Lessons learned from the "Mind the Gap" project: Improving Dissemination Strategies [突尼斯]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Joren Verbist
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
approaches_7123 - 突尼斯
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人员
Innovation specialist:
Rudiger Udo
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
突尼斯
Gender specialist:
Najjar Dina
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
摩洛哥
Natural Resource Economist:
Dhehibi Boubaker
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
突尼斯
Werner Jutta
German Ministry of Agriculture
Derbel Sondos
AVFA (National Agricultural Training and Extension Service)
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiative有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - 黎巴嫩1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
2019
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考

ICT2Scale – supporting smallholder farmers with cellphone-based services … [突尼斯]
The ICT2Scale project contributes to better land management by supplying smallholder farmers with targeted SMS messages on diverse agricultural practices. This enables them to optimize resources and adopt more sustainable methods, consequently improving livelihoods in remote areas.
- 编制者: Joren Verbist

Small-Scale Nutrient-Dense Pellet Production [突尼斯]
Compressing agro-industrial by-products produces nutrient-dense livestock feed pellets that can compete with expensive and imported alternatives. This innovation consists of a small-scale compressor or "pelletizer" and formulae to create feed pellets of sufficient quality with locally available inputs.
- 编制者: Joren Verbist
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
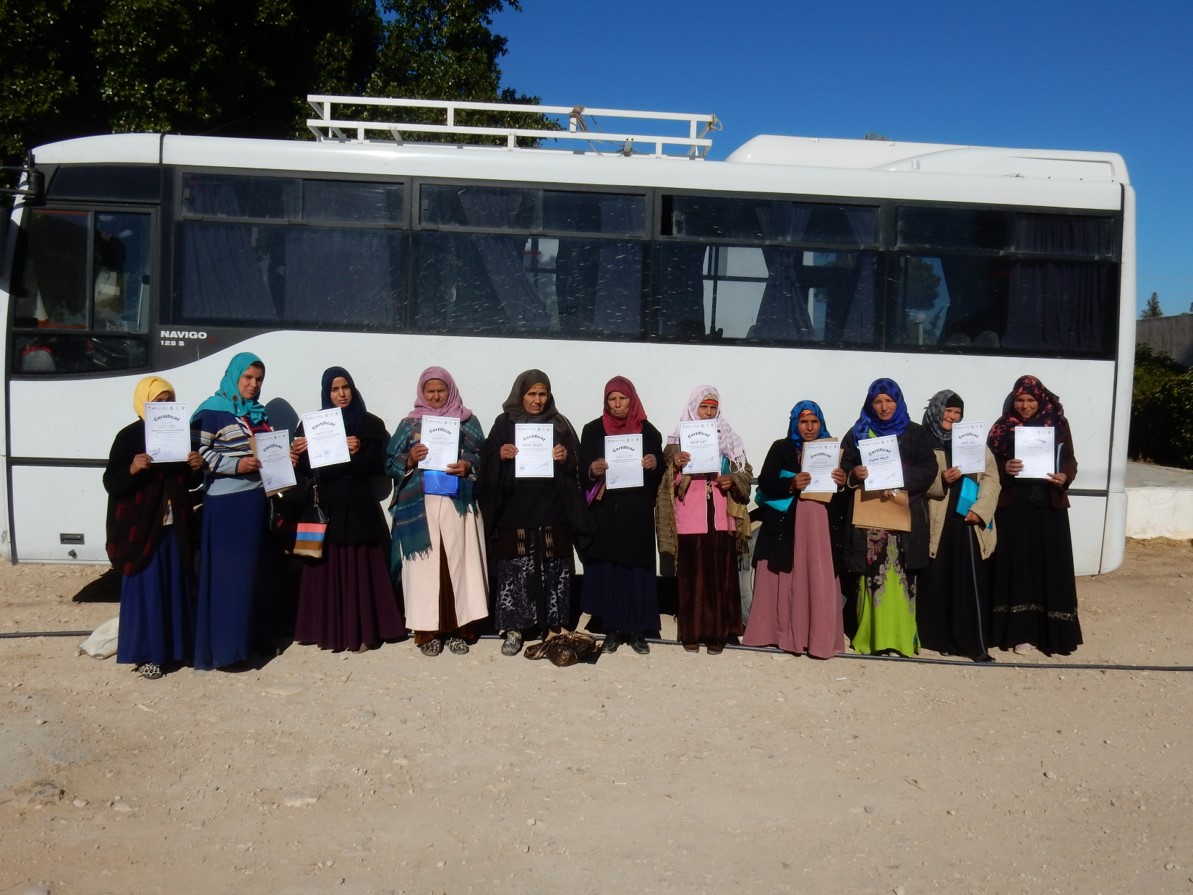
