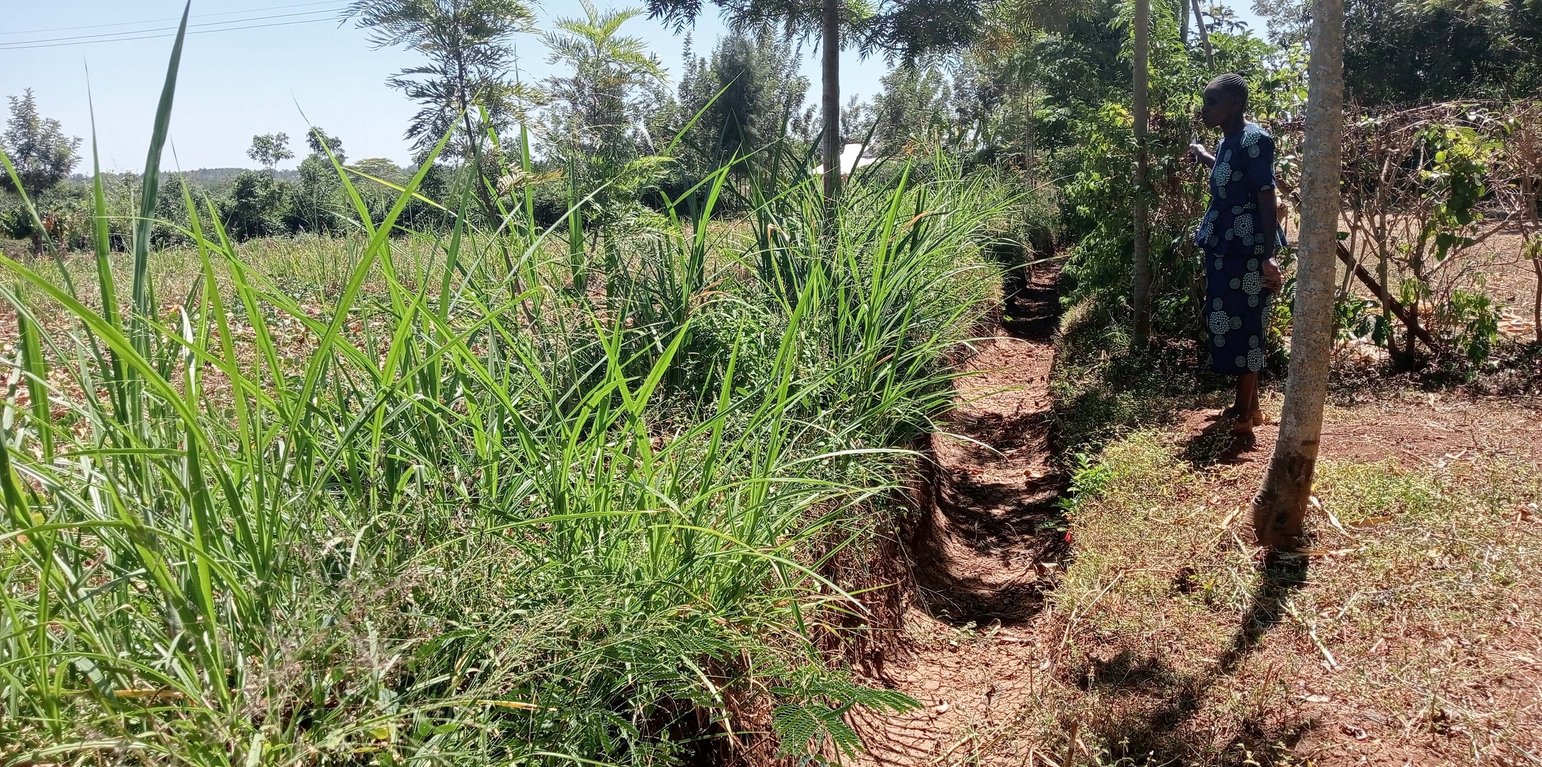




Retention ditches are soil and water conservation practices. They are channels dug along contours (i.e., across the slope), especially at the uppermost part of the farm to retain stormwater/ surface runoff. They typically comprise two components: (a) vegetational-biological and (b) mechanical-structural components which are integrated to collect surface runoff, allowing for sediment carried by runoff to settle as water infiltrates into the ground. The mechanical-structural component consists of channels dug in such a way that they follow the contour and run perpendicular to the flow of water in areas where runoff naturally flows or collects. The soil excavated from the ditch forms a bund below the ditch. Retention ditches prevent surface runoff from outside the farm from flowing into or through the farm. The vegetational-biological component consists of plants grown on the bunds. The plant roots bind the soil thus increasing the slope stability, especially of the bunds; thus, preventing soil from collapsing and falling back into the channel. Retention ditches thus harvest and retain water (especially in low rainfall areas) preventing fertile soil from being washed away by surface runoff and increasing water availability for plants. In high-rainfall areas, they play the role of discharging excessive runoff into waterways.
Retention ditches are dug to about 60 cm deep and about 50 cm wide. To ensure stability, especially in areas with unstable soils, the top width is made wider than the bottom width allowing for slanting walls that are more stable than vertical walls. An understanding of the slope angle is an important factor in the designing and construction of retention ditches. A line-level (a spirit level attached to a string suspended between two poles) can be used to determine the measure slope. The slope angle determines the size of the ditch (depth and width) and the spacing between successive ditches on the same piece of land. In low-rainfall areas (such as Siaya), retention ditches are spaced at about 50 – 70 m while in high-rainfall areas the space between the ditches are closer (about 20 m). Similarly, the size of the retention ditches increases with increasing slope.
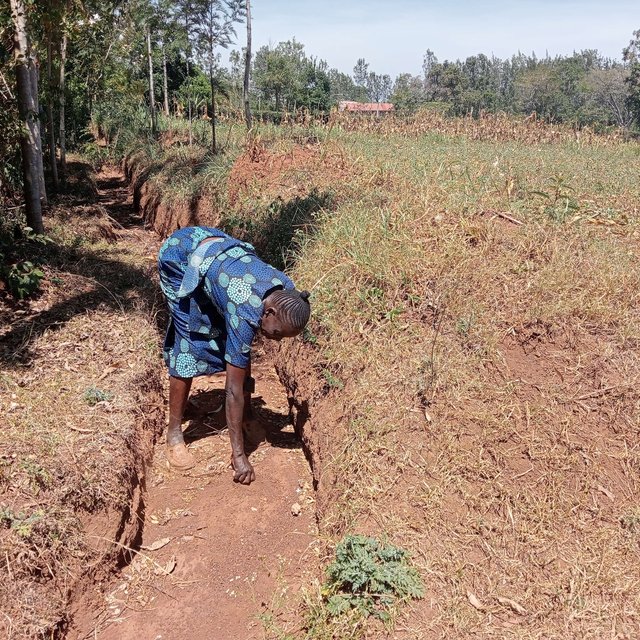
Some crops, especially bananas, arrowroot, etc. that demand a lot of water can be established in the ditches. Maintenance of retention ditches involves regular desilting, whenever the ditch is about 1/3 filled with silt. Hoes, shovels/ spades, and a panga (machete) are some of the tools used in digging and maintaining retention ditches. Farmers like retention ditches because they help in controlling soil erosion.
地点: Uloma Village, Bondo Municipality, Bondo Sub-county, Siaya County, Nyanza Region, 肯尼亚
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷))
在永久保护区?: 否
实施日期: 2018
介绍类型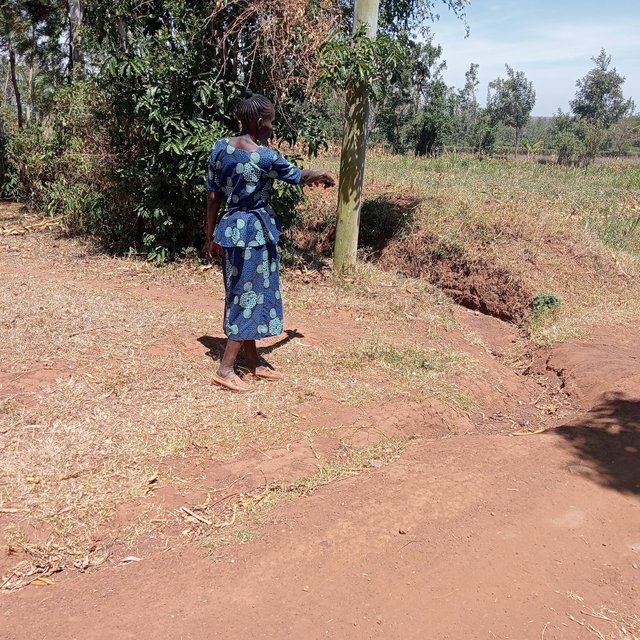



| 品种 | 计数 |
| cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu) | 3 |
| 家禽 | 100 |



| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (KES) | 每项投入的总成本 (KES) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Digging the ditches | Man days | 10.0 | 300.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Hoe | No. | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| Panga (broad blade) | No. | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Wheelbarrow | No. | 1.0 | 800.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 |
| Spade | No. | 1.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| Planting rope | No. | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Spirit level | No. | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | |
| 其它 | |||||
| Slope measurement and determination of position for the retention ditch (professional service) | Professional service | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 6'690.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 54.41 | ||||
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
SLM之前的数量: 2
SLM之后的数量: 4
Quantity refers to the number of 90 Kg bags of maize produced per acre. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Not easy to quantify but according to the farmer, the crops are doing better compared to how they were before the retention ditches were dug.
SLM之前的数量: 1
SLM之后的数量: 3
Quantity refers to harvesting cycles for nappier grass from the same farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Not easy to quantify but according to the farmer, fodder is doing better compared to how it was before the retention ditches were dug.
SLM之前的数量: 1
SLM之后的数量: 3
Quantity refers to the amount of milk in litres from one cow. Milk production is often at the peak during early lactation months. Based on estimation by the farmer.
SLM之前的数量: 80
SLM之后的数量: 40
Quantity refers to the percentage probability of the crop failing to do well. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Refers to the number of hours that the farmer can be free in any working day. During the rainy season, the farmer spends some time desilting the ditches. Based on estimation by the farmer.
SLM之前的数量: 5
SLM之后的数量: 2
Quantity refers to the number of months in a year when there is total lack of food in the house, and the farmer has to buy all the food required in the house. Based on estimation by the farmer.
SLM之前的数量: 10%
SLM之后的数量: 80%
Quantity refers to the estimated percentage of knowledge in SLM/ land management. This is a farmer's estimate.
Not easy to quantify. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Refers to the amount of water that flows through the farm. Not easy to quantify. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Not easy to quantify.
Refers to the farmer's estimated percentage vegetation cover at the farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Not easy to quantify. Retention ditches have reduced the amount of water that flows to the farms in the lower areas. This has reduced soil erosion in these farms.
Not easy to quantify. All silt is deposited in the retention ditches and scooped by the farmer for replenishing parts of the farm with low soil levels.
Not easy to quantify. Retention ditches have reduced the amount of water that flows to the farms in the lower areas. This has reduced soil erosion in these farms.