Participatory technology development [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Francis Turkelboom
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2631 - 阿拉伯叙利亚共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Tubeileh Ashraf
A.Tubeileh@cgiar.org
阿拉伯叙利亚共和国
SLM专业人员:
Bruggeman Adriana
The Cyprus Institute (CyI)
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
The Cyprus Institute (The Cyprus Institute) - 塞浦路斯1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考
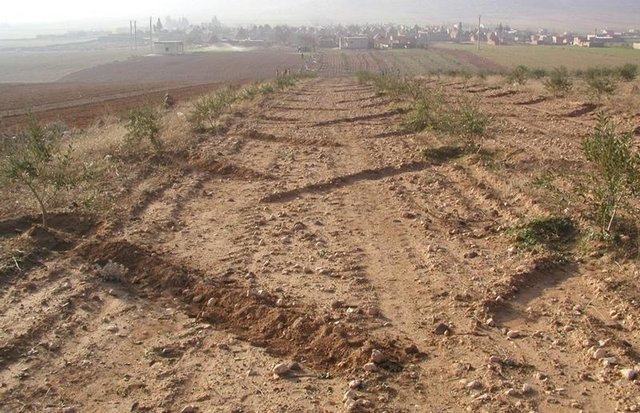

Furrow-enhanced runoff harvesting for olives [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
Runoff harvesting through annually constructed V-shaped microcatchments, enhanced by downslope ploughing.
- 编制者: Francis Turkelboom
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
