



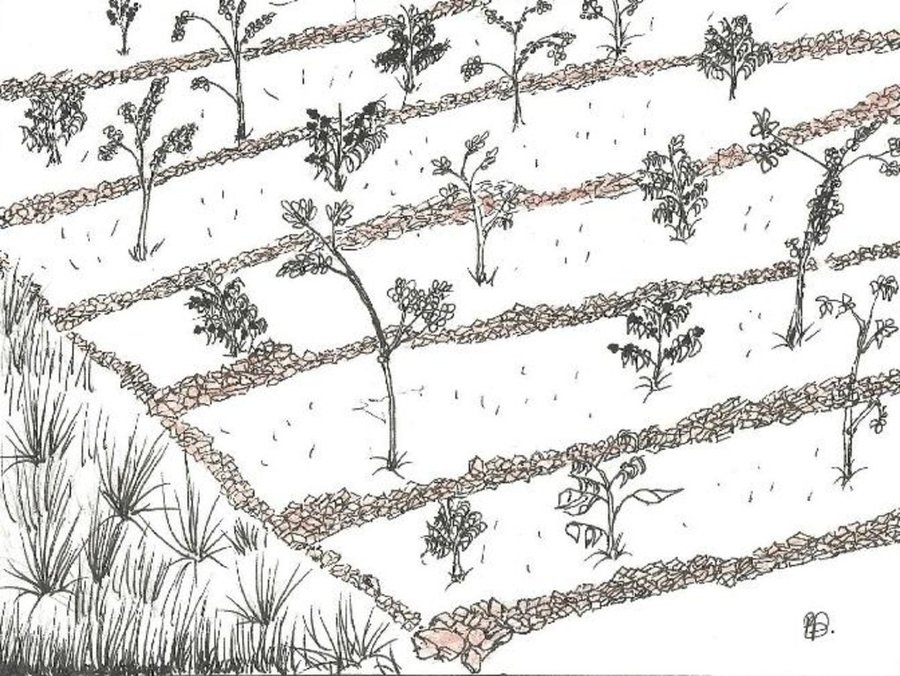
Ficus natalensis is traditionally scattered in crop fields as a land management practice in central and south-western Uganda. The improved technology designed through community participation involves planting lines of Ficus natalensis along the contour at an interval that enables the tree to provide shade to young crops without depriving them of sunshine. When planted together with coffee trees or in banana plantations, the tall Ficus tree forms the top storey that protects the crop from the hot sun.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of Ficus based agroforestry is to protect the soil from erosion. Within 3 to 5 years the Ficus tree forms a deep root system that stabilizes the soil. In addition, it drops leaves which quickly decay to provide both soil cover and manure thereby increasing the fertility of the soil. The trees provide firewood, fodder for livestock and bark cloth which can be used domestically or sold to supplement household income. They also act as wind breaks.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Ficus Natalensis is propagated using cuttings from young branches which are planted vertically 6 m apart along a contour. Propagation material is readily available and cheap, making the technology inexpensive to establish. Any annual or perennial crop can be inter-cropped with Ficus spp. provided the tree canopy is managed well. The tree is quite robust and can attain heights of over 20m, with a very extensive canopy if left to grow. Pruning raises its canopy to the desired height above the ground. In its early stages, fencing is required to protect the tree from damage by livestock. Within 12 to 18 months, however, the tree is established enough to withstand browsing. Only simple tools like hoes and garden forks for digging holes/pits are essential for establishment of the technology. The implementation of the technology on steep slopes (> 50%) is not possible without other supportive SLM interventions, in Rakai these include construction of stone lines and mulch application.
Natural / human environment: The pruned branches of Ficus natalensis are used as fuel wood when dry. Therefore scarcity of fuel wood may lead to over-harvesting of branches and destroying the canopy. Nonetheless, the tree regenerates quickly with the coming of the rains. Ficus tree can live for a hundred years.
地点: Rakai District (Kijonjo Parish), Uganda, 乌干达
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播:
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型







| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Ushs) | 每项投入的总成本 (Ushs) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Sourcing planting materials | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Making pits | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Planting cuttings | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| Spot weeding | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| 设备 | |||||
| 2 panga | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| 2 hoes | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Cuttings (500 stern cuttings) | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 122.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.05 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Ushs) | 每项投入的总成本 (Ushs) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Spot weeding | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| Pruning | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| Removing and processing the bark into bark cloth | ha | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | |
| 设备 | |||||
| 1 panga | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 1 hoe | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 38.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.02 | ||||
SLM之前的数量: 100
SLM之后的数量: 400
coffee and bananas
For wood fuel (firewood & charcoal). there was almost nothing before.
conservation of moisture, improved soil fertility
Agricultural land on which Ficus is planted
respondents reported increses in income but not documented.
Realization of the benefits has led many farmers to need more help therefore raising the cost of labour
incresed agricultural produce.
backcloth is used for cultural functions .eg. burying the dead.
The technology has improved availability of both food and fuel wood. Some products from trees used in agroforestry such as backcloth (Embugo - Luganda) are sold, diversifying household income.
dried tree leaves add humus and organic matter in the soil.
various tree species are used for agroforestry.
Prevention of predisposition towards landslides
windbreaks reduced wind velocity.