Collection, selection, breeding and dissemination of locally adapted rice varieties at the Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre LAREC. [柬埔寨]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Stefan Graf
- 编辑者: Christine Lottje, Christoph Kaufmann, Stefan Graf, Judith Macchi
- 审查者: Judith Macchi, Alexandra Gavilano, Boris Orlowsky
approaches_1880 - 柬埔寨
- Collection, selection, breeding and dissemination of locally adapted rice varieties at the Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre LAREC.: Aug. 29, 2017 (inactive)
- Collection, selection, breeding and dissemination of locally adapted rice varieties at the Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre LAREC.: March 12, 2021 (inactive)
- Collection, selection, breeding and dissemination of locally adapted rice varieties at the Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre LAREC.: March 12, 2021 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人员
SLM专业人员:
Khun Lean Hak
kleanghak@yahoo.com / sofdec@camintel.com
SOFDEC/LAREC
www.sofdec.com
柬埔寨
SLM专业人员:
Pith Khonhel
012 585892
khonhel@gmail.com
LAREC Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre
www.sofdec.org
柬埔寨
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/08/2014
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
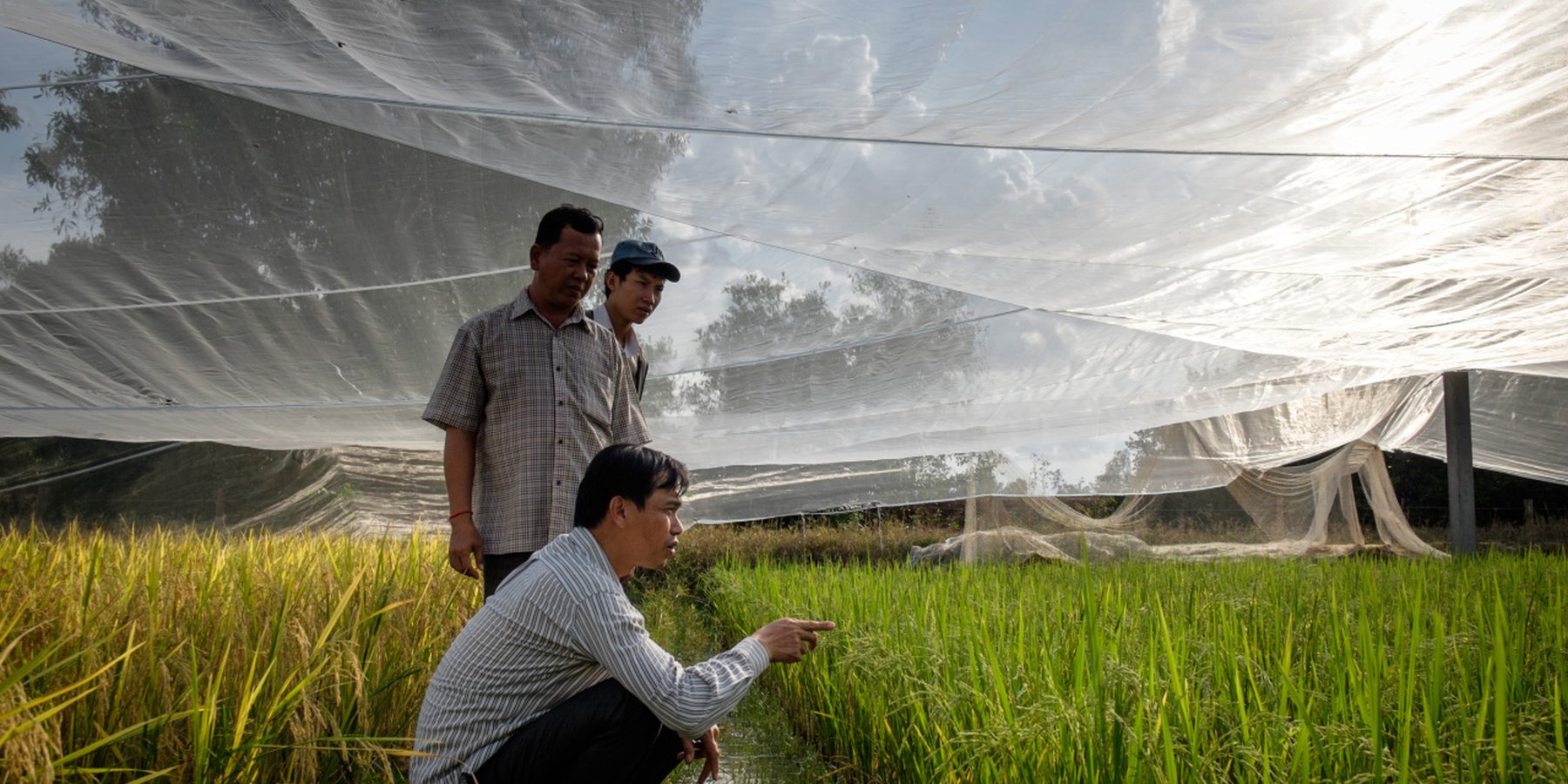
Local genetic rice varieties which are better adapted to changing climatic conditions are collected on farms, tested, described, selected or bred into new varieties and again distributed to farmers with the goal to increase their food security
