Participatory on-farm resarch and demonstration in UK arable cropping [英国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2547 - 英国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
SOWAP (SOWAP) - 匈牙利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考

Conservation tillage in UK arable cropping: Loddington [英国]
Surface cultivation of up to the top 10cm of soil but not complete inversion
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones

Conservation tillage in UK arable cropping systems: Tivington [英国]
Surface cultivation of up to the top 10cm of soil but not complete inversion
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
To find and demonstrate ways of better managing the land.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Objectives: to improve soil management, reduce soil erosion; to reduce water pollution; to enable farmer to maintain the economic viability of his operations; to disseminate project results; to engage with stakeholders; to encourage farmers to adopt the technology.
Methods: Presentation of technical and economic data; frequent discussions and field visits with farmers and their advisors, use of all dissemination options (opendays, presentations, agricultural press, radio, television).
Stages of implementation: Consultation bewteen project members and land manager on management practice; regular project meetings; collaboration with other organisations.
Role of stakeholders: Use of project experience to solve problems and set up appropriate trials, communication with various stakeholders.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
英国
区域/州/省:
Leicestershire and Somerset
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2003
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2006
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (soil quality, water quality, speed and cost of crop establishment, biodiversity)
To find and demonstrate ways of better managing the land. To demonstrate the viability and effectiveness of conservation oriented arable land management systems in protecting soil resources, improving catchment water quality and promoting biodiversity. To provide demonstrations of best practice in soil management for local farmers To provide practical field solutions to demonstrate sustainable farming practices to policy makers To demonstrate how information can be disseminated successfully at the local, regional, national and EU level via workshops, field visits, publications and the Internet.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Social: Insufficient awareness of environmental benefits of SWC and incoming regulation (eg CAP reform, Water Framework Directive), low level of confidence to try new techniques, getting farmers to own their (erosion) problem. Technical: link changes in soil management with effects on water quality and biodiversity
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 阻碍
traditional conservatism, perceptions, pride in a 'tidy' field
Treatment through the SLM Approach: discussion and demonstration
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
purchasing of appropriate equipment
Treatment through the SLM Approach: sourcing finance and creating business structure to justify expense; use of cost-benefit analysis information
