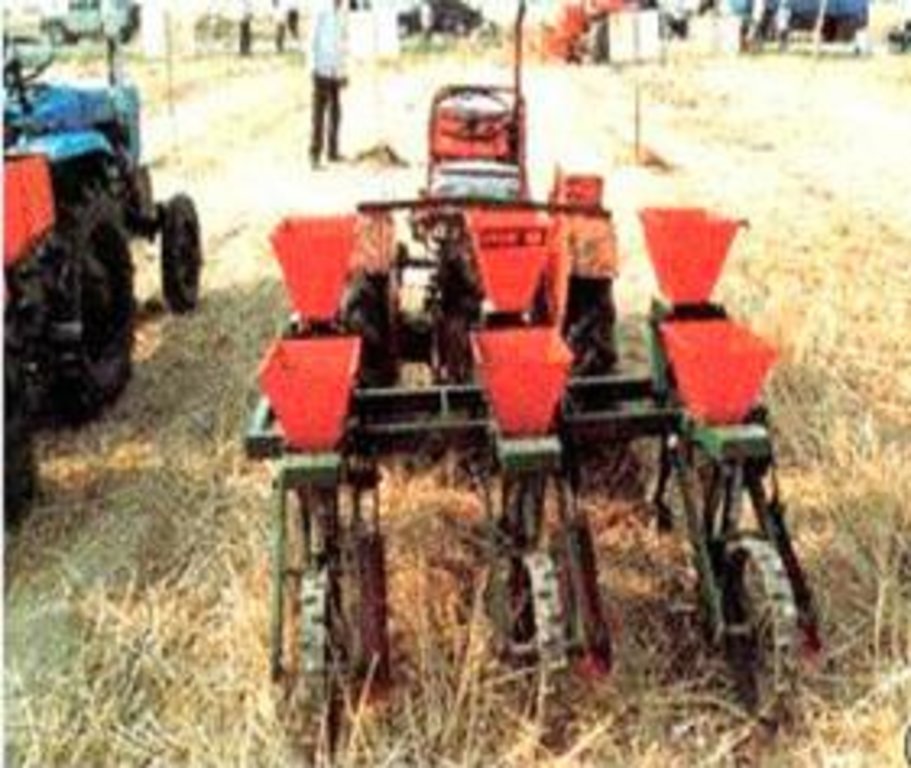
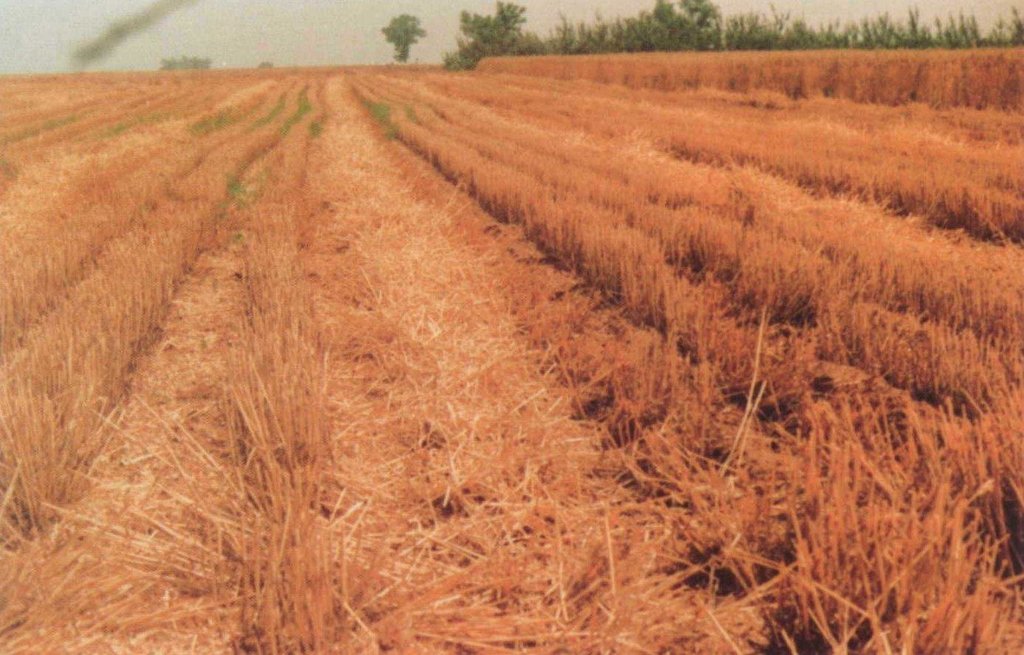
Zero Tillage [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Zhanguo Bai
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Laura Ebneter
approaches_2411 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Wang Deshui
(8610) 68918672
Institute of Soil & Fertilizer, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS)
12 zhong guan cun south street, Beijing 100081, P.R. of China
中国
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institute of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) - 中国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考

No-till agriculture [匈牙利]
No-till agriculture replaces conventional soil tillage in order to reduce costs and labour - and to provide a mulch layer on the soil surface from the residues of the previous crop: this protects the soil surface and its ecology.
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó
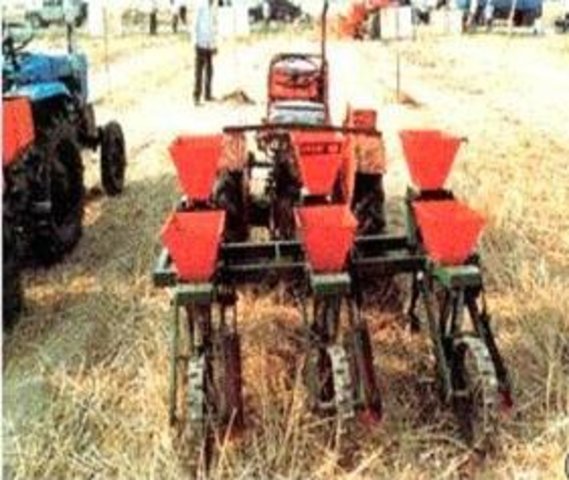

