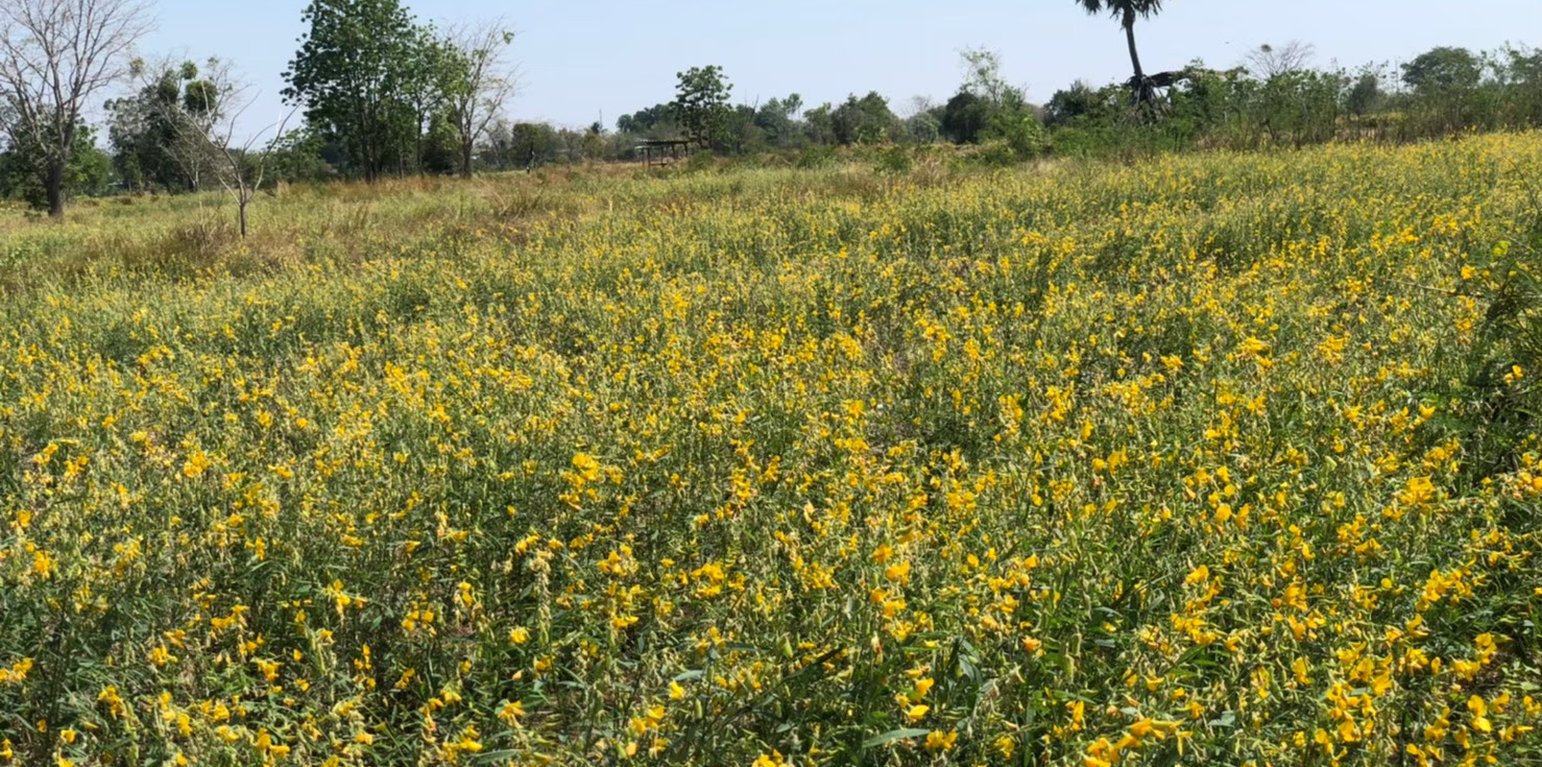




The Northeast of Thailand has the largest area dedicated to rice production in the country. However, the average yield per hectare remains low. Here, rice production heavily depends on rainfall, but distribution is inconsistent. Additionally, soil fertility is low, with a rapid decline in soil organic matter (SOM). Another significant threat to productivity in this area is salinity, with 17% of the rice production area affected.
