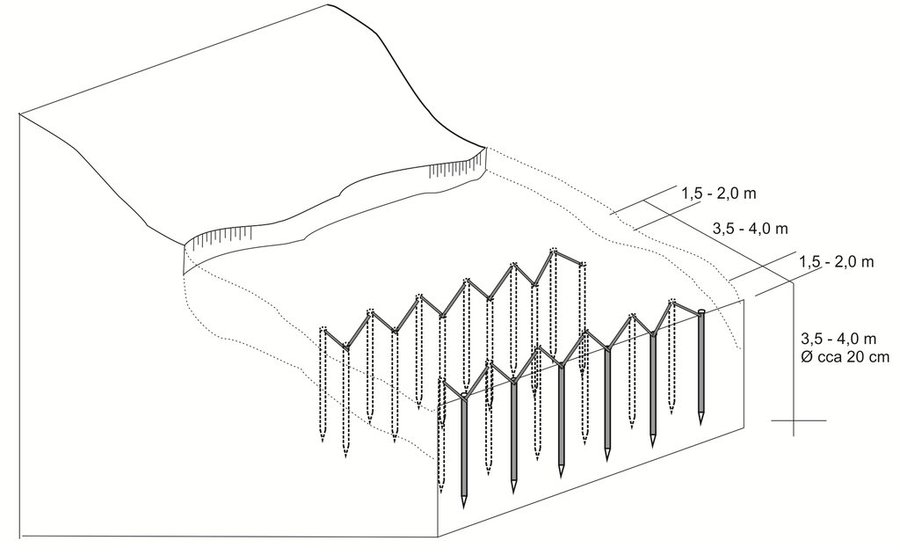
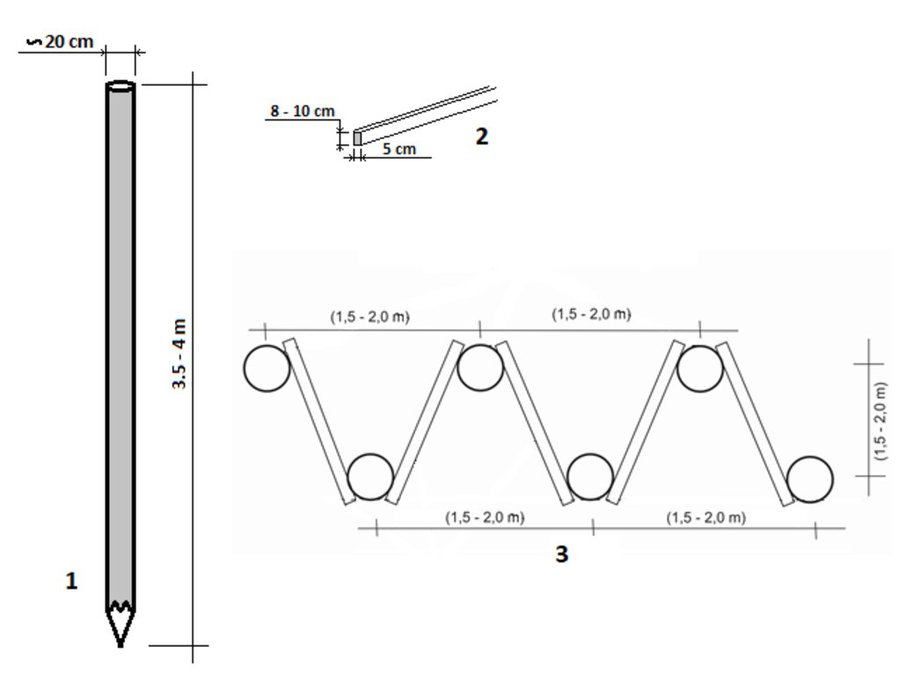
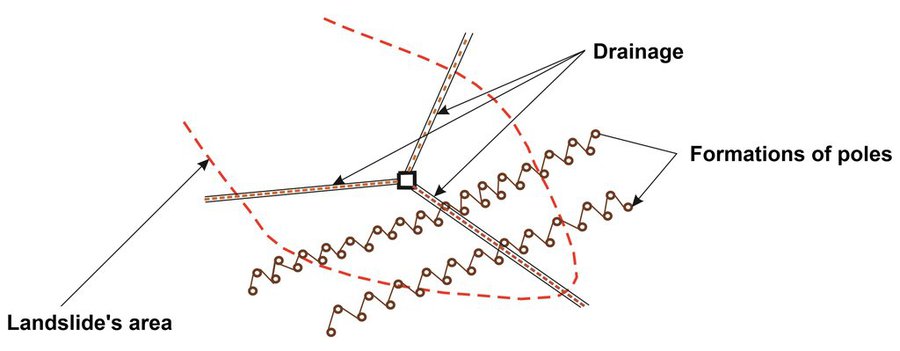
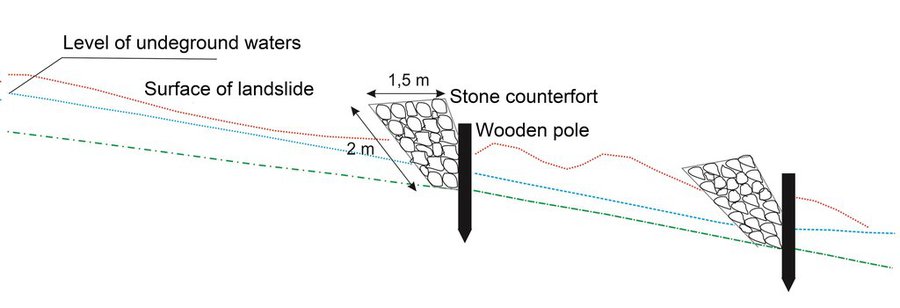
The technology implies pounding wooden poles in front (below) of the frontline of the landslide, along the contour, perpendicular to the slope. Land users recommend oaken pols due to their durability. The poles are usually 3.5 – 4 m long and 20 – 30 cm in diameter. One pole formation consists of two parallel lines of poles, with 1.5 to 2 m distance from line to line. The poles are positioned in a staggered way that a zigzag is formed. The poles are interconnected with wooden laths. One pole formation is usually enough to address smaller landslides, but in case of larger landslides, two formations are recommended. In the latter case, in combination with a drainage system, stone counterforts are formed in front (above) the poles' formation. See technical drawing for more details.
