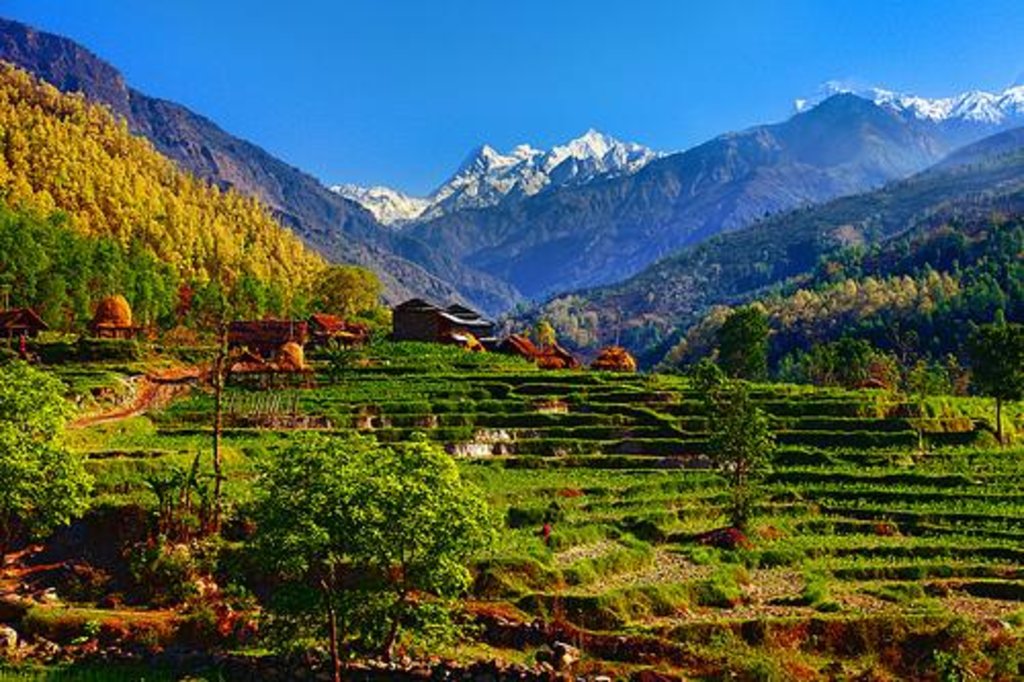
Terrace Demonstration For Soil Conservation [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Gara Sudhar (Nepali)
approaches_2480 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Singtan Gangaraj
Chyamramgbesi 2 Kavre
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Khanna Sabita
Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel
尼泊尔
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
The slopy land used for farming process or just for land management by planting trees or grasses on those areas is terrace farming.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Main aim of terrace farming is to conserve the soil, but the system not only conserve the soil,but also help in agriculture, so it also helps people to earn their living.
Methods: Terrace farming starts from the tillaging process of the sloppy area. Usually people do not plant, productive plants on those area mainly they plant fast growing grasses and plant on those sloppy and risky areas. After some years when the mud and soil of that area get settled there properly than people also start the agriculture on those land also, from which they can earn their living.
Stages of implementation: To implement the project on that area local people had provided a lot of support. The huge economic support was provided by the European Union. Specially the Bagmati watershed management project had given huge huge economic support to this area. Mainly for water management purpose but also for land management.
Role of stakeholders: No presence of such kind of stakeholder in the project but the economic support was provided by European Union to plant trees and manage soil erosion in common land but land owner has also given their support in this project by planting trees and grasses on their land by themselves.
Other important information: Terrace farming has really helped local people to manage the land of that area, but the road making process has created a lots of problem of soil erosion which is also suppose to be managed by applying same process additional with some new process.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Nepal
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kavre
Map
×2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Agriculture)
1. Soil conservation.
2. Agriculture
3. For fodder, grasses etc.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Low agricultural production is one of the main problem of this approach, because at initial period the soil is too loose so it may easily get lost from particular place. So, first trees were to be grown which supports the soil. Then only agriculture was to be performed. So, this is the main problem encountered by local peoples other problems were also faced by people but they were not big as the first one.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
The financial support was provided by European union. So there was not much financial crisis.
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: As the system helps for managing the soil and prevent different environmental calamities the land user do not create any problem while the system runs.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Lack of technical knowledge had created lots of difficulties.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Some kind of training given by technician had removed this kind of problems.
工作量、人力资源可用性
- 阻碍
Because of personal workload, all local people could not be present on the program on time.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Proper schedule making for program according to local people favorable time might remove this problem.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Whoever be the land users,does not matter with sex, basically for all age group farmers, with simple living standard are aimed to be focused by stakeholders(European union).
More male participation than female because female were busy in household works. Men particularly were more because women were mostly busy in theit home, preparing meal and performing internal task of he house. No discrimination
- 地方政府
Villagers itself were implementing.
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 外部支持 | European Union |
| 计划 | 互动 | Local people and specialist |
| 实施 | 互动 | Specialist and local people |
| 监测/评估 | 外部支持 | Specialist |
| Research | 自我动员 | individuals |
3.3 流程图(如可用)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
According to the advice of SLM specialist, the land users utilized their land in a systematic way.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Mainly soil conservation programs are lunched by local people in which the SLM specialist also help them providing various techniques, equipments and guidelines.
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
培训形式:
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
涵盖的主题:
The training was given to the land users so that they also can adopt those techniques of training for conservation of their soil from erosion and other wastage.
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: Meeting, field visit; Local people get gather and discuss.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The requirement was provided by the international supports for the project.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,非常
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
提供进一步细节:
European Union provided the equipments and training for local people
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: erosion rate was estimated
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 经济/市场营销
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
The research was part of approach because research was done on local area within a society by student of KU which help to give further information of technology and approach to local people.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (European Union): 95.0%; government (No support): 4.0%; international non-government (No support): 1.0%; national non-government (No support); private sector (No support); local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (from VDC); local community / land user(s) (Local people)
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 机械 | 部分融资 | |
| 工具 | 部分融资 | |
- 基建
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 道路 | 部分融资 | |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 以粮换工
注释:
Mostly the financial support was provided by the European union.
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Land management was done properly mainly from application of countering process.
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
By utilizing the terrace land for agriculture, economically backward people were helped.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The problem is unlikely to be overcome in the near future. No, I don't think any problem would be created in coming future if this runs smoothly
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Almost all of the land users adopted the approach.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
By growing different crops on terrace land, production was increased in some extent which also helped the local people to supports the living.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
By increasing the agricultural production and utilizing terrace land.
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加生产
- 增加利润(能力),提高成本效益比
- 环境意识
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
They can continue the task without any supports because initial support and finance from European Union was gained to established the project.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It has controlled soil erosion (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Can be sustain by controlling deforestation, firing in jungle, controlling over extracting of medical herbs and so on.) |
| Provide woods and other domestic products |
| Provide fodder grass etc. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Helps land management (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: By handling the process from generation to generation) |
| Increase productivity by controlling soil loss (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Awareness should be given to local people) |
| Prevent natural calamities (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: By plaining more plants soil erosion can be controlled) |
| Preserve water source (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Afforestation program helps to preserve water source) |
| Prevent land mass and control gullies formation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Planting trees also helps to prevent land from gullies formation.) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| None |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Lack of technical knowledge | By providing training and skills |
| Production is less at initial phase | By adopting process continuously can increase as time passes, the plan controlled the soil loss and add nutrition to the land. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块