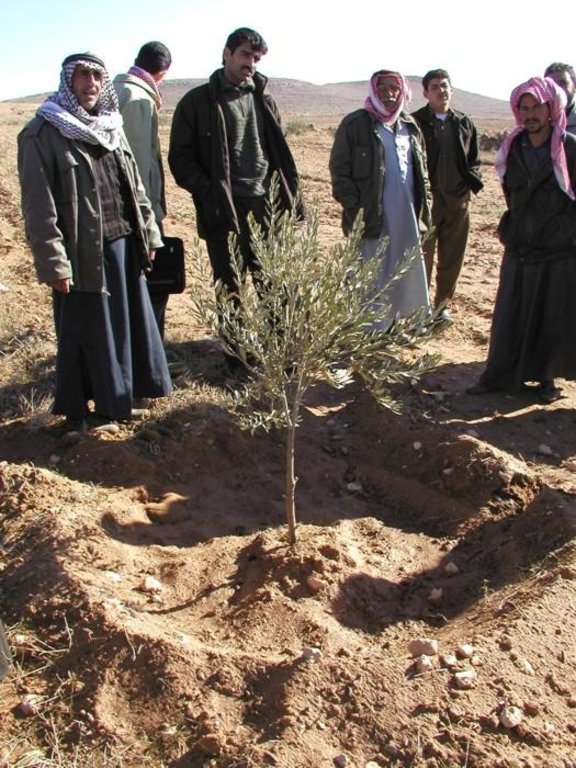
Participatory technology development, through close researcher-farmer interaction, for sustainable land management of olive orchards in dry marginal areas.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
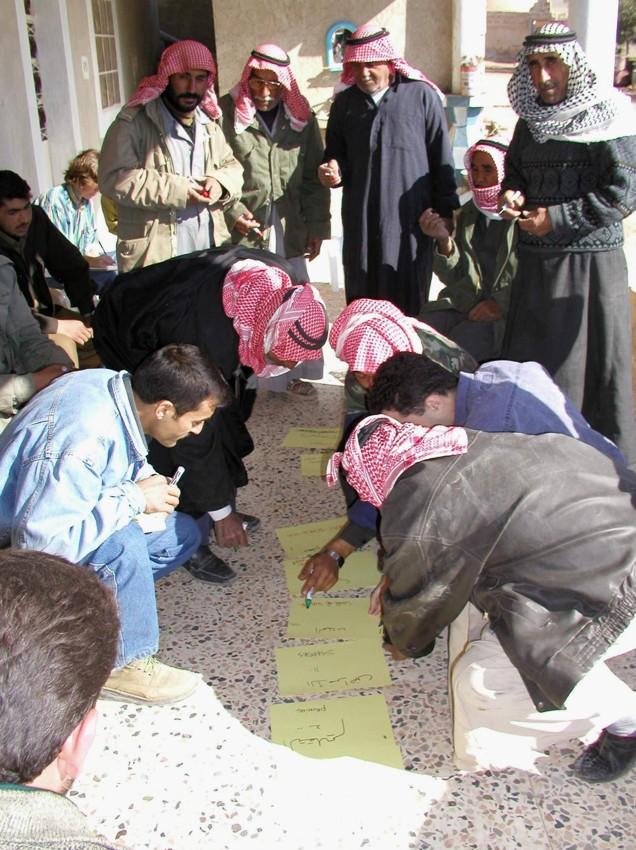
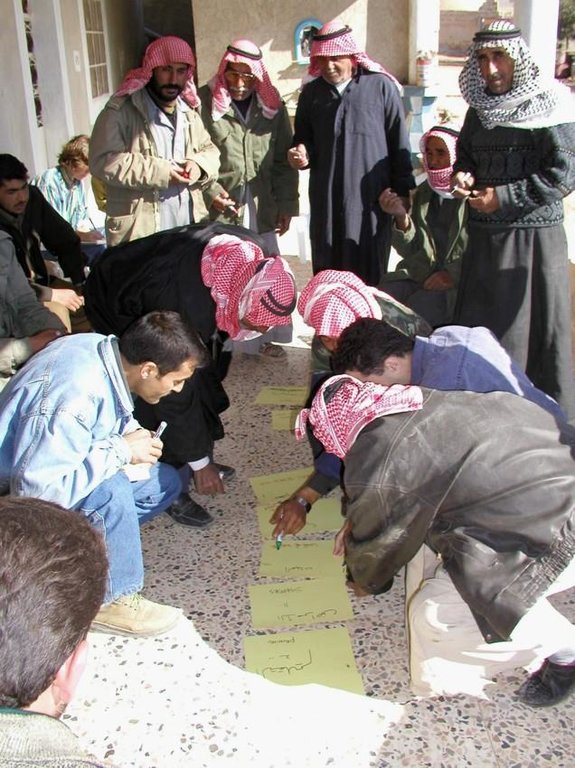
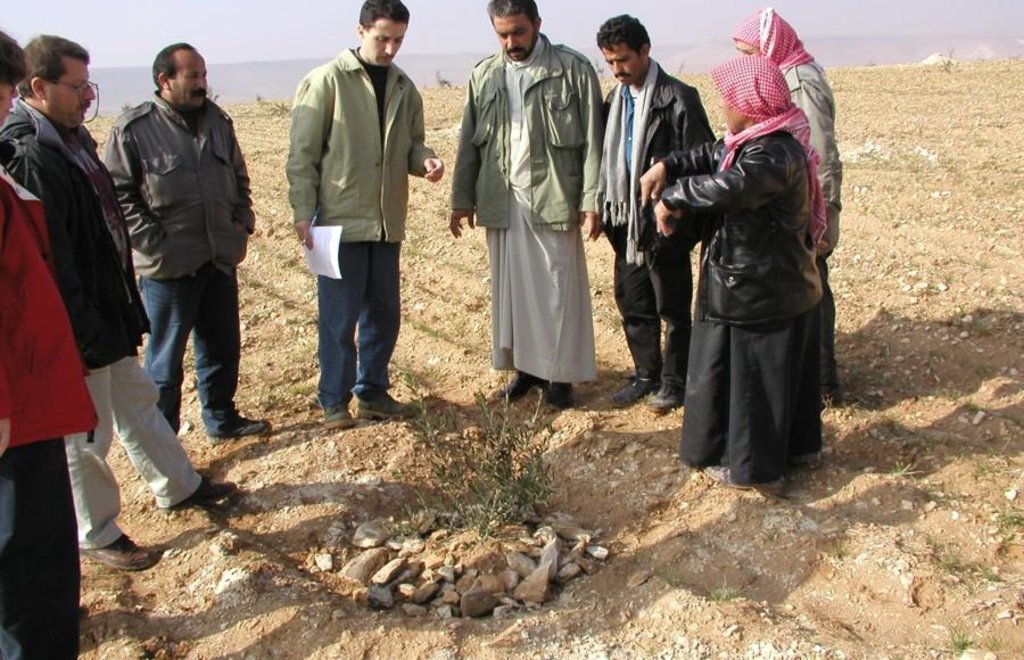
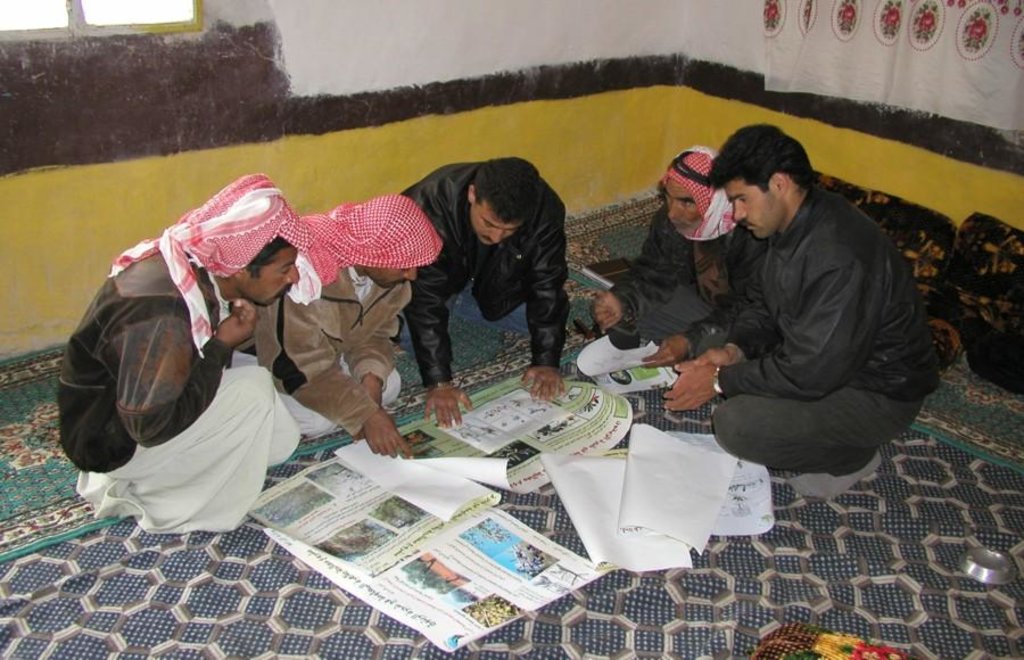
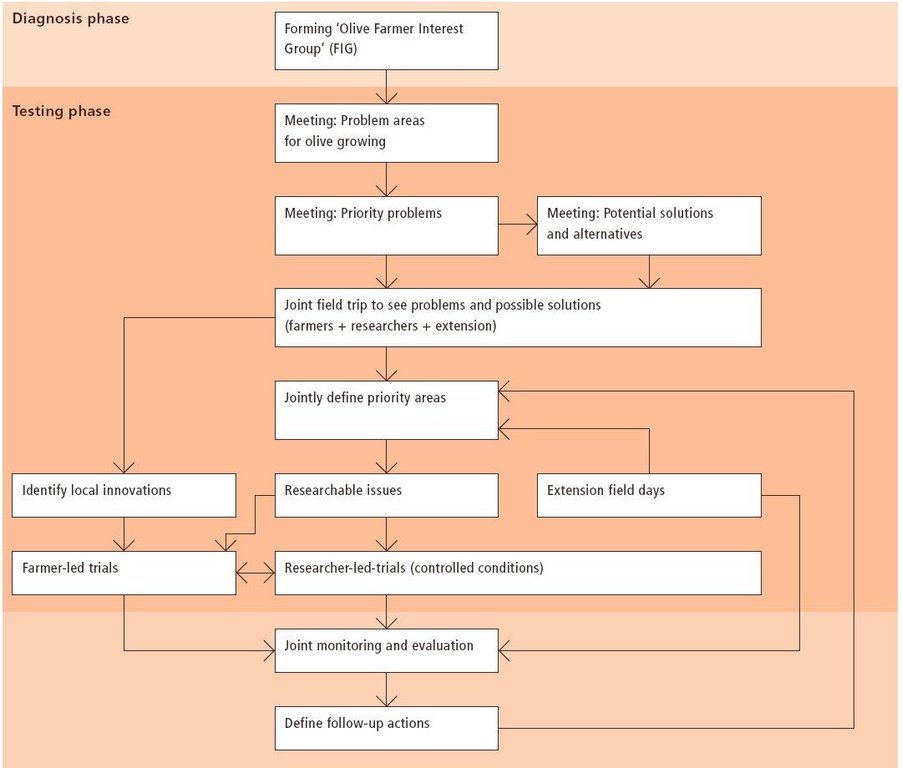
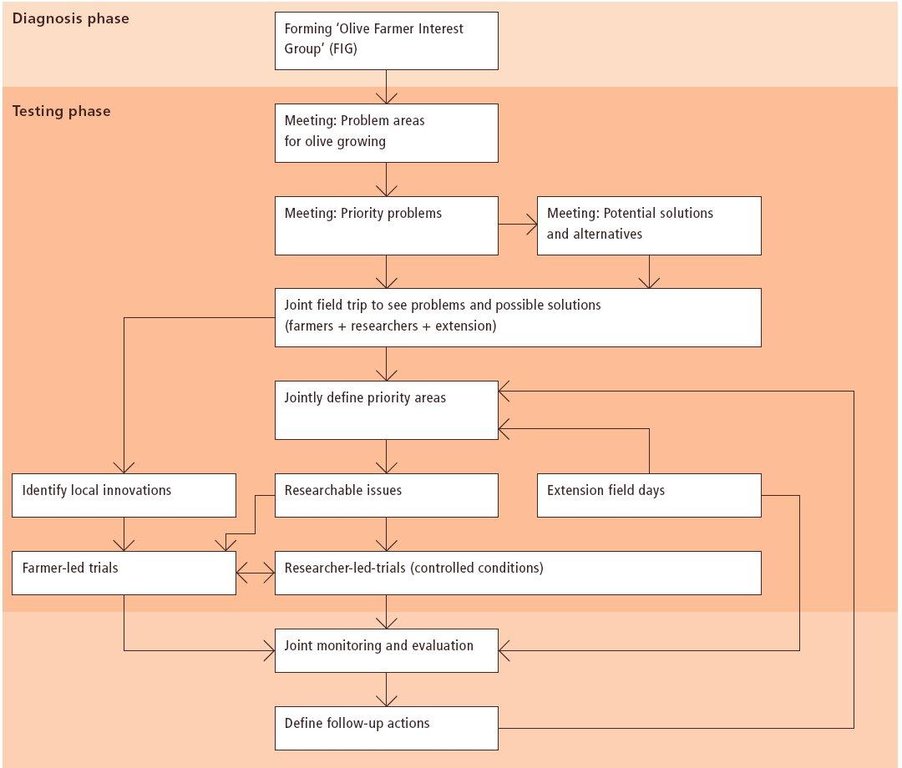
Aims / objectives: The purpose of participatory technology development is to gain from the synergy between indigenous knowledge and scientific expertise. The specific objective in this case was to develop and test water and land management techniques in order to sustainably improve olive production in a semi-arid area, while ensuring that the techniques were well adapted to local farming practices. The approach consists of group meetings, joint field trips, identification of local innovations, extension days, monitoring of farmer practices, and researcher-controlled experiments. The approach consists of a cycle with three major stages: a diagnostic phase, a testing phase, followed by monitoring and evaluation. In this case study, farmers were invited based on their interest in growing olives. Participation throughout the learning cycle was completely voluntary: no material or financial incentives were used (although they expected them in the beginning of the process). The role of farmers was to identify priority problems and potential solutions, to test new technologies on their farms, and to evaluate their suitability. Farmers observed the research experiment with water harvesting, and then adapted the technology to their needs. As shown, they built V-shaped bunds around their olive trees to capture rainwater runoff, but - contrary to the researchers??? suggestion - they continued to plough the olive orchards, as this is their standard weed control practice. Weeds attract sheep, lead to fires and compete for water with the olives. This simple runoff harvesting system is well adapted to farmers??? objectives, and their modification -the up-and-down slope furrows created through ploughing - actually serves to increase the efficiency of the water harvesting. The system is now being monitored by researchers to assess its technical and economic efficiency.