Zero Tillage [中国]
Zero tillage technology was developed to protect the soils from sealing rainfall, to achieve and maintain a open internal soil structure, to enhance biological processes in the soil, and to develop a means for safe disposal of any surface runoff that nevertheless will occur.
- 编制者: Zhanguo Bai
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Zero tillage approach was developed to protect the soils from sealing rainfall, to achieve and maintain a open internal soil structure, to enhance biological processes in the soil, and to develop a means for safe disposal of any surface runoff that nevertheless will occur.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Sustainable agriculture in the dry and semidry regions in the north China, especially on the slope farmland is searching always based on the ecological balance. Conservative tillage such as zero, reduced and subsoiling tillage are important to keep soil fertility. Mulching is also a way to improve the soil organic matter. So no tillage with mulching is an approach to do this. No tillage lets all rainfall in the soils and avoid runoff occur.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Henan province
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
1995
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2003
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Reduction of dust devil that occur in North China.)
The main objectives of the approach is to apply conservation tillage for sustainable agricultural development.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Traditional tillage (multi-till) with little return of organic matters to soils results in soil fertility decline and nutrient loss as well as yield decrease. This approach is designed to change the traditional cultivation ways to conservation tillage.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
buying no till machine and tractor
Treatment through the SLM Approach: subsidy and adjust crop planting pattern
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: Because land ownership belongs to state and land users can only lease land.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
organizing subdivided householders together
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Work equally divided between men and women (experimental areas selected on the basis of the landforms, contributed to diff, households). Householders organized by local committee or by implementation
- SLM专家/农业顾问
- 教师/学龄儿童/学生
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 被动 | Mainly:interviews/questionnaires; partly: public meetings; Generally local and/or village committee call land users who involved in the SWC project together and illustrate the purpose and obligation. |
| 计划 | 外部支持 | rapid/participatory rural appraisal; Detailed planning are addressed to whose who take part in the activities. |
| 实施 | 互动 | responsibility for minor steps; Each step and procedures are guided and checked for implementation. |
| 监测/评估 | 被动 | measurements/observations; Mainly done by the researchers and local government staffs not by local land users. |
| Research | 互动 | on-station; The effect and impacts of the SWC technology on the soil and environment are investigated and studied on experimental station and on farm. |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 政治家和领袖
解释:
Decisions on the choice of SLM Technology were made directive (top-down).
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users.
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- SWC specialists, extensionists/trainers
培训形式:
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
- 课程
涵盖的主题:
Teaching them how to operate tractor/tillage with mulching residuals and fertilizing as well as seeding; to understand the importance of the roles of the SWC etc.
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: In situ demonstration and training; Key elements: Demonstration, Training, farmer visit; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system, projects own extension structure and agents 2) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system, projects own extension structure and agents; Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: Demonstration, training
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Top-down agricultural/SWC technology extension service system has been established at variable government levels, they have capability of extension all kinds of the new techniques.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,非常
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 财务
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored through measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements
land users involved aspects were regular monitored through observations
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 生态学
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
The successful results of the SWC study obtained by the SWC approach are widely applied to the control of the dust devil, and ecological recover. Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 100,000-1,000,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s) (National - Central government): 30.0%; government: 60.0%; international: 5.0%; other: 5.0%
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 机械 | 部分融资 | |
- 农业
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 化肥 | 部分融资 | |
- 基建
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| community infrastructure | 部分融资 | |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
注释:
Labour was voluntary, paid in cash and rewarded with other material support.
In the past (before 1980's), SWC activities are mainly done by community members through obligation. Nowadays under the conditions of economic market, people unwill to do this voluntary, they concern return of their input for SWC.
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
是
对条件(利率、回报等)进行具体说明:
Interest rate charged: 2.3%; repayment conditions: After 2 to 5 years when SWC produces benefits, loaner should repay.
Interest was lower than market rate.
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Soil & water loss reduced much and soil fertility is greatly improved with increase in yield.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Subdivision and lease of the land would hinder SWC implementation. The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. Farmers worry that their land would transfer to others, well organizing could reduce the negative impact through prolong the lease period of land use.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Raising yield and soil moisture as well as fertility. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Leaving high residual straw and cover soil surface.) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Practical (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Financial support from various government) |
| Very welcome by farmers. Great economic and ecological benefits (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: enlarging extension) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Shortage of finance | Raising money |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Hard to widely extension due to expensive tillage machinery | Government should financially support |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Report of ninth-Five plan project on Dryland Farming, Jan 2002,
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
internal reference
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Introduction of Luoayng physicography
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
unpublished materials
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
No-till farming for sustainable rural development, 2002
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
World Bank
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
A road map from conventional to no-till farming, 2002
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
World Bank
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Conservation agriculture, 2001
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
FAO
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

No-till agriculture [匈牙利]
No-till agriculture replaces conventional soil tillage in order to reduce costs and labour - and to provide a mulch layer on the soil surface from the residues of the previous crop: this protects the soil surface and its ecology.
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó

Zero Tillage [中国]
Zero tillage technology was developed to protect the soils from sealing rainfall, to achieve and maintain a open internal soil structure, to enhance biological processes in the soil, and to develop a means for safe disposal of any surface runoff that nevertheless will occur.
- 编制者: Zhanguo Bai
模块
无模块