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Farmers in the central Cambodian province of Kampong Chhnang increasingly struggle with changing and unpredictable weather patterns and regular weather extremes. Lately, water supply has fluctuated annually due to alternating drought and flood extremes. Harvest yields from farmers in the region are low, amongst others, due to the use of low-quality seed, which is not adapted to local conditions, and which demands for an increase in the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
Acknowledging the fact that with changing climatic conditions, local genetic resources and genetic diversity play a vital role to guarantee food security of smallholder farmers, the Local Agricultural Research and Extension Center – LAREC collects, selects, tests, breeds and disseminates rice varieties, which are better adapted to local conditions. To answer to the climate extremes of drought and flood, LAREC focusses its research on flood tolerant and drought resistant rice varieties.
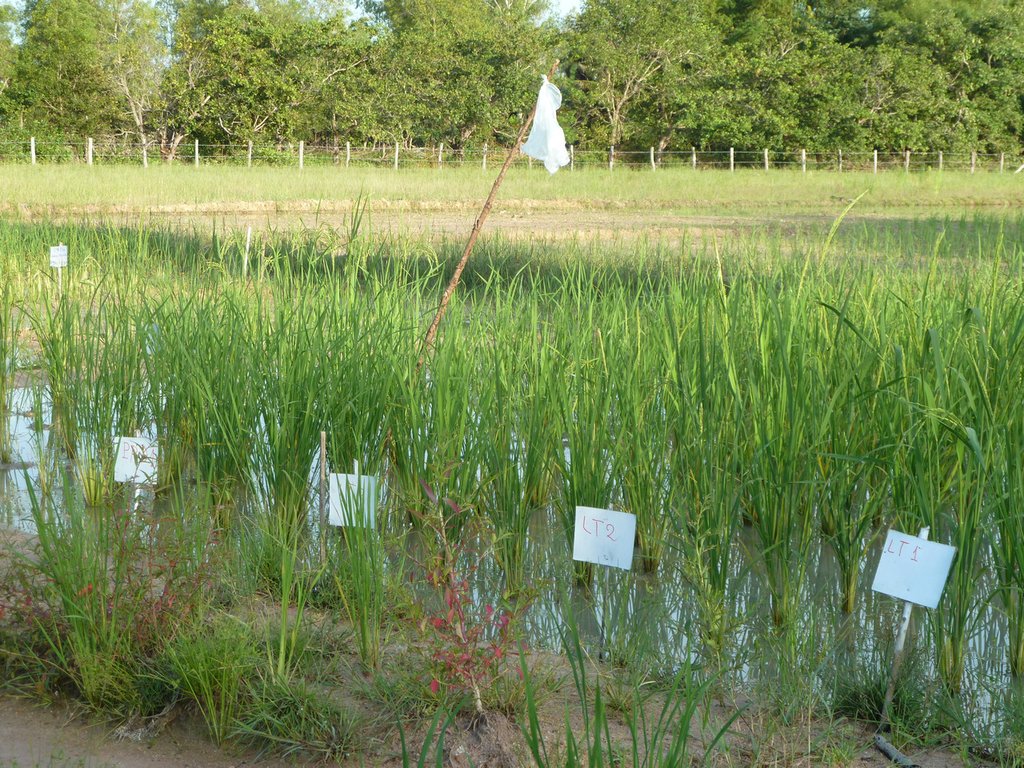
Over the past years 36 flood tolerant rice varieties have been investigated by LAREC research staff for their floating ability and submergence tolerance. 6 varieties among these are: Pork Kraham, Chung Banla-6, STR010, STR10, STR 011 and Chung Banla-2, have been defined as the most appropriated varieties in term of stem elongation, submergence tolerance and yield. These are multiplied and recommended for farmers in flood prone areas.
