



In the semi-arid regions of Morocco agricultural production is increasingly unstable as consequence of changing climate, variable rainfall and more frequent extreme weather events. There is a need, where possible, to intensify agricultural systems while improving food security - and increasing the resilience of the overall system.
Cultivating lentils in cereal-based systems is common practice in rural Morocco. To intensify this cropping system, taking into account the effects of climate change, the International Centre for Agricultural Research Dry Areas (ICARDA) introduced onions into the common lentil production system. This was a part of research trials to find suitability and economic profitability of crop rotation systems. The introduction of onions as a relay intercrop within lentils has multiple benefits and advantages. Firstly, with two crops are harvested from the same piece of land, thus overall farm profit increases. Secondly, the cultivation of two crops creates a more resilient overall system because the farmer is not dependent on one single crop. Thirdly, as onions are harvested later than lentils, the soil is covered for a longer period, consequently protecting it from degradation, hence soil quality is improved. Fourthly, lentils are leguminous, fixing nitrogen in the soil, thus improving soil fertility. Lastly, the market linkage for onions is very good in Morocco because it is a commonly cultivated crop with high cultural and culinary value: indeed, onions are a cash crop.
However, the technology has potential drawbacks. Firstly, onions require supplementary irrigation if there is not enough late season rainfall. Highly efficient irrigation systems (e.g. drip) require initial investment. In this case the Moroccan government supports 80% of the investment cost for installing drip irrigation. This establishment activity is thus a one-time cost. Secondly, if planted in small plots there may be risks of free grazing livestock as well as pest and insect infestations. This can be overcome by community farming and pest control.
In 2020 and 2021, ICARDA tested this Diversified Cropping System on a trial field of half a hectare, in an area with average annual precipitation of 400 mm. DCS is implemented in the following order of activities. The field is prepared by ploughing. In December, lentils are mechanically seeded. Two rows of lentils are planted 15 cm apart. The spacing between each two-row pair is roughly 95 cm. Compound fertilizer is applied during the seeding. In January, a single spray of herbicide is applied to control grassy weeds. The field is mechanically weeded twice, in mid-January and then again in February.