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: The Allerton Trust's objectives are to be economically viable while practising good environmental management
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
dealing with trash and weed management; conflicting advice from many sources
Treatment through the SLM Approach: sharing risks and responsibility; input of expertise
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Working land users were mainly men (This is a single farm but the farmer now co-farms with a neighbour)
- SLM专家/农业顾问
- 教师/学龄儿童/学生
- NGO
One national non-goverment (SMI)
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- 国际组织
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 无 | |
| 计划 | 无 | |
| 实施 | 无 | |
| 监测/评估 | 无 | |
| Research | 无 |
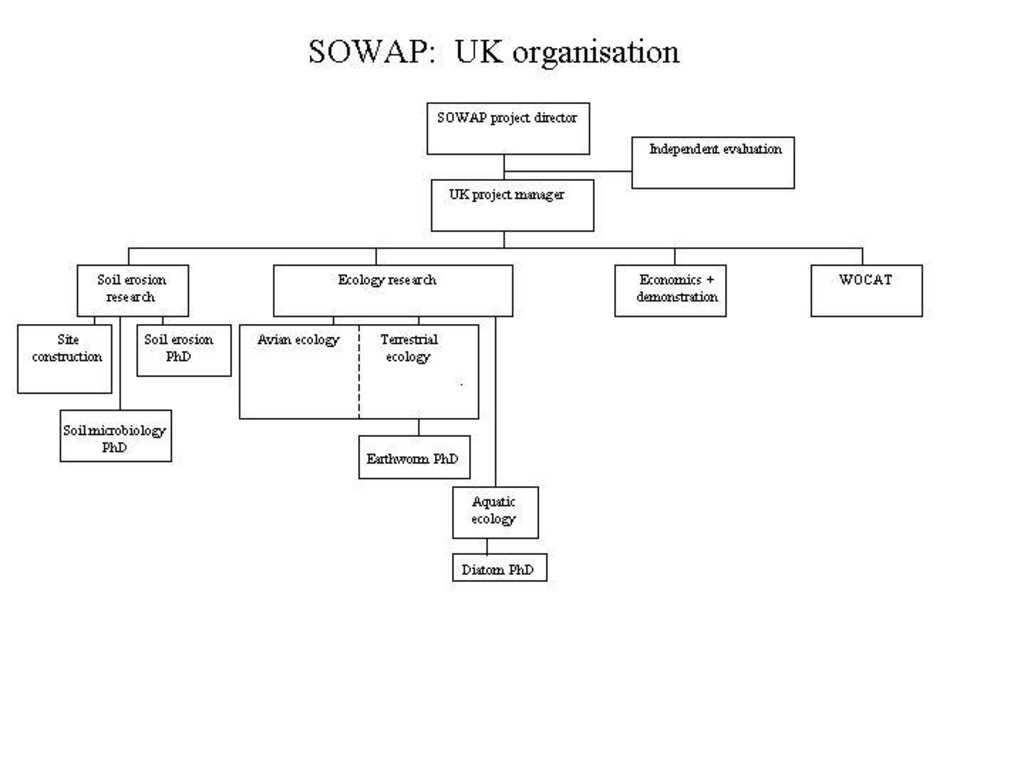
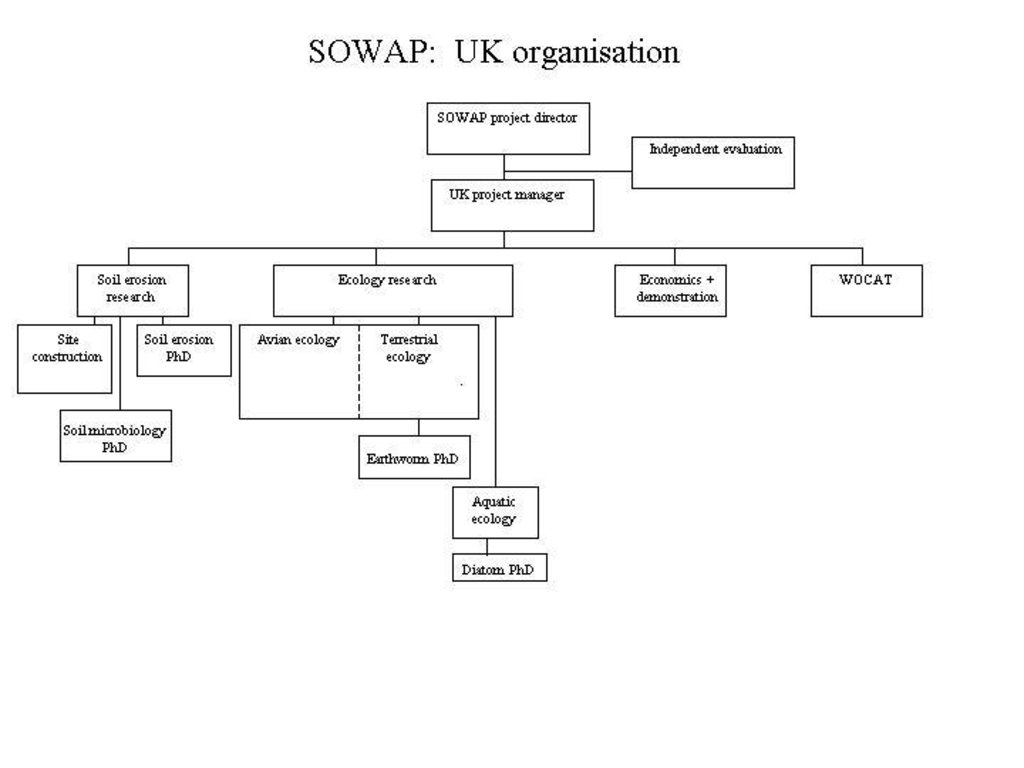
3.3 流程图(如可用)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是土地使用者,由SLM专家提供支持
解释:
On-farm discussion with project team members, the land manager and other experts.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Land manager needed to be comfortable with the decisions made
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- politicians/decision makers (1), agronomists (2),
培训形式:
- 在职
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
- 课程
培训形式:
- public meetings (1)
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 否
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through measurements
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 生态学
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Yields and gross margins; effects on biodiversity especially birds; rate of technology uptake
Research was carried out on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (EU-LIFE Environment/Syngenta): 100.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
否
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Soil and water management improved indirectly through the adoption of non-inversion tillage driven by the need to improve farm economics
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 不确定
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
Technical difficulties that may arise e.g. weed management, soil compaction, will require expert input and expertise from different areas
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| greater confidence |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| improved motivation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: continued support, technical advice and recognition of farmer's achievement) |
| improved education and awareness (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: continued support, technical advice and recognition of farmer's achievement) |
| greater confidence |
| improved problem solving capabilities |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| dependent on personalities I.e. with a more conservative farmer, this approach would be unsuccessful |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Conservation tillage in UK arable cropping: Loddington [英国]
Surface cultivation of up to the top 10cm of soil but not complete inversion
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones

Conservation tillage in UK arable cropping systems: Tivington [英国]
Surface cultivation of up to the top 10cm of soil but not complete inversion
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
模块
无模块