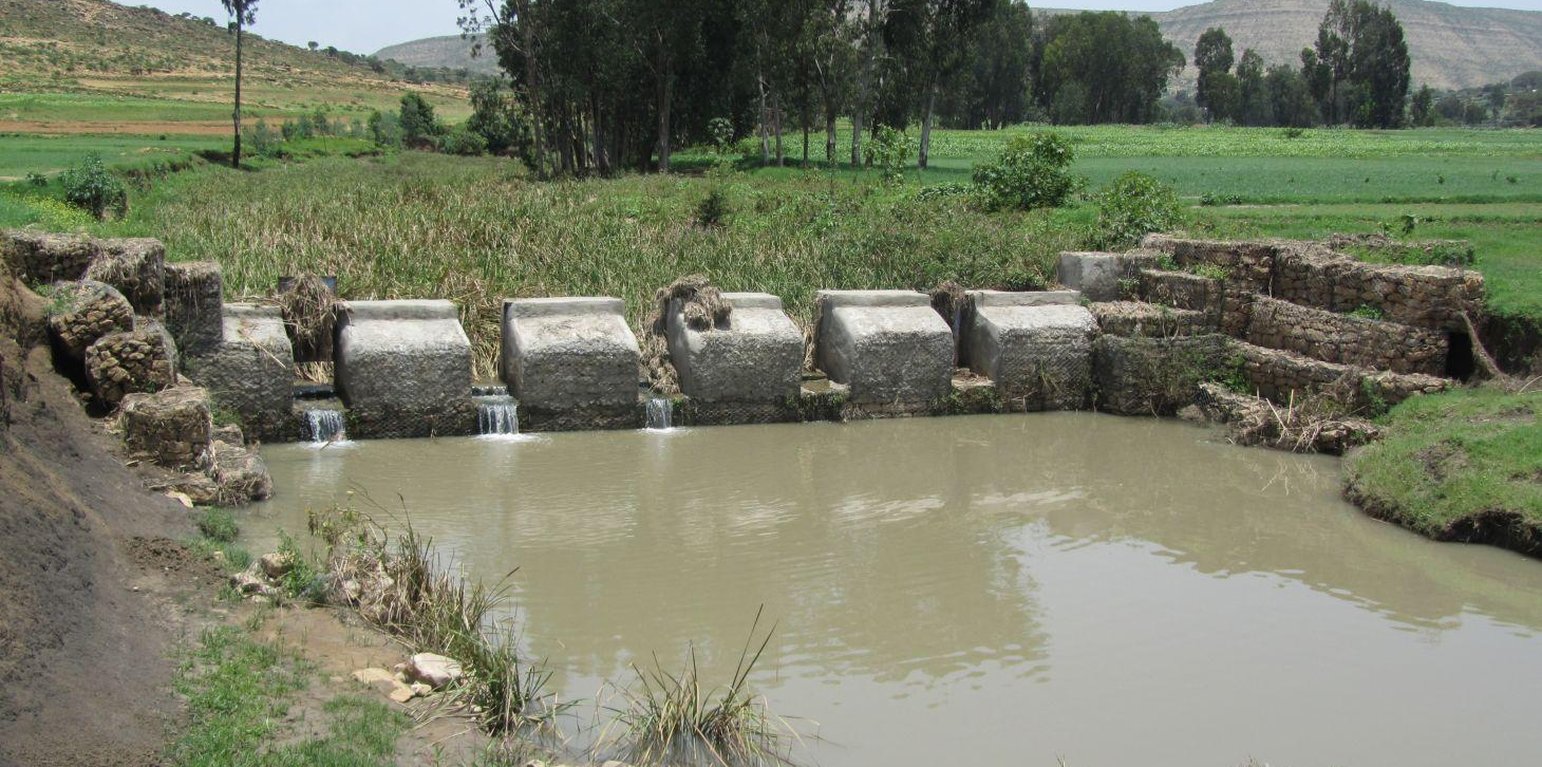




A check dam pond is a raised wall constructed across a gully from stone, concrete and/or gabion to store water behind it for irrigation purpose using either gravity or lifting mechanism. The structure generally consists of construction of foundation, apron, retaining wall and the checkdam. The width of the checkdam ranges between 1 - 2 m while the height varies between 1 - 2 m depending up on the gully depth. The length of the checkdam depends on the gully width. The spacing between adjacent checkdams is determined based on two factors, namely, the gradient of the river bed and the availability of potential land that can be irrigated. It is also provided with a number of sluice gates which will be removed during the main rainy season to minimize siltation.
Purpose of the Technology: In addition to storing water for irrigation, check dam ponds decrease slope length, slope angle, runoff velocity and minimize soil erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment of a check dam pond starts with collection and transportation of stone and sand. The construction is started by setting out the dimensions from the design on the selected site and excavating the foundation for the different parts, namely, key trench, apron and retaining wall. The check dam is then constructed using gabions filled with stones and tightly tied together with wire. Finally the superstructure is plastered using mortar to prevent the passage of water through the body. Gates of about 1 m wide are finally constructed at about 1 m interval and fitted with sluice gates. Maintenance usually involves fixing damaged gates and reinforcing gabions.
Natural / human environment: Check dam pond is implemented in gentle (2 - 5%) and moderate (5 - 8%) slopes and in medium and light soil types of at least 1 m depth. It increases water availability for irrigation and livestock consumption purposes. It also reduces runoff velocity thereby decreasing soil erosion and enhancing gully rehabilitation.
It requires skilled labour and high construction cost. As a result, it is constructed through external support. However, the number of communities seeking for external support and willing to contribute their share is at the rise. The technology minimizes greatly the risk of crop failure and improves the livelihood of the land users.
地点: Kilite Awlaelo, Tigray, 埃塞俄比亚
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. 1-10 平方千米)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型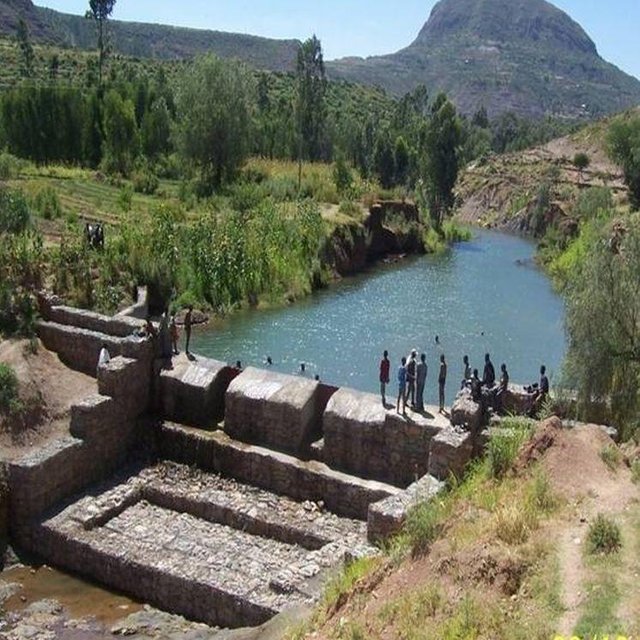



| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Birr) | 每项投入的总成本 (Birr) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4678.0 | 4678.0 | 25.0 |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Cement | ha | 1.0 | 953.0 | 953.0 | |
| Gabion | ha | 1.0 | 6268.0 | 6268.0 | |
| Sheet metal | ha | 1.0 | 44.0 | 44.0 | |
| Angle iron | ha | 1.0 | 56.0 | 56.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 11'999.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 666.61 | ||||
Also: Requires skilled labour
Increased investment in health care as a result of increased income.