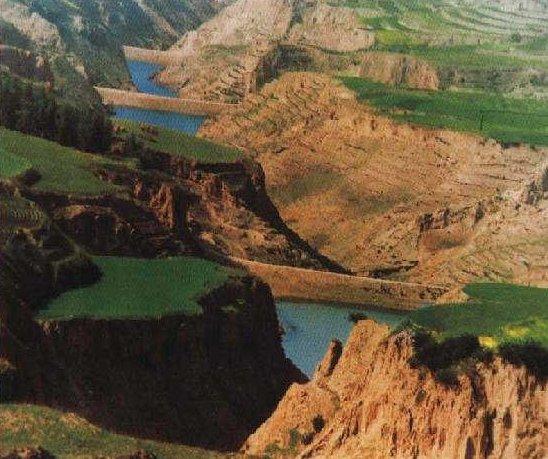
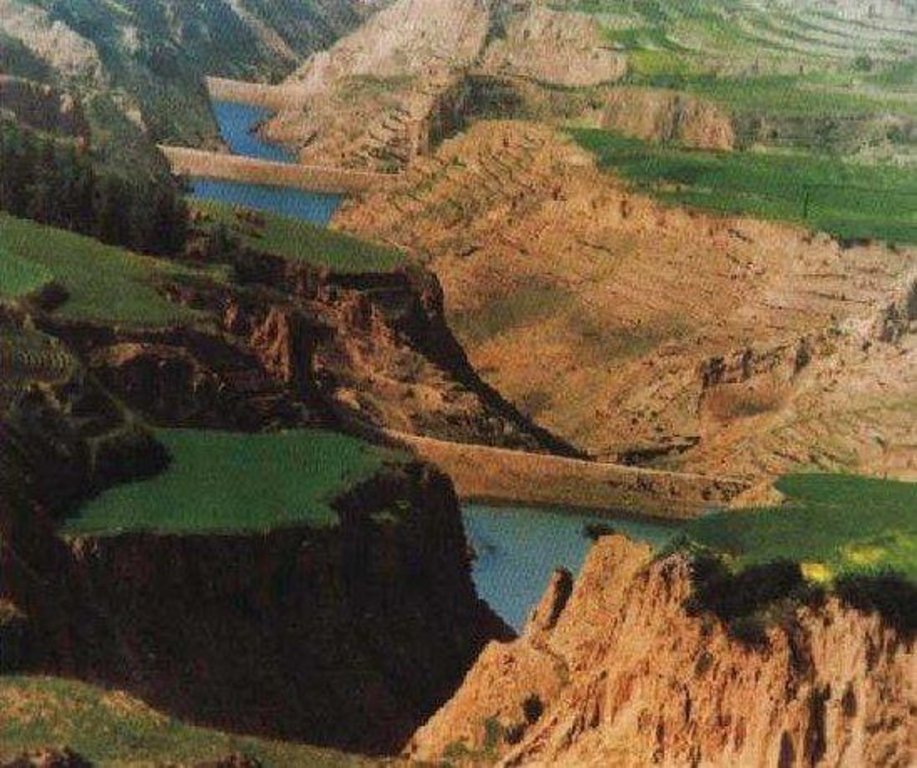
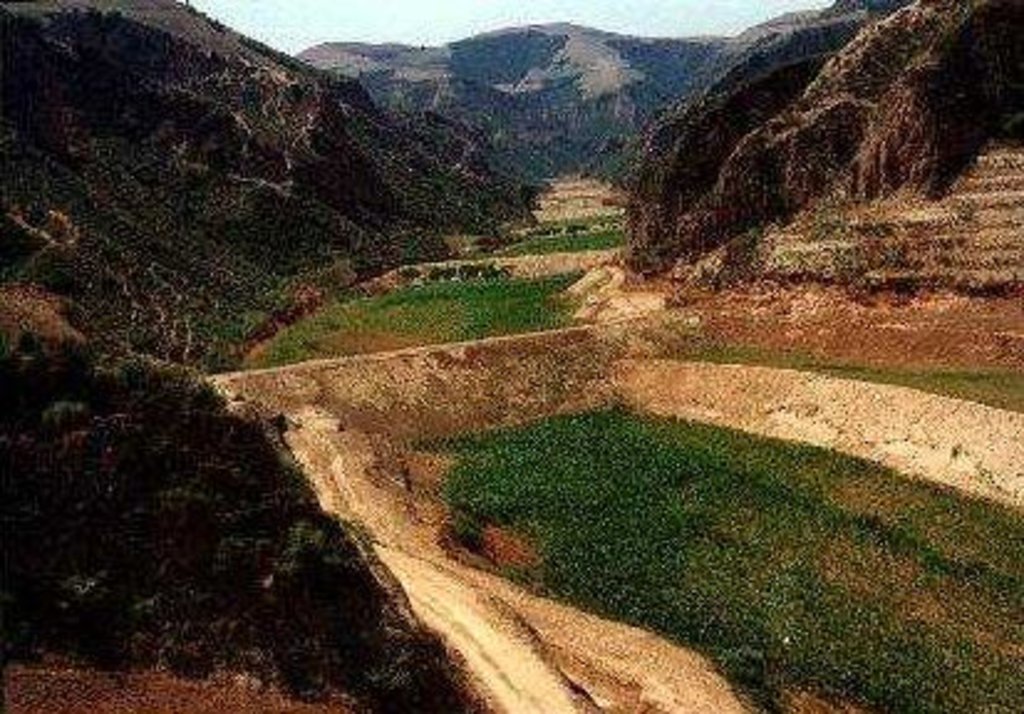
Falling Water Dam [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Yan ZHANG
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Laura Ebneter
approaches_2400 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - 中国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考
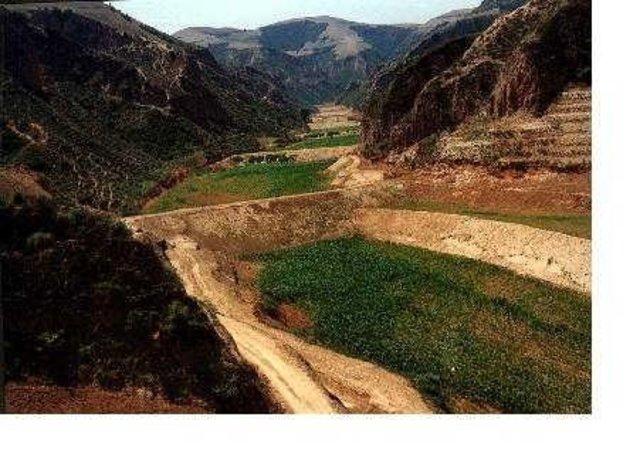

Auto-Flowing Slurry Dam [中国]
Auto-flowing slurry dams is filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland to maintain eroded soil particles and runoff.
