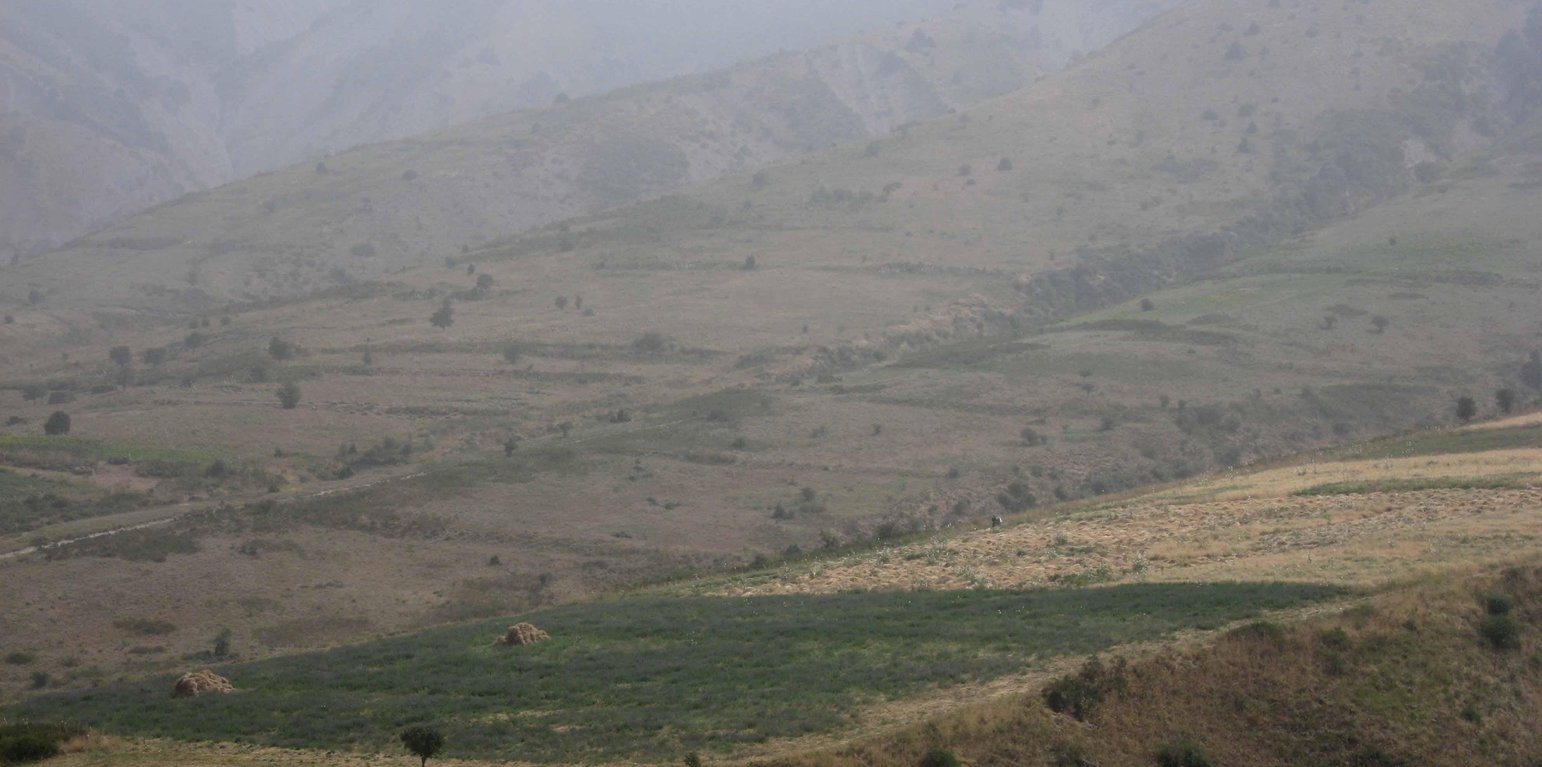




An Esparcet plot of one hectare is located on a hillslope in the Chukurak watershed. The owner lives in the valley far away from the plot. During the harvest, he is staying in the hills a whole week, because a daily journey to his house would take too much time. For the last three years, the farmer is cultivating Esparcet with the main aim to feed his cows. In two years, he will switch to a wheat or chickpea plot. In total, the farmer owns19 hectares of cropland, out of which the Esparcet plot accounts for 20% of his income. Next to the Esparcet plot, other farmers cultivate wheat and chickpea. In contrast to Esparcet, those plots must be protected from boars. Even though irrigation is impossible and the water point is situated far away, Esparcet grows very well because of the straight and spread-out roots. Esparcet is beneficial for the state of soil fertility and soil stabilization. Their seeds are more expensive than wheat seeds, but also result in a higher harvest. Esparcet can be harvested up to three times a year depending on water availability.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of Esparcet cultivation is fodder production for the cows. The farmer owns other plots where he cultivates wheat. Moreover, it’s a good location for an Esparcet plot: Even though water is not available Esparcet maintains the soil moisture and nutrients while reducing soil erosion. Thanks to the crop rotation, the soil is in a healthy state. Yield quantity and quality are very satisfying for the farmer.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The farmer stresses that good knowledge is needed to know where, what and how to cultivate. He learned from other farmers. Before establishing the perennial crop, he first planted a nurse crop of fodder grain in spring. Nurse crops strengthen soil stability while minimizing weed and overly sunlight. Plowing, sowing and cutting are initial as well as recurrent activities. No fertilizer and no plot guarding are needed. Initial costs when growing Esparcet are higher than for wheat, because Esparcet seeds are more expensive. Additionally, seeds of the nurse crop are needed.
