Participatory rural approach [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2340 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人员
SLM专业人员:
de Wet Saroné
School of Environmental Science and Development, North West University, South Africa
南非
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
School of Environmental Science and Development, North West University (NWU) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Participatory Rural Approach including a partly holistic approach; between social and environmental sciences.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Developing sustainable management of land and other natural resources in rural communities. Assess the historical process, causes, nature and extent of desertification and its human impact. An empirical study of the attitudes, perceptions and knowledge of the local population with regard to land use. Develop policy guidelines for integrated rural development focussing on spatial planning, settlement models, land use control measures, ecological restoration and sustainable farming practices. Pilot interviews with the extension officers were followed by interviews with members of the communities themselves. Plant surveys were conducted at the study areas.
Stages of implementation: There were 5 stages of implementation included in the pilot interviews, the main interviews and the plant surveys. Task 1: Preliminary negotiations with officials, authorities and local communities, including a literature and methodological review. Task 2: Data collection includes satellite data and aerial photographs, ground truth (site visits, meetings, surveys, interviews and questionnaires - a PRA approach. Task 3: Analysis and interpretation include archival research, image processing ad interpretation and analysis of surveys and questionnaires. Task 4: Validation and cross referencing by accuracy testing of remotely sensed results, historical cross referencing, comparison to Botswana results, comparison of results (communal land vs. commercial land). Task 5: Reporting.
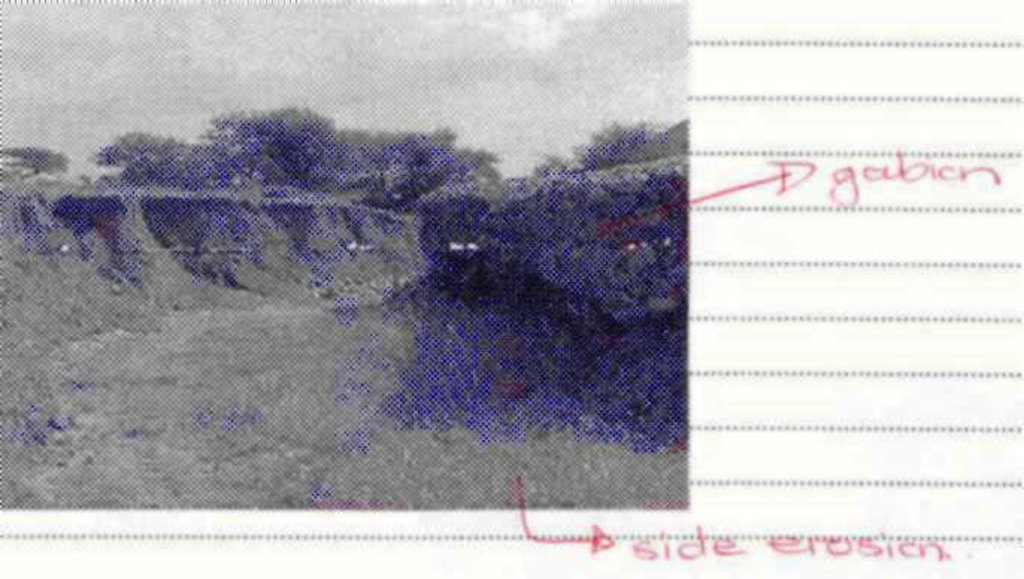
2.3 该方法的照片
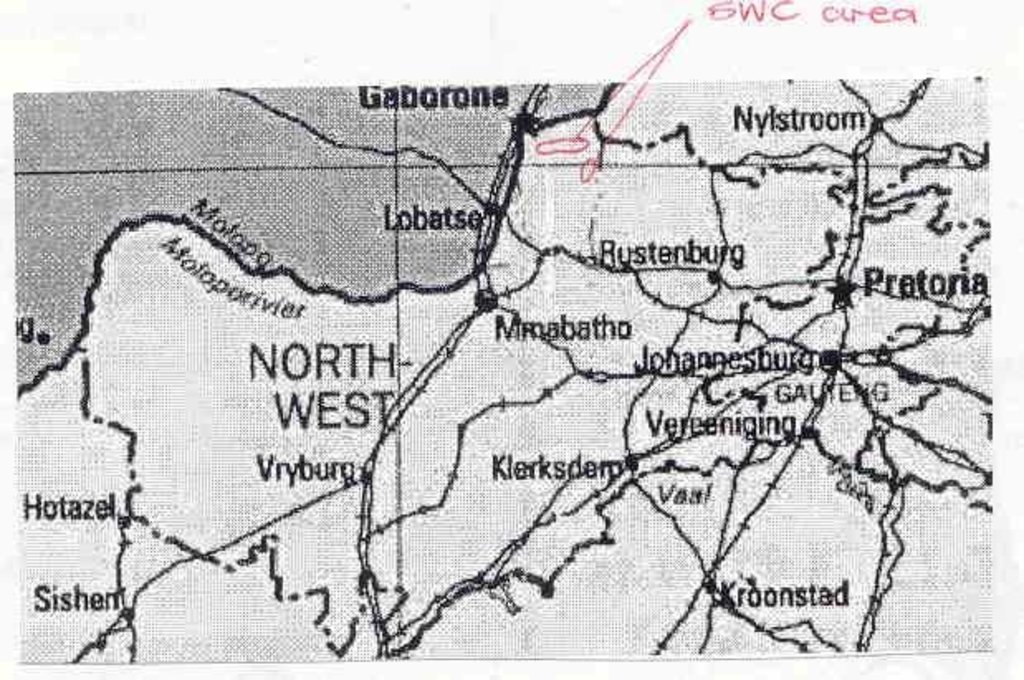
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
North West Province
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2000
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2003
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Suitable management, integrated community-base, rural development, land resources, natural resources.)