The Land Development Department (LDD) of the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives has promoted the use of soil amendments, such as green manure plants - including sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea) - to enhance organic matter and restore soil fertility under saline conditions. Green manures are ploughed under, and incorporated into the soil to achieve their effect.
In the Non Thai district of Nakhon Ratchasima province, farmers face water shortages during the dry season, as the area lies outside the irrigation zone. Farmers, along with officers from the Land Development Department, have worked to increase SOM in degraded soils through knowledge transfer. Volunteer soil doctors and local farmers have adopted technologies that combine SOM improvement with soil and water conservation measures.
One notable example is Mr. Mana Siangsuthia: since 1997, he has collaborated with LDD officers, receiving beneficial microorganisms (PD microorganisms), green manure plants, vetiver grass, and water resources for his paddy fields. He has implemented LDD guidelines to develop his 1.12 hectare rice plot. Previously, this land was unproductive due to soil degradation caused by long-term monoculture of industrial crops and excessive use of synthetic fertilizers.
Fermented bio-extracts from banana shoots and chemical fertilizers were applied according to recommended guidelines. In 2004, rice yields averaged 1,125–1,550 kg/ha. Continuous implementation of these practices raised yields to 2,500 kg/ha by 2011. Over 16 years, using sunn hemp as a soil amendment significantly improved soil aggregate stability and reduced salinity. This success led to a shift towards natural agriculture practices in 2013, where chemical fertilizers were no longer used.
Farmers in the area now employ weather observation techniques and efficient water management strategies during dry spells. Green manure plants are sown every two years, complemented by the cultivation of salt-tolerant rice varieties, which also exhibit drought and pest resistance. These practices have resulted in rice yields of 3,125–3,750 kg/ha.
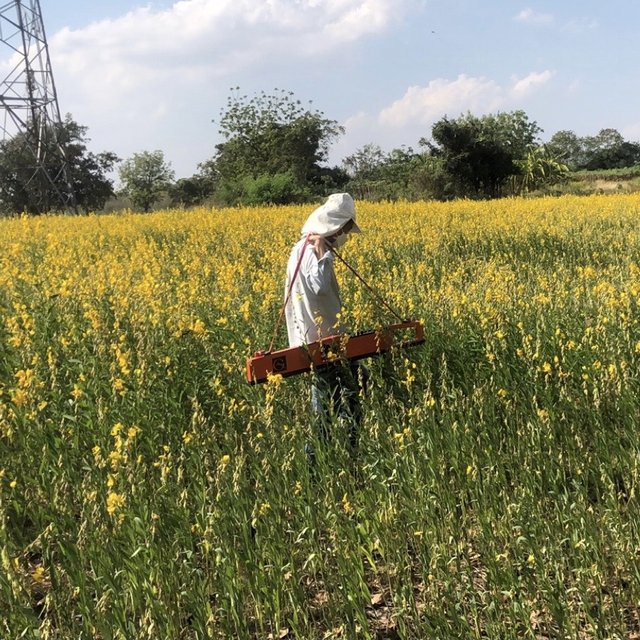
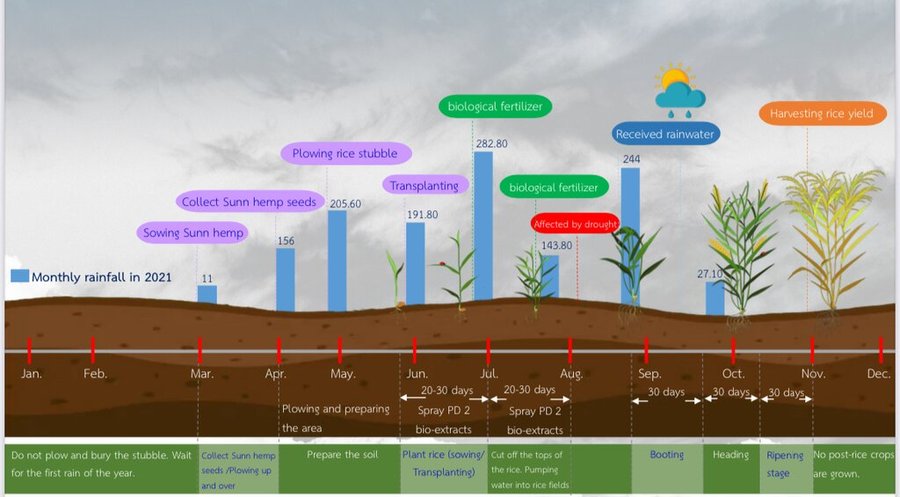
After rice harvesting, rice straw and stubble are ploughed in together with banana shoot PD 2 bio-extract. After approximately 2 weeks of decomposition, sunn hemp is sown at the rate of 31.25 kg/ha. When sunn hemp reaches 120 days, its seeds are collected. Then sunn hemp stems of around 1.2 meters height are ploughed in order to obtain more biomass.