The “Mind the Gap” project researched the adoption gap between agricultural research and women and men farmers. Its objective was to determine most effective and cost-efficient technology transfer strategies and give recommendations to national extension institutes and development partners to adapt their scaling strategy
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Research into innovative agricultural technologies for the livestock-barley system in semi-arid Tunisia has yielded success. However, adoption of these has remained low for decades, not only in Tunisia but across developing countries (Noltze et al. 2012; DFID 2014; Syngenta Foundation 2015). Bridging this 'adoption gap' has proved to be a challenge, and there has been limited emphasis on improving agricultural extension methods. In this context, the International Center for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) together with partners set up the "Mind the Gap" project, funded by the BMZ and GIZ.
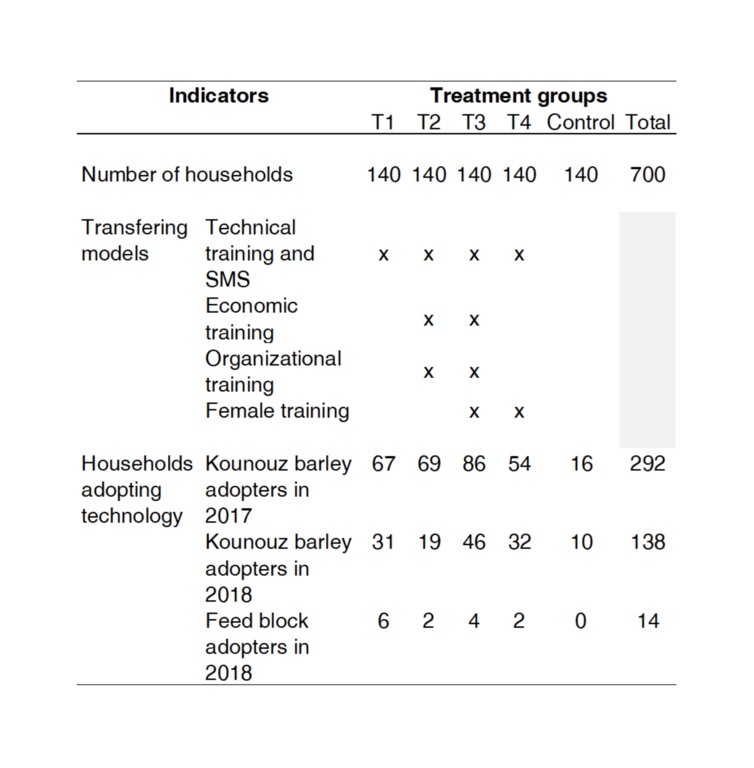
This project aimed to fill this gap by developing and testing new models for transferring sustainable technology packages to smallholder farmers. Four transfer models were implemented across four test groups:
T1: Technical training and SMS.
T2: Technical training, SMS, economic, and organizational training.
T3: Technical training, SMS, economic and organizational training, with a focus on female empowerment.
T4: Technical training, SMS, and female empowerment.
The transferring models are thus (a) Technical training and SMS; (b) Economic training; (c) Organization training; (d) Female empowerment.
Technical training and SMS involved sending weekly text messages containing technical and organizational information to 560 farmer households from August 2017. Workshops were conducted in 2017 and 2018 to develop these messages in collaboration with regional extension services and other stakeholders.