Not to neglect is the long way from the farmers’ house to the plot which takes time and fuel, but the farmers of that hillslope often give a lift to each other. Also during harvest the neighboring farmers are helping out.
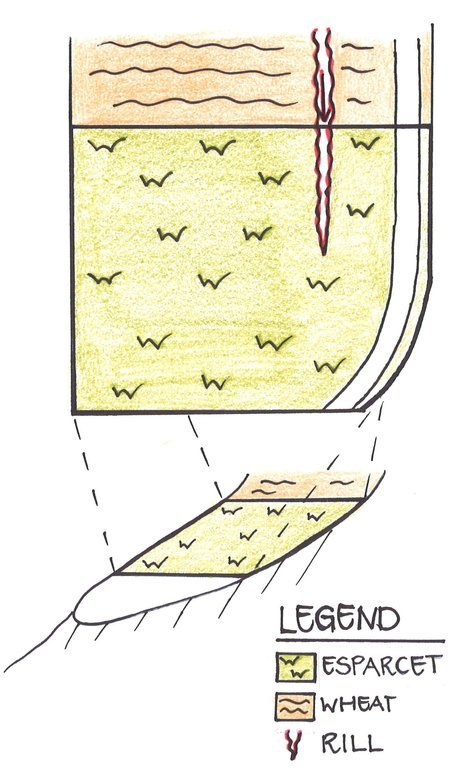
Natural / human environment: The plot on the hillslope is located far away from the farmer’s’ village Sarmaydon 2. It’s situated at around 2000m asl below the hill peaks, where boars are entering. On three sides, the plot is delimited naturally by incised riverbeds which make accessibility more difficult. Due to the high altitude, there are low temperatures and high moisture. Above the Esparcet cultivation, wheat and chickpea plots are cultivated leading to off-site effects on the Esparcet plot. In the Esparcet plot, a deep rill developed originating from the wheat plot situated upslope.
地点: Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan, 塔吉克斯坦
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷))
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型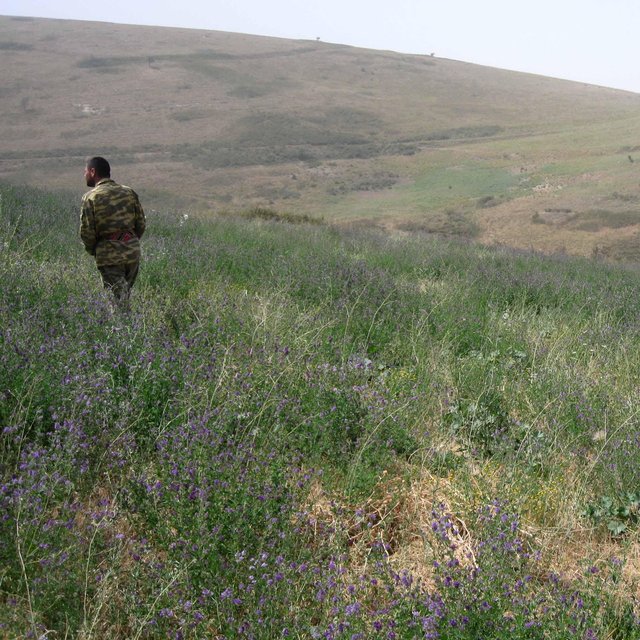






| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Plowing | Person/day | 0.2 | 15.5 | 3.1 | 100.0 |
| Sowing | Esparcet seeds | 0.2 | 15.5 | 3.1 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Tractor rent | hours | 3.0 | 6.9 | 20.7 | 100.0 |
| Petrol for plowing | litres | 40.0 | 1.14 | 45.6 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Fodder Grain seeds | kg | 70.0 | 0.414285 | 29.0 | 100.0 |
| Esparcet seeds | kg | 20.0 | 6.21 | 124.2 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 225.7 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 225.7 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Cutting Esparcet | Person/day | 94.5 | 12.43 | 1174.63 | 100.0 |
| machine use to cut | hours | 2.0 | 31.1 | 62.2 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Petrol | litres | 40.0 | 1.14 | 45.6 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1'282.43 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1'282.43 | ||||
First year only one cut possible but after that yield increases to a positive extent
Esparcet seeds are relatively expensive compared to other seed types
No guarding needed