



The shallow well is a structure created in the ground by digging or drilling to access water resources. This example of shallow wells is their use in recharge areas to lower groundwater tables. The technology is a subproject of a larger LDD initiative. The technology has been promoted by the Land Development Department at Bua Yai district Nakhon Ratchasima province since 2014. The objectives of the main project are (1) to provide water resources in recharge areas for agriculture: (2) to reduce the amount of saline groundwater and (3) to set up positive economic impact measures.
The process of technology establishment comprises 1) a recharge area survey in salt-affected areas, 2) drilling shallow wells to 25-30 meters depth, 3) installing 5.5 hp gasoline pumps and testing water quality, 4) pumping groundwater and distributing it to the cultivated areas.
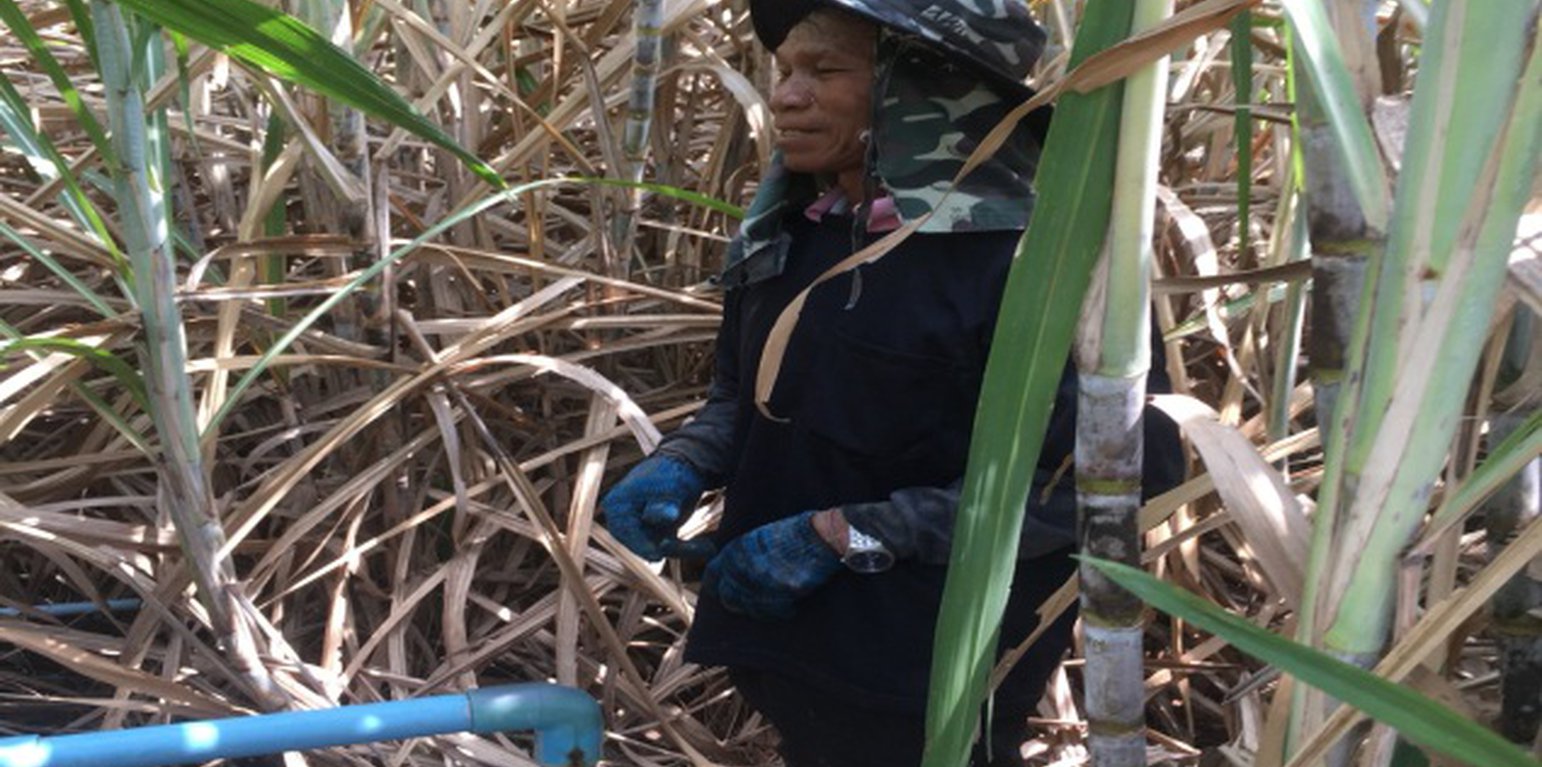
Shallow well technology has been implemented on the fields of Mr. Boonchu Supho, Ban Nong Mek, Moo 9, T.Dan Chang, A. Buayai, Nakhon Ratchasima Province. Mr. Boonchu Supho has 21 rai (approx. 3.4 hectares), undulating area with a 2-5% slope, situated at approx. 200 meters above sea level, with a tropical climate, and soil which is classified as being in the series of Kula Ronghai (Ki). This area is upland, and located in the recharge area. Mr. Boonchu Supho has 13 rai (approx. 2 hectares) of lowland rice fields and one shallow well.