Economic training included one-day sessions in 2017 to demonstrate the economic benefits of innovations. In 2018, a Farmer Business School (FBS) approach was adopted to enhance farmers' entrepreneurial skills, with a tailored curriculum and seven five-day courses delivered to 280 farmer households.
The organizational training aimed to enhance farmers' understanding cooperative management. Through classroom sessions and visits to existing cooperatives, farmers received insights into cooperative creation, management challenges, and the benefits of collective action.
Female empowerment activities engaged women from 280 farmer households, focusing on visits to female cooperatives and sensitization events to encourage their participation in agricultural activities and access to credit.
The adoption of two innovations was evaluated through this methodology. The first innovation, "Kounouz," is an improved barley variety designed to better withstand drought conditions. The second innovation involves feedblocks, also known as nutrient-dense pellets, which serve as an alternative livestock feed made from by-products.
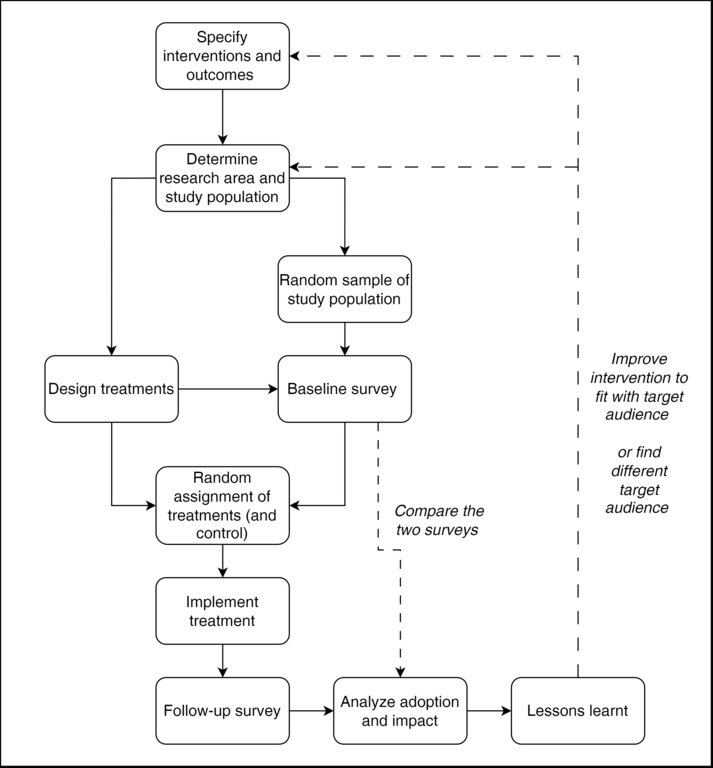
The project rigorously evaluated these transfer models through randomized controlled trials, focusing on their impact on innovation adoption rates and cost-efficiency. The combined approach, carried out under T3, showed the highest adoption rates, particularly among female-headed households. Field visits were identified as a significant contributor to technology adoption, while SMS proved most cost-effective.
Most importantly, it showed that the four transferring models should be used in combination for the highest adoption.
In conclusion, the research underscores that addressing the 'adoption gap' in agricultural innovation requires comprehensive approaches encompassing technical, economic, organizational, and gender empowerment training. By combining these elements significant strides can be made in cost-efficiently enhancing technology adoption rates among smallholder farmers, offering valuable insights for agricultural extension efforts not only in Tunisia but also across the MENA region and potentially beyond.