Onion seedlings are raised in January. These are then transplanted in March: also in paired lines (two rows at 20 cm apart). Compound fertilizer is applied before transplanting. Each pair-row of onion seedlings is planted between two pair-rows of lentils. Because the onions are planted within an already growing crop of lentils, this form of intercropping is termed "relay planting".
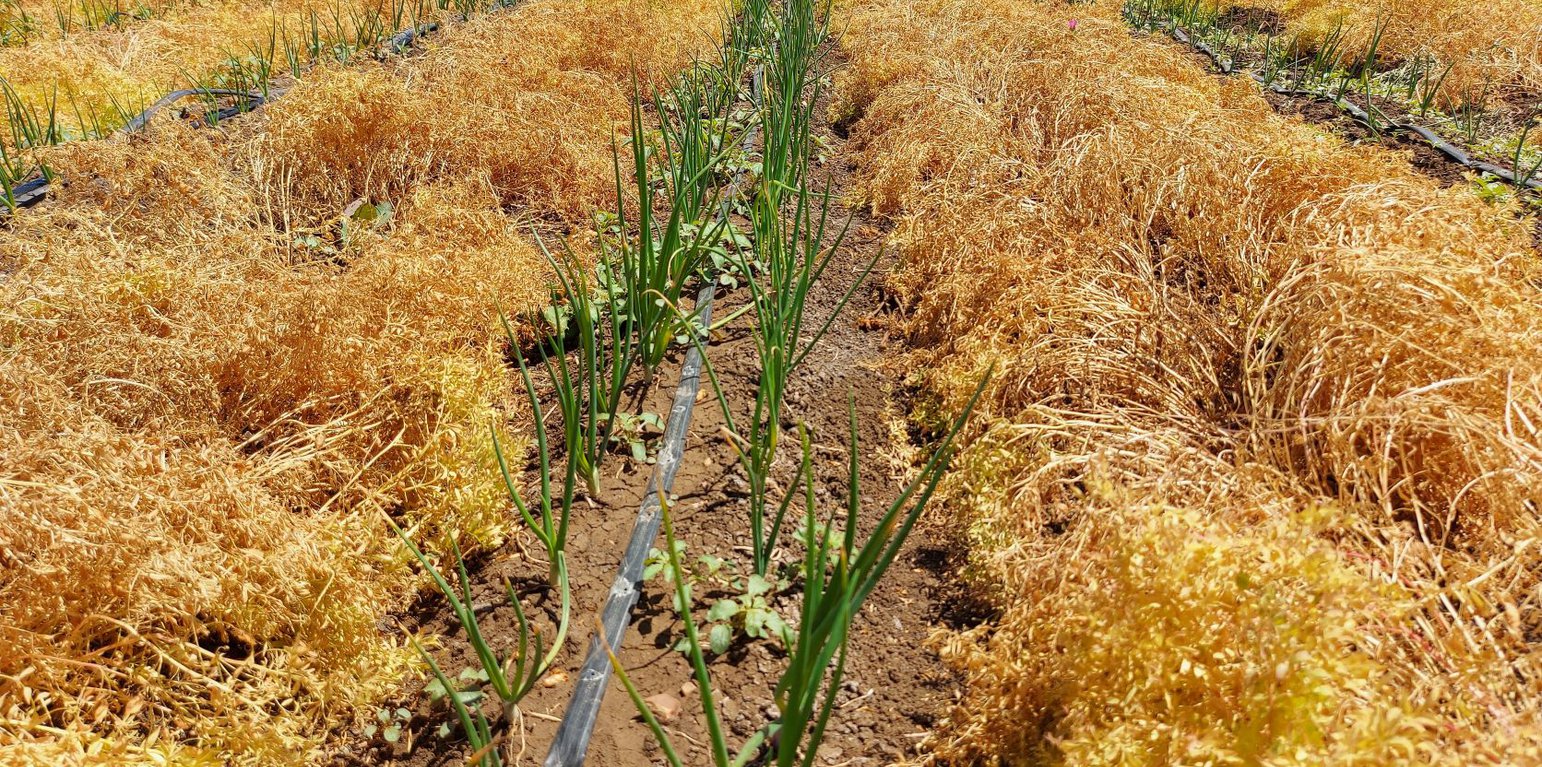
The onions are manually weeded in March-April. In April, the lentils are manually harvested and mechanically threshed. Finally, in June, the onions are manually harvested.
During a period from March until May, the onions are irrigated three times. Because the irrigation is just partial, it is termed "supplementary irrigation". The average irrigation amount per event was 15 millimetres. This is done through drip irrigation.
地点: Merchouch, 摩洛哥
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷))
在永久保护区?: 否
实施日期: 2020
介绍类型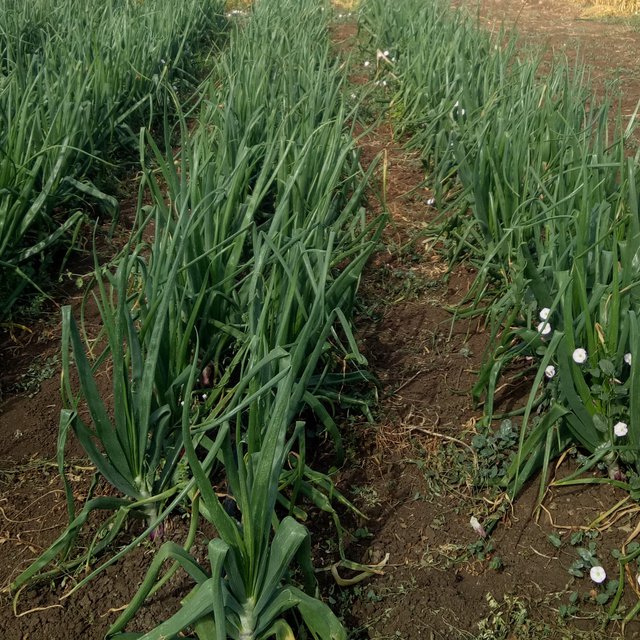







| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (MDH) | 每项投入的总成本 (MDH) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 其它 | |||||
| Total Cost for Drip Irrigation | Total | 1.0 | 40000.0 | 40000.0 | 20.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 40'000.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 4'484.3 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (MDH) | 每项投入的总成本 (MDH) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Onion Seedling Planting | Person-Days | 15.0 | 75.0 | 1125.0 | 100.0 |
| Onion Seedling raising | Person-Days | 20.0 | 75.0 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| Weeding | Person-Days | 30.0 | 75.0 | 2250.0 | 100.0 |
| Harvesting | Person-Days | 20.0 | 75.0 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Lentil Seeding | Machine-Hours | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Lentil Weeding | Machine-Hours | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| Threshing of Lentils | Machine-Hours | 2.0 | 150.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| Herbicide Application | Machine-Hours | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Fungicide Application | Machine-Hours | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Lentil Seeds | Kilogram | 45.0 | 8.0 | 360.0 | 100.0 |
| Onion Seeds | Kilogram | 4.0 | 600.0 | 2400.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| Fertilizer (NPK 10-20-20) for Lentil | Kilogram | 100.0 | 3.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizer (NPK 10-20-20) for Onion | Kilogram | 100.0 | 3.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| Herbicide for Lentils | Liter | 0.5 | 100.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Fungicide for Lentils | Liter | 0.5 | 150.0 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | |||||
| Irrigation Costs | Per Event | 3.0 | 200.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 11'230.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1'258.97 | ||||