The primary purpose of the technology is to recover shallow and small landslides on slopping terrains. Stopping the movement of agricultural land after reparation of cracks and land gaps caused by landfall enables re-utilization of the land for either agricultural production or agro-forestry. In the municipality of Kladanj walnuts or other wooden fruit species with strong roots are often planted on recovered landslides.
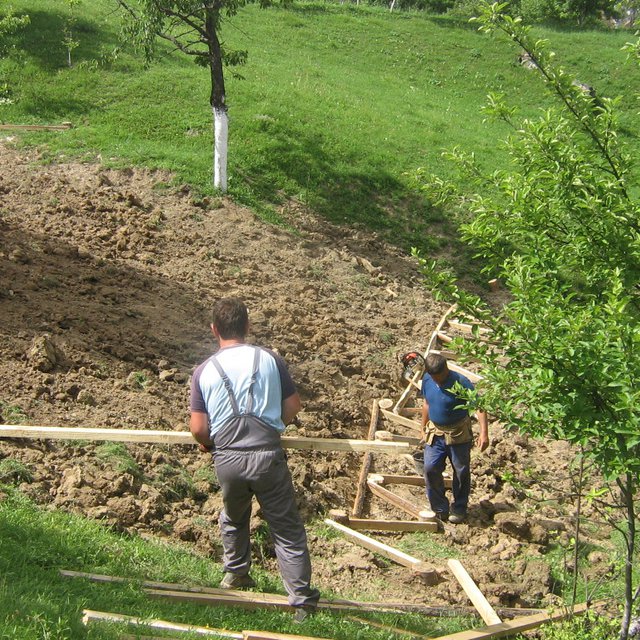
After a prior assessment of the depth and surface of the landslide, an expert or a technician prepares simple project sketches. The sketches define configuration of pole formations and materials needed for the construction (oak poles, laths). The realization of the technology is not particularly demanding. Nowadays machines are used to pound poles in the ground (mainly by a dredge's spoon).