Water conservation remains a focus in the cultivation area. During the rainy season, excess rainwater is stored for use during dry periods. Additionally, farmers employ techniques to wash salt from the soil surface into drainage channels. Water quality is enhanced using fermented bio-extracts, ensuring adequate water for dry-season cultivation.
地点: Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district, Nakhonratchasima, 泰国
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (11200.0 km²)
在永久保护区?: 否
实施日期: 1999; 10-50年前
介绍类型





| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| 植物材料 | |||||
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| 其它 | |||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Plow to prepare plots | Time | 1.0 | 14.71 | 14.71 | 100.0 |
| Sow rice | Time | 1.0 | 17.65 | 17.65 | 100.0 |
| Pump water | Time | 2.0 | 58.82 | 117.64 | 100.0 |
| Harvest yield | Time | 1.0 | 183.82 | 183.82 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Rice seeds | Kilogram | 8.0 | 0.53 | 4.24 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| Weight | Liter | 40.0 | 0.29 | 11.6 | 100.0 |
| Green Manure | Kilogram | 5.0 | 0.68 | 3.4 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | |||||
| Oil costs for farm truck | Time | 1.0 | 58.82 | 58.82 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 411.88 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 12.11 | ||||
SLM之前的数量: Being areas with saline soils with salt stain on the soil surface, yields per hectare
SLM之后的数量: Soil properties become better, the quantity of products increases
SLM之前的数量: Yields per hectare are low.
SLM之后的数量: The plants receive nutrients and the soil quality improves resulting in better product quality.
SLM之前的数量: Factors and soil amendment materials are used continuously every year.
SLM之后的数量: Good soil properties make soil management for cultivation become easier.
Using a questionnaire
SLM之前的数量: Rainwater is used for conducting agricultural farming.
SLM之后的数量: Water resources in the paddy field
SLM之前的数量: Affected by salt water
SLM之后的数量: Water qualities are improved by using fermented bio-extracts.
Salt meter
SLM之前的数量: A large quantity of factors and soil amendment materials were used
SLM之后的数量: Materials easily found in the area such as fermented extracts, green manure are used.
Using a quetionnaire
SLM之前的数量: Low productivity
SLM之后的数量: Received higher quantity of rice products
Using a quetionnaire
SLM之前的数量: Yields not enough for consumption in the household
SLM之后的数量: Having the quantity of rice products for household consumption enough throughout the year accounting for 700 kg./year
Using a quetionnaire
SLM之前的数量: --
SLM之后的数量: Conducting natural farming by avoiding fertilizer and chemical application
Using a questionnaire
SLM之前的数量: Study how to solve proStudy how to solve problems by themselvesblems by themselves
SLM之后的数量: Building interaction of farmers groups in the area based on consulting and mutual problem solving
SLM之前的数量: There is no knowledge propagation.
SLM之后的数量: Farmers in the adjacent plot accept the technology and implement methods of soil management in their own areas.
SLM之前的数量: The soil is arid with flaky salt on the soil surface.
SLM之后的数量: There has been accumulation of organic matter and mulch keeps moistures and reduces water evaporation in the soil.
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
SLM之前的数量: --
SLM之后的数量: Nutrients increase due to planting different crops such as sunn hemp and plowing up and over rice stubble.
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
SLM之前的数量: Moisture in the soil was low. The soil was characterized by having flaky salt appearing on the soil surface.
SLM之后的数量: Salinity measured from the soil surface decreased. Organic matter and the number of microbes accumulating in the soil increased.
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
SLM之前的数量: --
SLM之后的数量: Organic matter from plowing up and over to cover rice stubble, green manure plants
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
SLM之前的数量: --
SLM之后的数量: Plant varieties which can be planted and grow in the area more such as rice, sunn hemp
Observation
SLM之前的数量: Small-scale water resources
SLM之后的数量: Expansion of digging ponds resulting in more areas of water storage