Experimental Farm Network for collaborative plant breeding and sustainable agriculture research. [美国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Stefan Graf
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
approaches_4199 - 美国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人员
土地使用者:
Kleinman Nate
nathankleinman@gmail.com / https://www.experimentalfarmnetwork.org/
Experimental Farm Network
美国
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/11/2018
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
The Experimental Farm Network is an online platform facilitating collaborative plant breeding as well as other sustainable agricultural research.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
The experimental farm network started when Nate Kleinman and Dusty Hinz saw the threats of climate change, and wanted to have an agriculture able to cope with it. Breeding for crops like trees, or perennial wheat, takes decades and is often part of university programs which phase out with the retirement of the responsible person. These are the reasons which lead the two to build up a decentralized network for plant breeding and other experimental farming techniques.
The network is online based, open source, and with a free access to everyone having an internet connection. In the network, there are two positions for each project: researcher and volunteer. A researcher who wants to start a project describes the goals, the needs from the volunteers, and the required climatic and soil conditions. A volunteer, who has a profile where the growing conditions are described, can sign up for the project. The researcher can then contact the volunteers which seem suitable, and send genetic material. Usually, the work involves planting the seeds, growing it out, measuring some characteristics (size, yield, etc.) and sending a part of the seeds with some data back.
The EFN is organized as a non-profit cooperative with two permanent employees and a board of advisors. The sources of income were initially a crowdsourcing and the sale of seeds. Financially it is not yet totally self-carrying, as the employees are working sometimes for free. With the increase of seed sales, also from experimental and diverse varieties, it is changing.
The website helps putting people in touch and keeping records of who is working on which project, as well as for volunteers to stay updated with the projects. Some projects, with annuals, are only short term, while others, for example with slow growing perennials, may need decades if not more to produce a selected cultivar or variety of a crop.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
美国
有关地点的进一步说明:
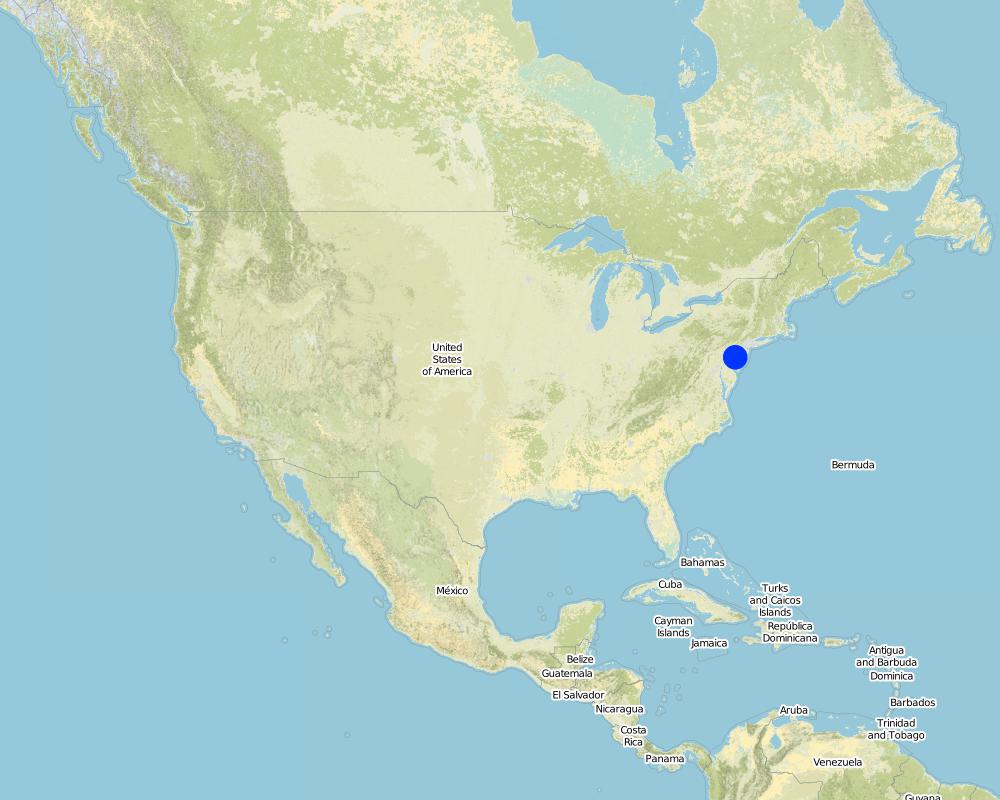
This is where the non-profit cooperative is registered. Projects take place around the world, in the USA, Canada and Australia so far.
注释:
The Network is global, with members in the USA, Australia as of 2018. Shown is Philadelphia, where the non-profit cooperative is registered.
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2013
若不知道准确的年份,请注明该方法的大致开始日期。:
不到10年前(最近)
2.7 方法的类型
- 最近的本地倡议/创新
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
Develop farming systems for a future, while tackling problems with climate change.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 启动
More and more people are aware of the problems with the narrow genetics of current varieties.
参与者的的协作/协调
- 启动
It only works as collaborative projects.
- 阻碍
Some volunteers do not return seeds, it is difficult to get reliable people.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 启动
The exchange of the different actors in plant breeding and sustainable farming enables the work of the experimental farm network
工作量、人力资源可用性
- 启动
Many breeding projects can only be done on huge areas, for example tree breeding. Spreading the workload on many people, all of them having only a limited work, enables to make
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Volunteers
Volunteers help researchers with their experiments, for example by looking out for promising wild specimen, by growing out varieties under specific conditions to assess the resistance, by selecting experimental varieties, or by similar work.
- 社区组织
The non-profit cooperative "Experimental Farm Network"
Provides an online platform where researchers and volunteers can meet.
