Integrated Land Use Plans for Municipalities in Georgia [乔治亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Daniel Zollner
- 编辑者: Anneliese Fuchs, Michael Huber
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Integrated Land Use Plans for Georgia
approaches_5897 - 乔治亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Zumbulidze Maia
REC Caucasus
13, Badri Shoshitaishvili Street D. Arakishvili 1st dead-end 0179 Tbilisi, Georgia
乔治亚
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia (GREENLANDS)有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Global Environment Facility Georgia (GEF Georgia) - 乔治亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
14/11/2019
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Under the framework of the project ‘Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia’, four Integrated Land Use Plans (ILUPs) were developed to support sustainable agriculture and rural development in the Georgian municipalities of Gori, Kareli, Kvareli and Sagarejo. The objective of the ILUPs is to provide strategic guidelines for decision makers and authorities for the spatial development of agriculture at the landscape unit level over the period of 2021 to 2030.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
The project ‘Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia’, financed by the Global Environment Facility (GEF) and implemented by the Regional Environmental Center (REC) for the Caucasus, aims to develop new sustainable land management (SLM) systems at both the commune and farmer plot levels, that integrate climate-smart agricultural production, food security and resilience and thereby contribute to Georgia’s objectives for Land Degradation Neutrality.
This WOCAT-based approach describes the development of four Integrated Land Use Plans (ILUPs) for sustainable agriculture and rural development in the municipalities of Gori, Kareli, Kvareli and Sagarejo (each 1000-2500km2).
The objective of the ILUPs is to provide strategic guidelines for decision makers and authorities for the spatial development of agriculture in the four municipalities for the period from 2021 to 2030 at the landscape level. This takes into consideration the balance of nature and human needs, and integrates different sectors and perspectives in the plan. This is to create synergies on the one hand, and to avoid conflicting goals on the other. Special attention is paid to the complex interactions between agriculture, climate change and land degradation. Thus, the ILUPs aim to develop and strengthen Sustainable Land Management (SLM) practices, Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) and Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) and to provide different options for further development. Above all, the plans aim to bring together relevant aspects from existing strategies and policies with local needs and ideas and link them at the spatial level as far as possible.
