

Banana is planted for commercial purposes on a medium sized farm in Elbatinah, Oman It is planted in a well prepared land, where ridges and furrows are made by machinery and manual labour. Seedlings are raised from tissue cultures that are imported. Before the seedlings are planted in the field the land is pulverized and watered. It is fertilized by combination of organic and inorganic fertilizers before seedlings are planted. After planting the seedlings get water through babblers from the pipes network. Water is delivered from a center, where soil nutrients are injected. Harvest takes place twice a year. Old banana plants are removed and chopped to be incorporated in the soils
The harvested banana is sold both in domestic market and mostly exported to neighboring countries. The most dominant variety cultivated is Cavendish. Hired labor coming from other countries are involved in most of the farm activities. Some are permanent workers, while most are temporary laborers who come and go depending on availability of seasonal jobs.
Purpose of the Technology: Managing land to control salinity of soils that impede normal growth and affect productivity of banana plants which produce banana for market.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The land is cleared first from weeds and dead plants using machinery. Mostly scrapers and cleaning machinery are used to remove dead banana plants and weeds. Following this the scraped material is incorporated into the soil or removed away. Then the land is harrowed and pulverized well before banana seedlings are planted. Tissue culture is imported from other countries and transplanted in plastic houses before planted out in the field. While planting the young seedlings are spaced at a given interval between plants and rows.
Natural / human environment: The farm is situated in one of the agricultural potential areas in the country. The land is nearly level to level. Some leveling is required wherever there is need to level. Land users in the surroundings include small holders, some with medium size farms and also there are large scale farms. The current farm where the documentation has been undertaken is among the top medium sized farms.
地点: Almusina, Al Batinah, 阿曼
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (60.0 km²)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型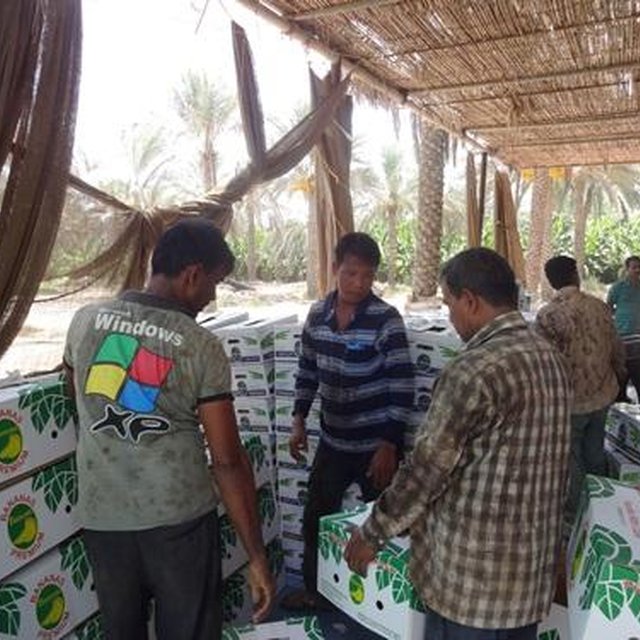
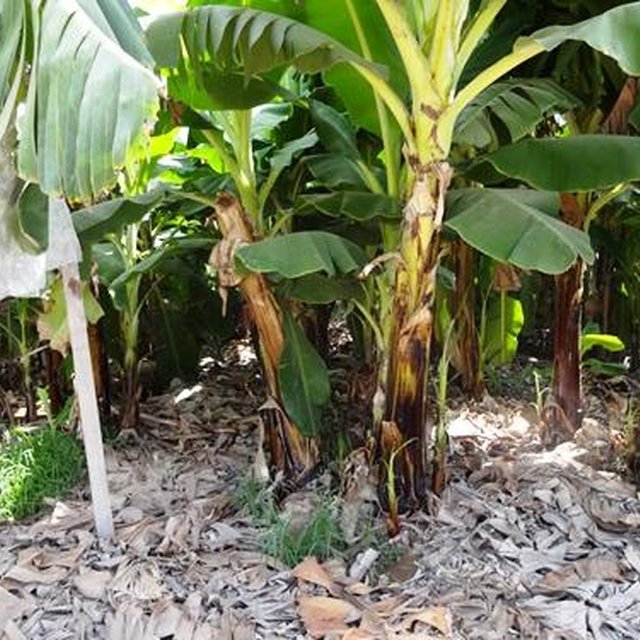





The farm is commercial and gets good return from the investment. Banana is at local market outlets and exported as well.The farm has skilled laborers to perform activities