- 研究人员
Researchers
They can find volunteers if more people are needed to carry out an experiment, specially in plant breeding for sustainable farming.
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
The non-profit cooperative "Experimental Farm Network" has the lead, but each researcher leads his or her own project.
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 自我动员 | |
| 计划 | 互动 | |
| 实施 | 互动 | |
| 监测/评估 | 无 |
3.3 流程图(如可用)
具体说明:
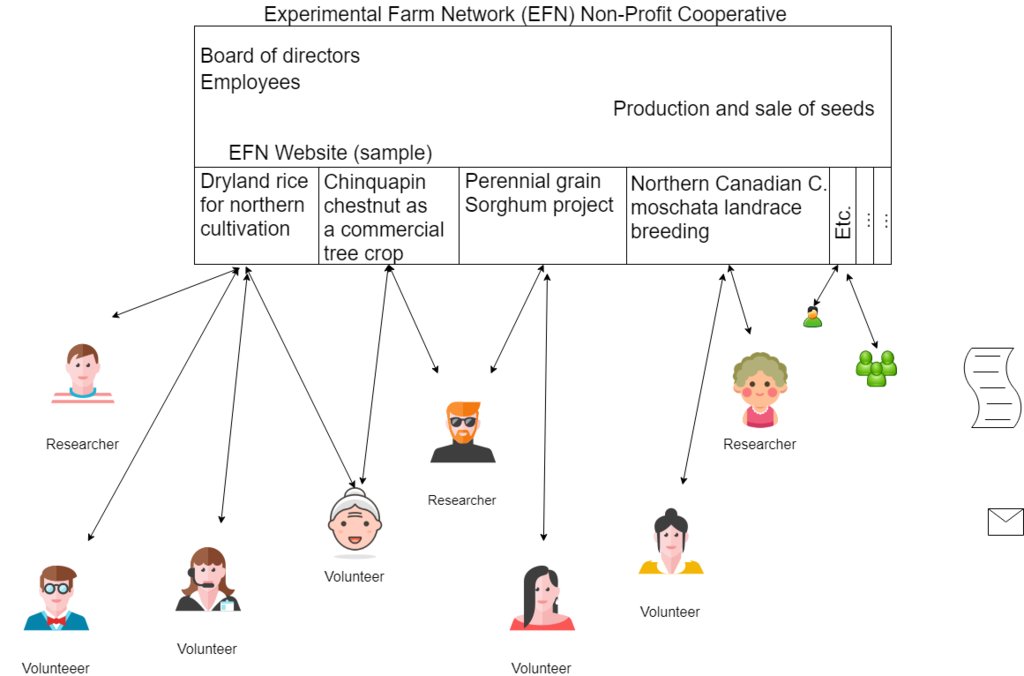
The Experimental Farm Network is organised as a Non-Profit Cooperative. It consists of a board of directors overseeing the the whole, and of employees. The EFN lives from donations and from the sale of seeds which are cultivated on kindly lent land.
The EFN has a website, experimentalfarmnetwork.org, on which researchers can create an account describe projects for which they want volunteers. Volunteers can also creat an account, on which they describe their soil and climatic conditions. Researchers can then contact volunteers and ask them for help. The work for the volunteer often involves growing recieved seeds and send back records about the growth, and send back seeds to the researcher. The volunteers and researcher can connect trough the website, but some work as well trough other networks like facebook.
作者:
Stefan Graf
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是土地使用者,由SLM专家提供支持
解释:
Each volunteer grows a crop only if he or she wants to grow it, and gets support for it.
明确做出决策的依据:
- 对充分记录的SLM知识进行评估(基于证据的决策)
- 研究结果
- 个人经验和意见(无记录)
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
培训形式:
- Support for the volunteers
涵盖的主题:
Depending on the crop grown, the researcher helps with information about how best to grow it.
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
否
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,适度
- Online
说明机构、角色和职责、成员等。:
The online network was established within the approach.
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
否
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 生态学
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Breeding is always research for better adapted crops or varieties.
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
说明该方法中SLM部分的年度预算,单位为美元:
10000.00
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Crowdsourcing was used in the beginning, now the sale of seeds is taking over in supporting the cooperative financially.
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
否
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 农业
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 种子 | 部分融资 | Depending on the project, seeds are given and a return of the subsequent generation asked. |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
5.5 其它激励或手段
是否有其他激励措施或工具用于促进SLM技术的实施?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否有助于当地土地使用者,提高利益相关者的参与度?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否建立/加强了机构、利益相关者之间的合作?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否提高了土地使用者适应气候变化/极端情况和减轻气候相关灾害的能力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 环境意识
- 提高SLM知识和技能
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 不确定
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
It depends on the project, but usually the land users can continue to grow the crops they are testing as a part of the network.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Allows farmers who are isolated on the countryside to have research projects together with others. |
| Allows a decentralized approach, in which the research can continue even if the initial researcher did not continue. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The transparency allows other projects to be inspired to do similar breeding projects. |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Some volunteers only take the seeds, and do not give back as promised. | EFN wants to implement a rating system for volunteers, in a way that researchers can see if they are reliable. |
| Some people do not want to create an account in another social network. | They can contact some researchers directly, and work without having an account. This requires more organisational work for the researchers, but is done by some. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| As an english speaking platform, it crosses many countries, while some seed regulation do not allow imports or translocations of genetic material due to the risks of disease transfer. | Arrange the platform into countries where adequate. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Reading trough the website.
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Plant Breeding and Farmer Participation, Ceccarelli et al., 2009,ISBN 978-92-5-106382-8
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.fao.org/docrep/012/i1070e/i1070e00.htm
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Experimental Farm Network website.
URL:
https://www.experimentalfarmnetwork.org/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块