It is a relatively inexpensive technology which could be financed by even small farmers who can protect or recover their, under Bosnia and Herzegovina conditions, usually small agricultural land parcels.
Although not an integral part of the technology, modification with water drainage from the body of bigger landslide ensures additional, long lasting stability of the terrain. If performed, the drainage is carried out by depositing drainage material (perforated pipes, pebbles, tiny stone fractions) in the lower zone of drainage trenches whose configuration and depth depends on the terrain conditions. Another modification of the technology could include construction of a stone counterfort in front (above) the pole formation. These modifications are briefly presented in the technical specification of the technology, but they were not applied on the site (Borak locality) where activities, establishment and maintenance costs of the technology were observed.
地点: Kladanj municipality, Tuzla canton, 波斯尼亚和黑塞哥维那
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
在永久保护区?: 否
实施日期: 10-50年前
介绍类型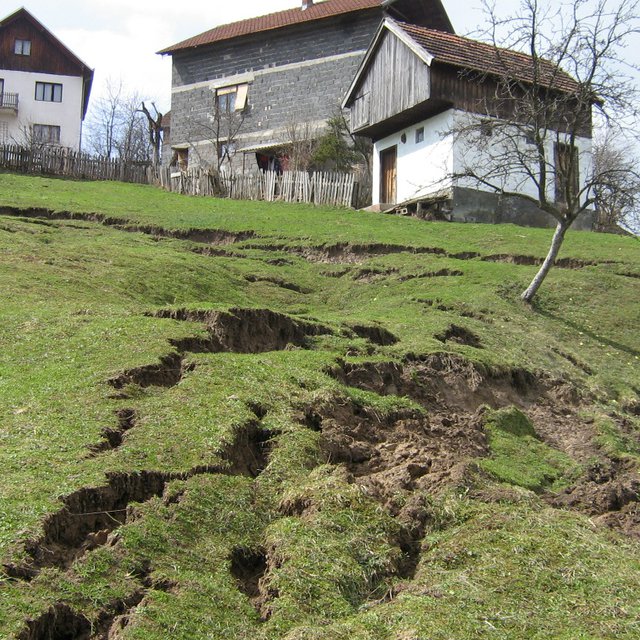






| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Expert's characterization of landslide, designing of construction, specification of materials | Working day | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| Pounding the poles into the ground | Working day | 10.0 | 29.24 | 292.4 | 100.0 |
| Connecting poles with lathes | Working day | 1.0 | 29.24 | 29.24 | 100.0 |
| Planting of walnut seedlings | Working day | 10.0 | 29.24 | 292.4 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Heavy machinery (dredge) work on pounding poles into the ground (hired) | Hour | 16.0 | 46.78 | 748.48 | 30.0 |
| Heavy machinery (dredge) work on leveling of terrain | Hour | 4.0 | 46.78 | 187.12 | 30.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Walnut seedlings | Piece | 300.0 | 2.92 | 876.0 | 30.0 |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Wooden (oak) poles | Piece | 100.0 | 17.5 | 1750.0 | 30.0 |
| Wooden connecting laths | m | 200.0 | 0.5 | 100.0 | 30.0 |
| Other auxiliary materials (nails, wire, etc.) | Lump sum | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4'487.64 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 4'487.64 | ||||