Regarding drought tolerance LAREC bred a new variety derived from a cross between Phka Rumduol and IRRI breeding line. This variety is tested in an on farm adaptive trial to see crop performance under farmer practice. The two lines have a short growth duration range from 75 days to 90 days and are non-photo period sensitive. Besides the short growth duration, which makes them appropriate for drought prone areas, the new variety also has a desirable aroma which is important for acceptance and marketing purposes. However, to provide scientific evidence, thorough testing in on-farm trials is needed to see yield performance under farmers’ condition, seed rate application based on cultivation method and fertilizer application.
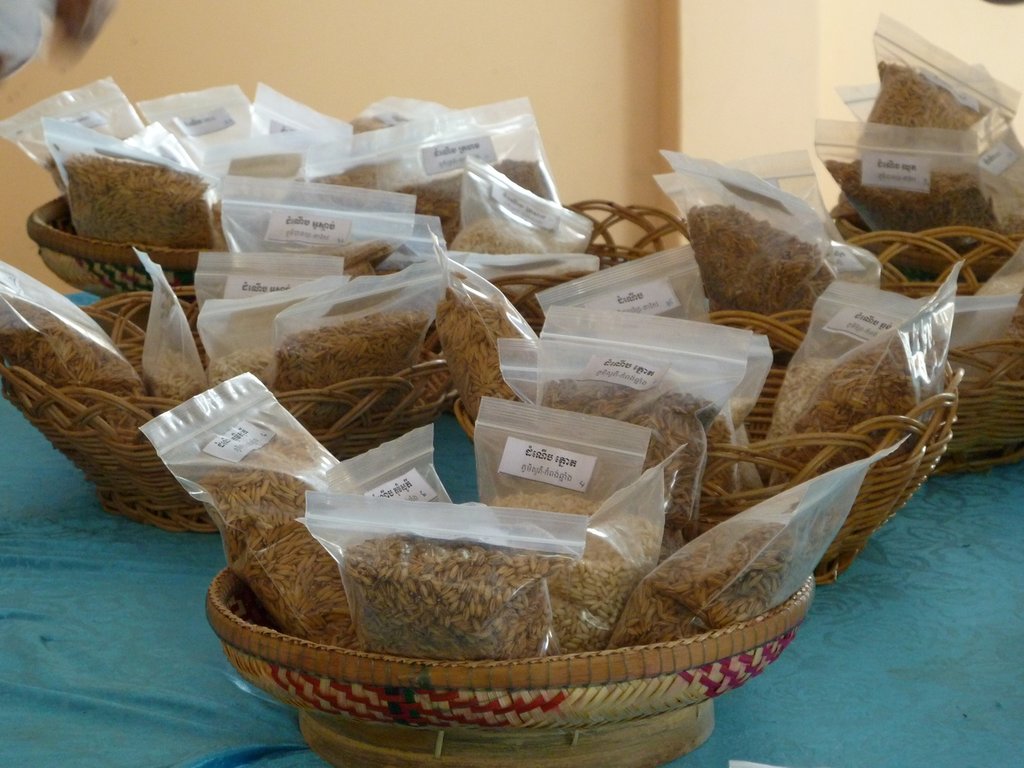
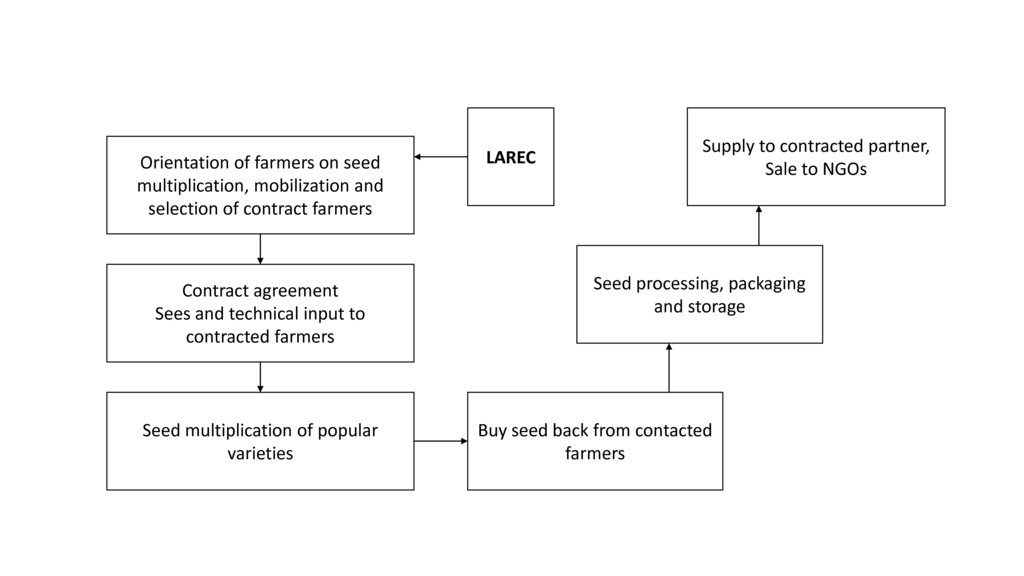
After the production of basic seed for rice LAREC distributes the seed to contract farmers for multiplication under the supervision of LAREC staff. The multiplied seed is distributed to interested buyers through LAREC and the local farmers' associations.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
柬埔寨
区域/州/省:
Kampong Chhnang
有关地点的进一步说明:
Rolea Pha-ear
注释:
Area where the seeds are used is 10-100 km2
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2010
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
Provide high quality seeds of local varieties which are better adapted to changing climatic conditions to the farmers in the area.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 启动
The founding of LAREC as a local research station was needs-based, as a consequence of increasing exposure of farmer's rice yields to extreme weather events (drought and flood)
- 阻碍
Farmers are consulted in the selection of seed varieties, but not engaged in the research process.
There is a certain degree of aversion towards local varieties by the farmers, due to lower yields.
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 启动
The building up of LAREC (warehouse, office building, greenhouse, drying site, trial field) was rendered possible due to funding by SOFDEC/HEKS
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 启动
Highly specialized research personnel working with local varieties adapted to local conditions
- 阻碍