Developing sustainable management of land and other natural resources in rural communities. Specific objectives: Assess the historical process, courses, nature and extent of desertification and its human impact. Did an empirical study of the attitudes, perceptions and knowledge of the local population with regard to land use. Finally, we want to develop policy guidelines for integrated rural development focussing on spatial planning, settlement models, land use control measures, ecological restoration and sustainable farming practices.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Desertification and its human impact, with the specific incorporation of indigenous or traditional knowledge. Inadequate policy towards integrated rural development.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Funding not sufficient
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Involved with greater Department of Agriculture and subsequent funding
机构设置
- 阻碍
Part of previous disadvantaged homeland
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Policy recommendations
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 阻碍
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly hindered the approach implementation No one takes responsibility for maintaining the applied technology.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
No contracts with large equipment companies
Treatment through the SLM Approach: With the Department of Agriculture, theses contract have been established
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Supingstad members. Specific ethnic groups: Tswana speaking (Ba-Suping)
- SLM专家/农业顾问
- 教师/学龄儿童/学生
University
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- 国际组织
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 无 | |
| 计划 | 互动 | interviews/questionnaires, public meetings; Interviews with most viable group. Public meetings: what should we look at in the areas. |
| 实施 | 互动 | casual labour, responsibility for minor steps; Erosion control. |
| 监测/评估 | 无 | |
| Research | 无 |
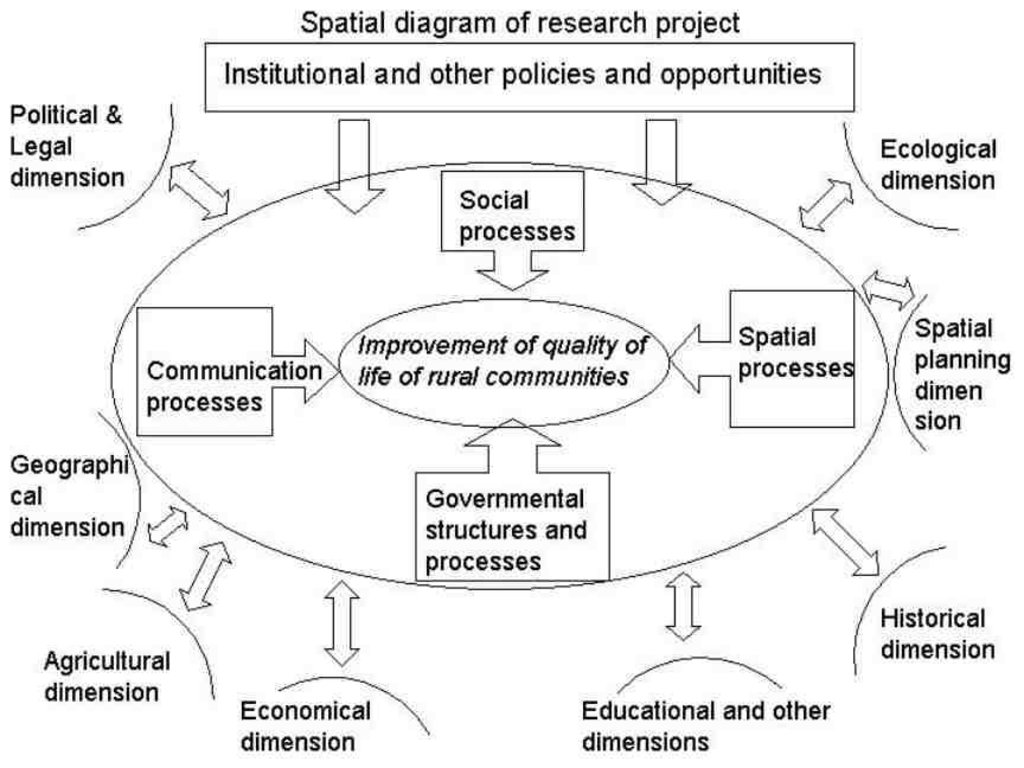
3.3 流程图(如可用)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是土地使用者,由SLM专家提供支持
解释:
consultative.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. consultative.
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- school children/students
培训形式:
- 在职
涵盖的主题:
Gabion construction
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Participatory rural approach; Key elements: Involvement in gabion construction; 1) Mainly: government's existing extension system, Partly: projects own extension structure and agent. Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: erosion control through gabion construction
Advisory service is inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Extension officers available for information on erosion and encroachment control.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,适度
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored through measurements
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements
There were several changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Initially only the extension officers were interviewed in groups; the communities as well, but in the end individual interviews proofed more effective. Woody component analysis: Where all members worked on one quadrate at the start, we changed the strategy to three teams of two people each, each team having their own specific responsibilities.
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 生态学
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Sociology: interviews/trust building. Ecology: explain what we are doing. Technology: gabion construction
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 10,000-100,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (funding): 80.0%; local community / land user(s) (labour, material): 20.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 以粮换工
注释:
Guides received food parcels. Other incentives; future change in policy.
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
They did not adapt, but their awareness were raised.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The people worked with the specialist in establishing the technology.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 否
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
No: Erosion - the wire mesh baskets must be supplied by the appropriate companies, but otherwise they might pack stones without the wire mesh baskets. Yes for bush encroachment.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Awareness of erosion and bush encroachment as well as possible solution to it (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: School available; provide with poster, books, etc. Farmer's meetings.) |
| A community member can make a difference. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Trust of people obtained (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Deliver on the promises) |
| The community was motivated to implement their own water supply |
| Awareness of grazing strategy on the condition of the grazing field (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Motivate extension officer to really provide appropriate solutions) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The projects do not address the problems the land users have | Refer identified problems to the relevant experts |
| Implementation of project takes a long time | Explain to the involved person the planned time schedule |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Number of available SWC specialist insufficient for amount of work | Train the amount of specialist/give the necessary background. |
| Use of translators | Make it clear to exact translations are given |
| Linguistic abilities not sufficient | Use translators |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块