Acknowledgement:
We would like to thank BMZ/ GIZ who supported this innovative research through their contributions to the “Mind the Gap” project as well as Tunisian NARES (INRAT, AVFA, OEP, CRDA) for co-implementing project activities.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
突尼斯
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2016
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2019
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
To better understand the adoption gap of new sustainable farming technologies, and discover cost-efficient and effective approaches to improve adoption of these technologies.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 阻碍
Participation of women at trainings was sometimes low (no availability to due household tasks)
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 启动
Access to financial resources allowed purchase of technologies (Kounouz seeds or feed blocks)
机构设置
- 启动
The right institutions were selected (OEP, INRAT, AVFA) to implement MtG project activities
参与者的的协作/协调
- 启动
Collaboration between the partners (NARES) was good and important; eg INRAT multiplied Kounouz seeds ; OEP and CRDA distributed Kounouz seeds and AVFA trained farmers on Kounouz production
政策
- 阻碍
Feed block production has strict regulations
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 启动
Technical support to practice the technology (eg feed block composition) is important and was guaranteed by OEP
市场(购买投入,销售产品)和价格
- 阻碍
Prices of substitute feed like subsidized wheat bran and barley hinder the adoption of feed blocks.
工作量、人力资源可用性
- 阻碍
Workload for feedblock production is high and manpower not always available.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
No communities but individual farmers
Inviting farmers to trainings,
Organization of baseline and follow up survey with OEP
- SLM专家/农业顾问
AVFA (National Agricultural Training and Extension Service)
CTV (Local Extension Service)
OEP (Livestock and Pasture Office)
AVFA:
Organizational and economic trainings (FBS, BUS, cooperatives, etc) to 280 HH
Organized logistics (transport, restoration, training room)
OEP:
Technical training on feed blocks to 560 HH
Distribution of inputs to CTV, selection of cooperatives.
- 研究人员
University of Goettingen
INRAT (National Agricultural Research Institute)
University of Goettingen:
Project development, PhD students, data collection for baseline and follow up survey
INRAT:
Development of new barley variety (Kounouz) in collaboration with ICARDA
Technical training on barley with OEP to 560 HH
- 国际组织
ICARDA
GIZ
ICARDA: Overall technical and administrative coordination
GIZ: Trained AVFA trainers on FBS and BUS
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
ICARDA
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 被动 | The experiments were designed and set up by the research agency. |
| 计划 | 被动 | Methodology was also determined by the research agency. |
| 实施 | 互动 | The approach to dissemination that proved successful was interactive. |
| 监测/评估 | 被动 | The experiment was monitored by the research agency. |
3.3 流程图(如可用)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
There was a strong focus on research rather than implementation, which required scientific expertise rather than land user knowledge.
明确做出决策的依据:
- 对充分记录的SLM知识进行评估(基于证据的决策)
- 研究结果
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
如果相关,请说明性别、年龄、地位、种族等。:
Land user, with a strong focus on females for two treatment groups.
培训形式:
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
- 课程
涵盖的主题:
The four main trainings were given:
-Technical with SMS
-Economic (e.g., better farm management)
-Organizational (e.g., setting up farmer cooperatives)
-Female empowerment
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
- 在固定中心
说明/注释:
Advice was given through the training which included both on-site (e.g., demonstration fields) and meetings
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,适度
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
说明机构、角色和职责、成员等。:
Training sessions regarding cooperation can be organized.
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
Four treatment groups were made based on different combinations of training, they were evaluated for their adoption of Kounouz barley and feed blocks.
若是,该文件是否用于监测和评估?:
是
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 经济/市场营销
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Several research papers were published with authors from different partners.