Only limited knowledge transfer to farmers, as research is conducted in the center, not through a participatory breeding approach
市场(购买投入,销售产品)和价格
- 阻碍
LAREC struggels to become self-sustained by selling the seeds on the local market.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Farmers
Farmers are involved in the selection of seeds and some contracted farmers act as seed multipliers for LAREC
- 社区组织
Community committees
They play a role to facilitate and promote the seed produced by LAREC. They also support the selection of seeds and follow up on the contracting farmers
- 研究人员
LAREC reserach personnel
Selection, testing, breeding of adapted varieties
- NGO
SOFDEC
HEKS (Swiss Church Aid)
SOFDEC provided 100% of the funding. SOFDEC staff links LAREC to the farmers and support the collection, dissemination promotion of the seeds and are also collecting feedback from farmers for discussion with LAREC team to find the solution.
HEKS (Swiss Church Aid) is the main backdonor of SOFDEC and hence of LAREC.
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
Cambodian Agricultural Research and Development Institute (CARDI)
CARDI plays an advisory role and also supports the promotion of LAREC.
LAREC is linked to CARDI to exchange on seed multiplication
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 被动 | LAREC was initiated by SOFDEC, as a consequence of an increasing exposure of farmer's rice yields to weather extremes (drought/flood) |
| 计划 | 无 | Planning of the center by SOFDEC |
| 实施 | 被动 | LAREC collects seed varieties on farms, tests, selects, breeds and disseminates seed again to farmers. Farmers do the multiplication of seeds and use the adapted varieties for their rice production (own consumption and for the market) |
| 监测/评估 | 无 | M+E is conducted by LAREC, SOFDEC and HEKS ((internally) as well as by external evaluators (at the end of each project phase) |
| Research | 被动 | Selection of promising varieties is done in consultation with the farmers. Research with the selected crops is done entirely on the LAREC site. |
3.3 流程图(如可用)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
The selection of the breeding lines is conducted with farmers. Research and testing of the selected varieties is done entirely on the LAREC site, without farmers involvement.