Methods: Improved farmer-researcher interaction helps farmers learn about a useful basic technique from researchers, while researchers learn in turn about potential improvements to the technology from local innovators. A community facilitator of ICARDA (International Centre for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas) facilitated the group discussions, and the researchers were asked to be open-minded to new approaches while conducting and monitoring field trials. The approach was tested by an interdisciplinary team of ICARDA as part of the ???Khanasser Valley Integrated Research Site???. This project aimed to develop local-adapted options for agriculture in dry marginal areas alongside a generally applicable integrated approach for sustainable land management in these zones.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿拉伯叙利亚共和国
区域/州/省:
Khanasser Valley
有关地点的进一步说明:
NW Syria
Map
×2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
- design, test and disseminate alternative technologies adapted to local conditions - strengthen local knowledge of SWC measures - strengthen joint learning by farmers and researchers
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The lack of appropriate ways to develop sustainable technologies to remedy loss of runoff water and poor olive growth -in the context of low-input agriculture on gentle undulating land in water scarce areas with an absence of soil conservation measures.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Water harvesting is considered expensive due to labour cost.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Identification of a low-cost water harvesting measure, which can be implemented during the off-season. Cost-benefit analysis.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Difficulty in tilling the land when water harvesting structures are in place.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Integrating local innovations into the water harvesting system.
其他
- 阻碍
Uncertainty about appropriate size of micro-catchment area. Uncertainty about the amount of water harvested. Lack of technical expertise for olive crop husbandry in dry areas.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Researcher-controlled research and carry out farmer field days, desseminate and elaborate extension leaflets as a help.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Mainly men were involved, as most activities in olive orchards are managed by men. In addition, culturally bound gender segregation in public makes it difficult to organise gender-mixed meetings. Therefore, separate meetings were organised for women. In the case of one household, the de facto partner was a woman who takes most of the orchard-related decisions and does the work herself.
- researchers
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 被动 | public meetings |
| 计划 | 互动 | public meetings |
| 实施 | 互动 | completely conducted by land-users |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | interviews/questionnaires, public meetings; |
| Research | 互动 | on-farm; farmer experiments and controlled on-farm experiments |
3.3 流程图(如可用)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是土地使用者,由SLM专家提供支持
解释:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
培训形式:
- 在职
- 农民对农民
- 公开会议
涵盖的主题:
Demand-driven training of olive husbandry techniques (eg pruning, grafting, pest management)
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Farmer-to-farmer extension; Key elements: innovative farmers showed their technique to other olive farmers during farm visits
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 否
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: soil moisture
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: water harvesting structures and management measures
technical aspects were regular monitored by None through observations; indicators: perceptions of the technology
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through measurements; indicators: cost and benefits
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through measurements; indicators: annual field survey using GPS
area treated aspects were regular monitored by None through measurements; indicators: annual farmer interview
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by None through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: There were few changes: interest in the farmers??? orchards and questions about the technology stimulated some other farmers to apply water harvesting.
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 经济/市场营销
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Research was an important part of this approach. Technical and socio-economic topics were treated as follows: (1) Researcher-controlled on-farm experiments: this helped evaluate the impact of water harvesting design on the amount of water harvested and the olive crop response. (2) Monitoring of farmer-managed trials: to evaluate the performance of water harvesting under on-farm conditions. (3) Cos
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - ICARDA, Atomic Energy Commission Syria): 10.0%; international non-government (BMZ (Germany)): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 40.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Adoption of the furrow-enhanced runoff-water harvesting technique resulted in a concentration of scarce rainwater and nutrients in the basins around the olive trees. The consequence is a significant reduction of soil loss and runoff at the field level.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
This approach is now being applied in other ICARDA-coordinated projects in the region.
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
The complete PTD process/learning cycle needs outsider facilitation, but lack of outsiders will not stop farmers experimenting further by themselves. In terms of the technology itself, farmers can continue independently with water harvesting structures, as the system is very simple and relatively cheap.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Engagement of researchers with local innovators and thus interaction between scientific and indigenous knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: This approach can only be sustained if it is mainstreamed into national research and extension services.) |
| Attitude changes by researchers about farmers??? knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Building on local knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Capacity building of both land users and researchers (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Demand-driven technologies (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Time demanding | Less time needed after the first experience. |
| Appropriate facilitating skills required | Mainstreaming facilitation skills. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Tubeileh A and Turkelboom F (2004) Participatory research on water and soil management with olive growers in the Khanasservan Veldhuizen L, Waters-Bayer A, Abd de Zeeuw H (1997) Developing technology with farmers:
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Furrow-enhanced runoff harvesting for olives [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
Runoff harvesting through annually constructed V-shaped microcatchments, enhanced by downslope ploughing.
- 编制者: Francis Turkelboom
模块
无模块