- 编制者: Yan ZHANG
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
The falling water dams are widely built in the middle reach of the Yellow River, the typical dams are filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland. The approach is implemented mainly by government investment.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Falling water filled dams distribute widely in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. They are used to store water, wrap sediment which results from soil and water loss. On the Loess Plateau, in addition to the conditions of deep gully and steep slope, earth above the top of the dams can be used to build dams. First, soil is loosed with squirt guns, explosion or manually digging. Then, water is pumped up to the loose earth so as to rush the soil down along transporting ditch, turning the soil into dense mud, to dams level surrounded by tamped banks. Under the press of gravity, the mud dehydrates, consolidates and becomes uniformly dense body of the dams. Compared with dams in other areas, the water power filled dams in the Yellow River basin are characterized by much denser mud, uniform particles and body texture, smaller transect of dams body, and wide applicability to soil materials such as sand soil, loess soil and weathering residue. The types of dams have widely applied to build middle and small reservoirs and silt arresters in the middle reaches of the Yellow River, playing an important role in agricultural production and reduction of sediment into the Yellow River.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Shanxi, Shaanxi, etc.
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
1950
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2005
2.7 方法的类型
- 传统/本土
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The objectives of the approach are to control soil & water loss so as to reduce flood; to make more crop land.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The main existing issues are unreasonable land use planning and low use rate; Lower standard of SWC design and poor quality in construction which would lead to flood danger; low administrative level and economic benefits.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Only when government invests, the technology can be implemented
Treatment through the SLM Approach: investment
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: Because land resources belongs to state and land user can lease the land.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- 国际组织
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 自我动员 | rapid/participatory rural appraisal; The approach is a traditional way to harvest water and wrap soils, SWC applied land users easy to understand and accept it if some subsidy being obtained. |
| 计划 | 互动 | workshops/seminars; After a program granted, implementing agency and local communities working together. |
| 实施 | 外部支持 | responsibility for major steps; In practice, local communities are the major part to manager and carry out. |
| 监测/评估 | 被动 | interviews/questionnaires; When monitoring procedures are clear, the local communities could do this and evaluate. |
| Research | 互动 | Only can give some suggestions or questionnaire. |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 政治家和领袖
解释:
Decisions on the choice of SLM Technology were made directive (top-down).
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by politicians / leaders (directive, top-down).
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
培训形式:
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
涵盖的主题:
How to maintain and reinforce the dams
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在固定中心
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: Falling water dam show; Key elements: Selection of site for dam building, size of dam, materials and methods; 1) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: government's existing extension system 2) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: government's existing extension system; Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: demonstration
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; At each government level, there is a SWC office which is in charge of SWC activities including extension.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,非常
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 财务
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 生态学
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Pattern and standards for the dam design.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- > 1,000,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - The central government): 85.0%; local community / land user(s) (Village committee): 5.0%; other (World Bank): 10.0%
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 机械 | 充分融资 | subsidy |
- 基建
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| community infrastructure | 充分融资 | financed by government |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
注释:
If managed by administrative way, land users' input are mainly voluntary, if through a project, usually paid in cash.
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
是
对条件(利率、回报等)进行具体说明:
Interest rate charged: 4.0%; repayment conditions: After 4 or 5 years when SWC produces benefits, loaner should return.
Interest was lower than market rate.
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
They can harvest water and irrigate crops in dry seasons. Meanwhile, more crop land area is made.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The policies of land contract distribute land to individuals so that land users who involved in SWC activities need to be organized together for implementation of the SWC. The organization need much time and hard work. The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. Administrative management can adjust and assort with this issue.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Raising crop production and return (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: applying fertilizers as possible as can) |
| water can be irrigated in dry seasons and drinks both for cattle and man (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: maintaining and repairing if needed.) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Storing water (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: reducing vapour and leak as possible as can) |
| Enlarge cropland and raising yield (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: shifting food crops to cash crops) |
| reducing flooding (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: reinforce the dams timely) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Costly and frenquently reinforce |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The dams' quality are not high | standardization for design and construction |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Special Planning Of Soil And Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region , Shanxi Province, 1986-1990
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department, Beijing Normal University.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing, 2000
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department, Beijing Normal University.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Auto-Flowing Slurry Dam [中国]
Auto-flowing slurry dams is filled with dense slurry by water flow from upland to maintain eroded soil particles and runoff.
- 编制者: Yan ZHANG
模块
无模块