LAREC decides on how and where the adapted varieties were distributed.
明确做出决策的依据:
- 研究结果
- 个人经验和意见(无记录)
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
培训形式:
- 课程
涵盖的主题:
Contract farmers are trained on seed production and seed storage.
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
否
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,非常
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
说明机构、角色和职责、成员等。:
Establishment of a local agricultural research center
具体说明支持类型:
- 财务
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
Yearly monitoring of number of land users using selected of new varieties. Ad-hoc measurements of yield (carried out by project staff)
若是,该文件是否用于监测和评估?:
是
注释:
The documentation of yield and land users involved is used for measuring outputs and outcomes of the project based on the indicators set in proposal. This is also used for routine monitoring by project staff as well as for mid-term and end project-phase evaluations.
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Research to select and improve local rice varieties to be better adapted to changing climatic conditions is the main activity of the approach.
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 10,000-100,000
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
否
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 机械 | 充分融资 | |
| 工具 | 充分融资 | |
- 建筑
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 石料 | 充分融资 | |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
5.5 其它激励或手段
是否有其他激励措施或工具用于促进SLM技术的实施?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Farmers have access to seed varieties which are adapted to local conditions (e.g. drought and flood resistance), ensuring that yields are also generated in case of an extreme weather event.
该方法是否改善了粮食安全/改善了营养?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Through the use of seed varieties which are adapted to local conditions, (e.g. drought and flood resistance) farmers increase their food security by ensuring that yields are also generated in case of an extreme weather event. Farmers are more resilient against extreme weather events.
该方法是否提高了土地使用者适应气候变化/极端情况和减轻气候相关灾害的能力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Through the use of seed varieties which are adapted to local conditions, (e.g. drought and flood resistance) farmers increase their food security by ensuring that yields are also generated in case of an extreme weather event. Farmers are more resilient against extreme weather events.
该方法是否会带来就业、收入机会?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Additional income for contract farmers through seed multiplication
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 降低灾害风险
Adapted varieties also perform in the case of an extreme weather event (drought/flood)
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 不确定
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
If the seeds are not promoted through a project (e.g. by SOFDEC), it is up to the farmers to buy the adapted varieties.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Seeds of high quality are provided by LAREC. |
| Quality of crops from LAREC-seed is uniform and varieties are demanded on the market, thus contributing to an increasing farmer income. |
| Increased food-security as adapted seeds also perform in the likelihood of an extreme weather event. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Seeds are collected in the region from the farmers, thus adapted to the local conditions. (They are collected in the research center and in addition the center buys foundation seeds from the Cambodian Agricultural Research and Development Institute (CARDI) in order to scale up). |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Farmers are still dependent on getting new seeds of the selected varieties (every 3 years for rice) as seeds get mixed and cross pollination occurs. | |
| Lack of money to store the seeds in a proper way. Lack of material (silica gel, oven). | Find external financing sources. Connect with international seed saving organisations if collection and distribution of local ecotypes gets a higher priority. |
| Breeding and selection is not happening on-farm, only at the LAREC centre. Land users remain highly dependent on LAREC to provide new seeds every few years. | Implement participatory plant breeding. Train farmers in selection (already happening with mung bean and rice) and breeding. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Paris, T., et al. 2011. Guide to participatory varietal selection for submergence-tolerant rice. IRRI
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.irri.org
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
The Society for Community Development in Cambodia (SOFDEC) is a Cambodian Non-Governmental Organization, established in 2006 through the localization of HEKS (the Swiss Church Aid) project in Kampong Chhnang province, Cambodia. The vision of SOFDEC is that Cambodian people living in Cambodia live a state of comfort, equality, equity, and have ownership over the sustainable development of their community. The mission of SOFDEC works in partnership with community based organizations and relevant institutions through integrated community development, research, human resource development, enhancement of family economies, in the hopes to uplift the living standards of the people in the target areas. Our goal aims to uplift the living standards of the rural people of Cambodia through the improvement in income generation, sustainable agricultural practices, microfinance, health, human resource development, and sustainable natural resource management.
URL:
www.sofdec.com
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块