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
说明该方法中SLM部分的年度预算,单位为美元:
400000.00
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
GIZ/BMZ
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
否
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 无
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
5.5 其它激励或手段
是否有其他激励措施或工具用于促进SLM技术的实施?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否有助于当地土地使用者,提高利益相关者的参与度?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否调动/改善了使用财务资源实施SLM的途径?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否改善了性别平等并赋予女性权力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否改善了粮食安全/改善了营养?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加生产
- 增加利润(能力),提高成本效益比
- 降低灾害风险
- 加入运动/项目/团体/网络
- 提高SLM知识和技能
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Highest adoption rate for Kounouz was in T3 (61% in 2017 and 33% in 2018) where the whole package of extension was provided (technical training, SMS + economic and organizational training +female empowerment + access to input). This indicates that different adoption models should be combined rather than singled out. |
| The treatment groups T3 and T4 which received the female empowerment training have the highest Kounouz variety adoption rates in 2018 (T3 = 33%, T4 =24%). The implication of women in the project has a positive influence on the adoption of innovative technologies. The gender dimension should be considered as a vector of adoption of new technologies especially in Tunisian agriculture. |
|
In terms of cost, the government can choose according to the available budgetary resources: i) Highest level of technology adoption with the highest cost of trainings 34% in T3 with a total cost of trainings estimated at 900 TND per person ii) Medium technology adoption rate with a lower cost of trainings 22% in T1 with a total cost of trainings estimated to 230 TND per person). T3 is most effective but T1 is more cost efficient. |
| The strong collaboration between four public research and extension institutions (OEP, INRAT, AVFA and CTV) and one international agricultural institution (ICARDA) is one of the important factors for adoption and transfer of knowledge |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Concerning the technical extension methods, the field visit (with an intermediate cost) especially done in the similar areas is more efficient than the training (with a high cost) and the SMS text message (with a very low cost). | However, these extension methods are complementary and encourage the project’s farmers to adopt innovative technologies. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mohamed Zied Dhraief, Udo Rudiger, Aymen Frija, Jutta Werner, Liza Straussberger, Barbara Rischkowsky. (13/4/2022). Impact of improved agricultural extension approaches on technology adoption: Evidence from a randomised controlled trial in rural Tunisia. Experimental Agriculture, 58, pp. 1-16.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/67344
标题/说明:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Udo Rudiger. (24/12/2019). Synthesis Mind the Gap.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10505
标题/说明:
Udo Rudiger. (16/12/2019). Mind the Gap: Improving Dissemination Strategies to Increase Technology Adoption by Smallholders. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10471
标题/说明:
Samar Zaidi, Boubaker Dhehibi, Mohamed Zied Dhraief, Mohamed Arbi Abdeladhim. (22/3/2023). Résilience des ménages face à l’insécurité alimentaire et au changement climatique dans les régions du centre et du nord-est de la Tunisie: Une analyse empirique. New Medit, 22 (1), pp. 19-34.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68229
标题/说明:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Jutta Werner, Matin Qaim. (7/3/2018). Designing and Conducting Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) for Impact Evaluations of Agricultural Development Research: A Case Study from ICARDA’s ‘Mind the Gap’ Project in Tunisia. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8209
标题/说明:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Jutta Werner, Hloniphani Moyo. (18/9/2018). Developing a policy framework for agricultural extension systems in Tunisia. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8390
标题/说明:
Quang Bao Le, Jutta Werner, Boubaker Dhehibi, Mounir Louhaichi, Chandrashekhar Biradar. (10/11/2019). Functionally context socio-ecological type (fCSET) approach to support outscaling of agricultural innovation options.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10801
标题/说明:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Udo Rudiger, Mohamed Zied Dhraief. (9/9/2019). Factors Influencing Farmers’ Decisions to Adopt Improved Technologies in Semi-Arid Farming Systems: A case study of the barley variety Kounouz and feed blocks technology in Tunisia. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10223
标题/说明:
Hloniphani Moyo, Jutta Werner, Boubaker Dhehibi, Udo Rudiger, Cherifa Saidi. (14/4/2019). Improving dissemination strategies to increase technology adoption by smallholder farmers in Tunisia. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9813
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

ICT2Scale – supporting smallholder farmers with cellphone-based services … [突尼斯]
The ICT2Scale project contributes to better land management by supplying smallholder farmers with targeted SMS messages on diverse agricultural practices. This enables them to optimize resources and adopt more sustainable methods, consequently improving livelihoods in remote areas.
- 编制者: Joren Verbist

Small-Scale Nutrient-Dense Pellet Production [突尼斯]
Compressing agro-industrial by-products produces nutrient-dense livestock feed pellets that can compete with expensive and imported alternatives. This innovation consists of a small-scale compressor or "pelletizer" and formulae to create feed pellets of sufficient quality with locally available inputs.
- 编制者: Joren Verbist
模块
无模块