In the past, water scarcity was the main issue with his land. Droughts resulted in water scarcity and low productivity. After excavating a shallow well in 2014, groundwater was used for 19 rai of cultivation. Due to soil salinity reduction, rice yields increased to 590 kg/rai (approx. 3700 kg/ha: an increase of approx. 47.4%). Sugar cane yield increased to 30 ton/rai. Moreover, land users can use land more efficiently with mixed plantations of banana, pineapples, sweet bamboo, chilies, galangal and lemongrass to generate income. Even with a drought in 2018, his land had enough water for cultivation, while rice fields in the surrounding area faced water scarcity problem.
In conclusion, the benefits of the shallow well are 1) lowering the groundwater table and reducing salinity, 2) enhancing rice and sugar cane yields, 3) ability to cultivate throughout the year and 4) better soil properties and a better environment. However, the disadvantage of the shallow well is that farmers have to pay for electricity (around 1,200 THB/ 9 months or 10,800 THB/year).
地点: Ban Koksa-ard Moo 10 T.Danchang, A.Buayai, Nakhon Ratchasima, 泰国
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播:
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 2014; 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型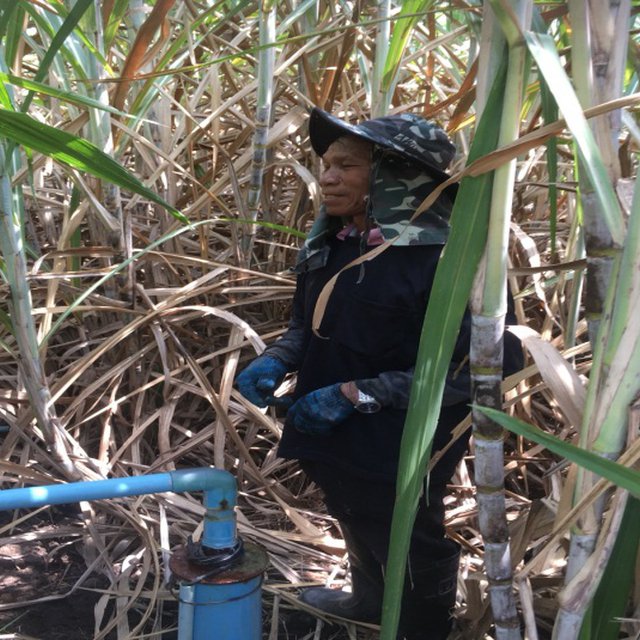










| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (THB) | 每项投入的总成本 (THB) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Costs of labor for sugarcane cultivation | puddle | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | |
| Costs of labor for rice cultivation. | rai | 13.0 | 1150.0 | 14950.0 | |
| Costs of labor for sugar cane cultivation. | rai | 1.5 | 1200.0 | 1800.0 | |
| Costs of labor for pineapple cultivation. | rai | 1.0 | 1200.0 | 1200.0 | |
| 设备 | |||||
| Costs of labor for Banana cultivation | rai | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | |
| Costs of labor for Papyrus cultivation. | rai | 0.5 | 900.0 | 450.0 | |
| Costs of labor for Sweet bamboo cultivation. | rai | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | |
| Costs of labor for Chilli, galangal, lemon grass cultivation | rai | 1.0 | 900.0 | 900.0 | |
| Cost of shallow water well drilling equipment | puddle | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Bud seedling sugarcane | seedling | 2250.0 | 0.9 | 2025.0 | |
| Bud seedling Pineapple | seedling | 2500.0 | 2.0 | 5000.0 | |
| Bud seedling Banana | seedling | 100.0 | 10.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Bud seedling Papyrus | seedling | 3000.0 | 0.2 | 600.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| Bud seedling sweet bamboo | seedling | 25.0 | 80.0 | 2000.0 | |
| Bud seedling Chilli, galangal, lemon grass | seedling | 2000.0 | 1.0 | 2000.0 | |
| Seedling rice KDML105 | seedling | 65.0 | 25.0 | 1625.0 | |
| Chemical fertilizer 15-15-15 | kg | 300.0 | 13.0 | 3900.0 | |
| Chicken manure | kg | 2000.0 | 2.0 | 4000.0 | |
| 其它 | |||||
| Electricity charge | hr | 240.0 | 5.0 | 1200.0 | |
| Machinery | rai | 19.0 | 500.0 | 9500.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 155'850.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 155'850.0 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (THB) | 每项投入的总成本 (THB) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 设备 | |||||
| electricity charge,5 baht per unit 8 hours per day, 360 days / year | time | 2880.0 | 5.0 | 14400.0 | |
| Machinery | time | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 16'400.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 16'400.0 | ||||