The ILUP project was implemented between the years 2019 and 2021. The development of the plan needs different approaches and methods - including literature research, statistical data evaluation, field mission, GIS analysis, and suitability assessment. With inception and field visits, workshops with the municipal LDN working group, interviews with farmers, and analyses of different base maps, the land use, the suitability for their development options, and the degradation risks of the area were identified and reflected step by step. The intersection and aggregation of the data led to the definition of the following main basic functional units:
- High Production Value (HPV) Farmland (for perennials, annual cropland and grassland)
- High Nature Value (HNV) Farmland
- High Social Value (HSV) Farmland and, as a specific output,
- Hot Spots of degradation (water erosion, wind erosion, and salinization).
The results were documented in a sectoral, technical plan for each municipality. The ILUP is intended to serve as a basis for further planning, capacity building and decision making procedures within the framework of legal responsibilities and requirements (e. g. for the municipal spatial plan). A second document (also recorded under WOCAT) is based on the outcome of this showcase and predominantly focuses on LDN implementation options by the application and adoption of various SLM and CSA practices.
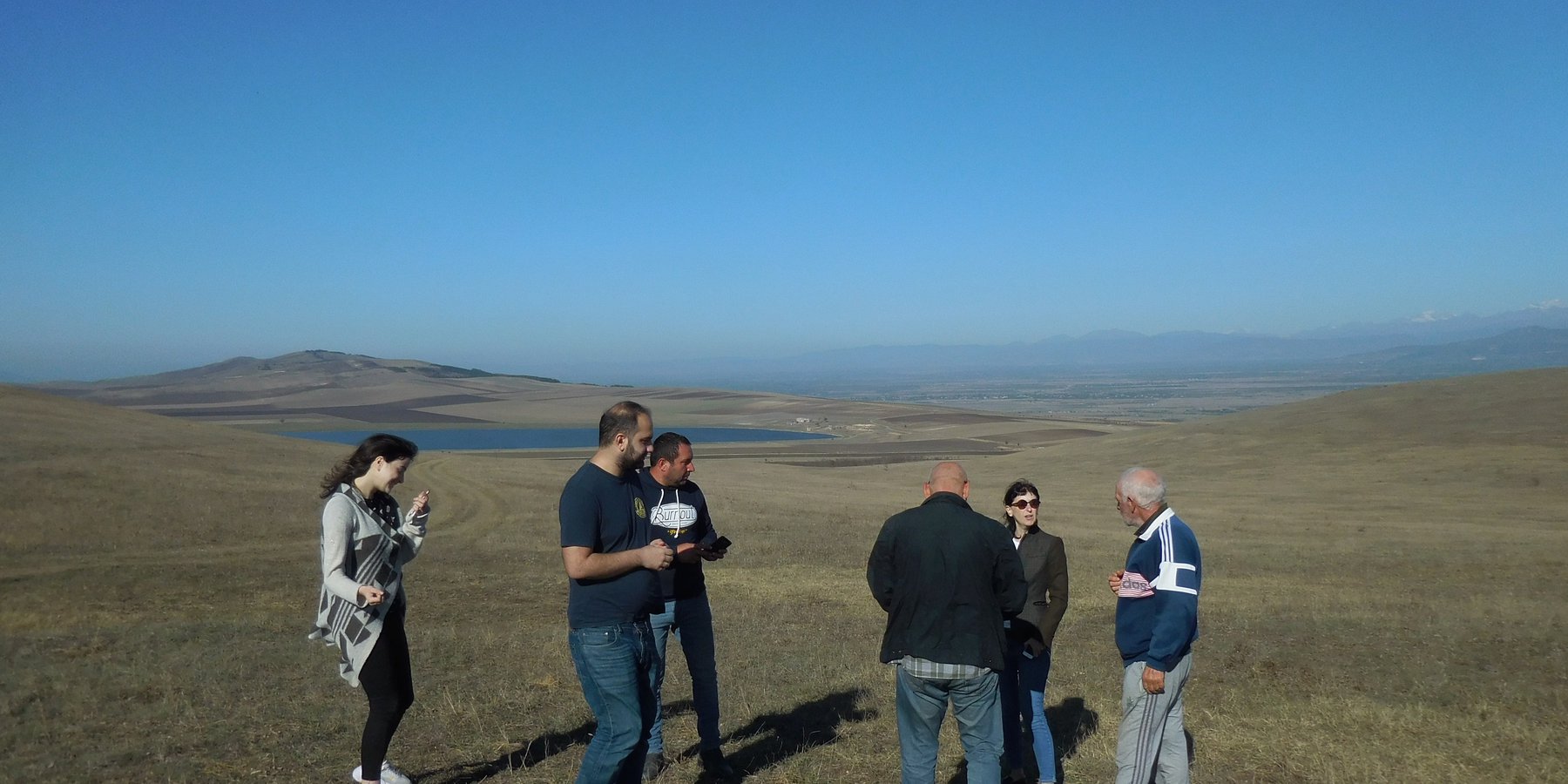
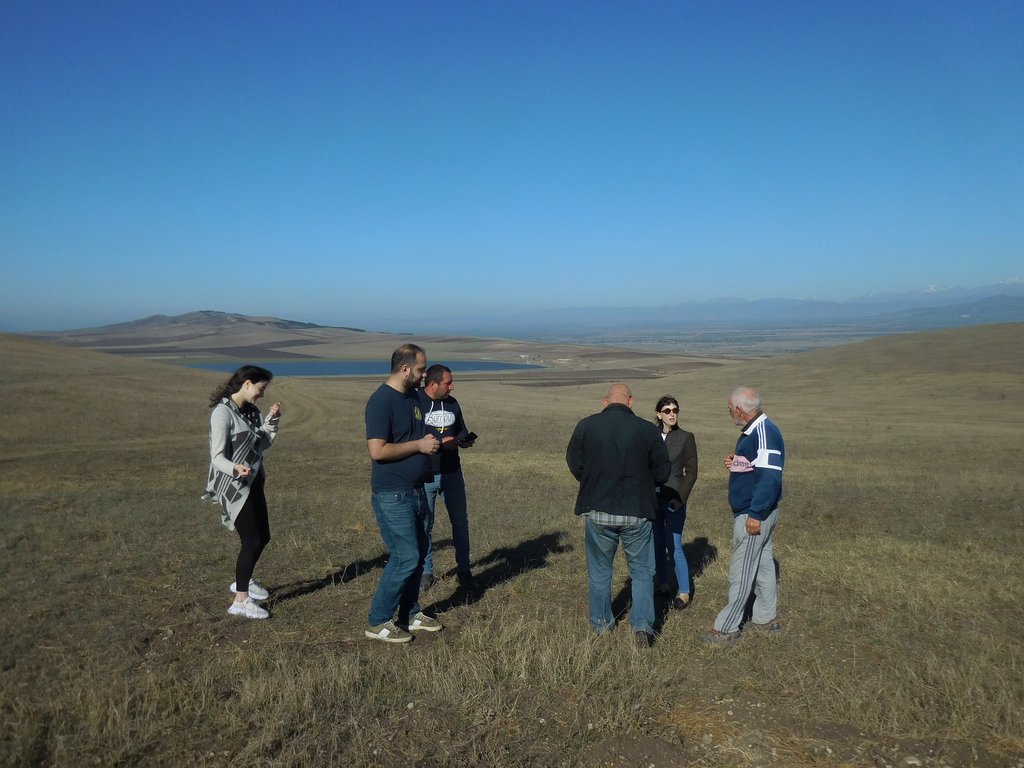
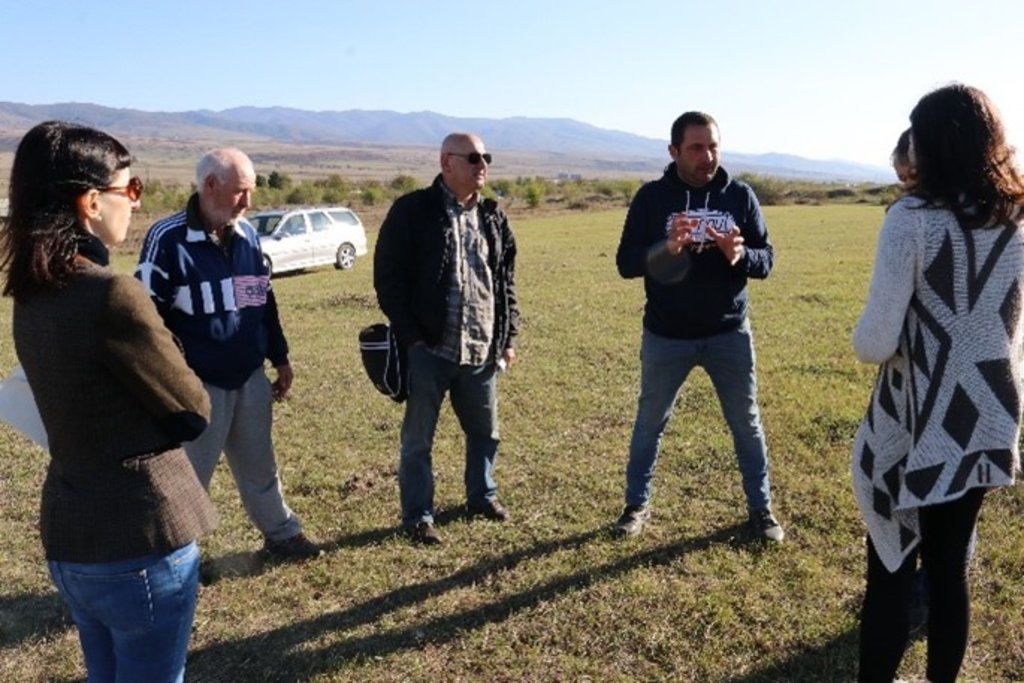
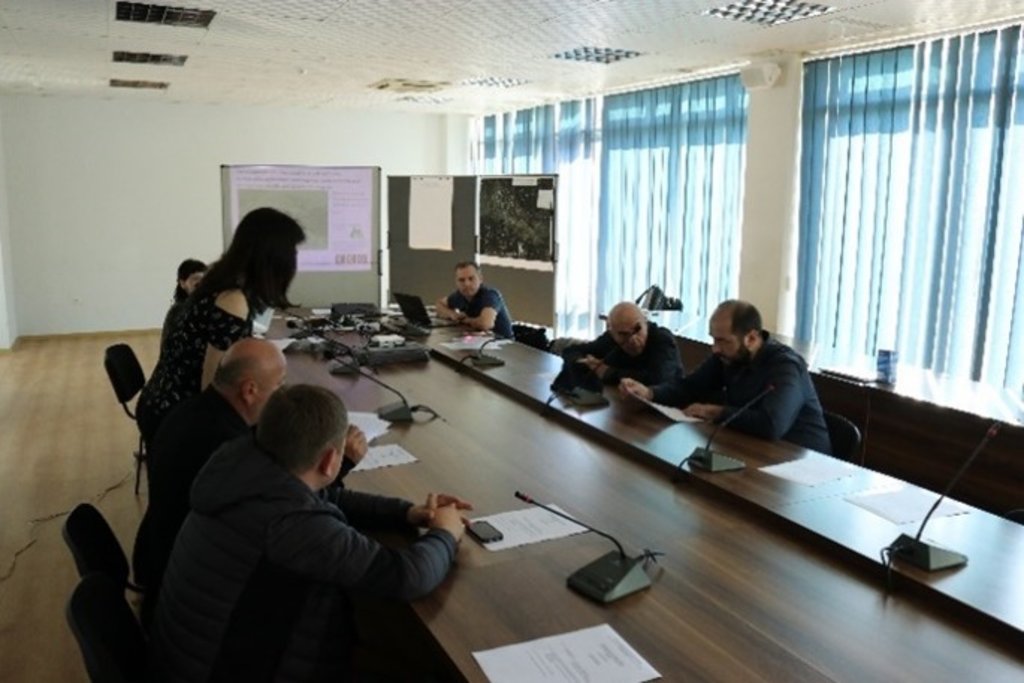
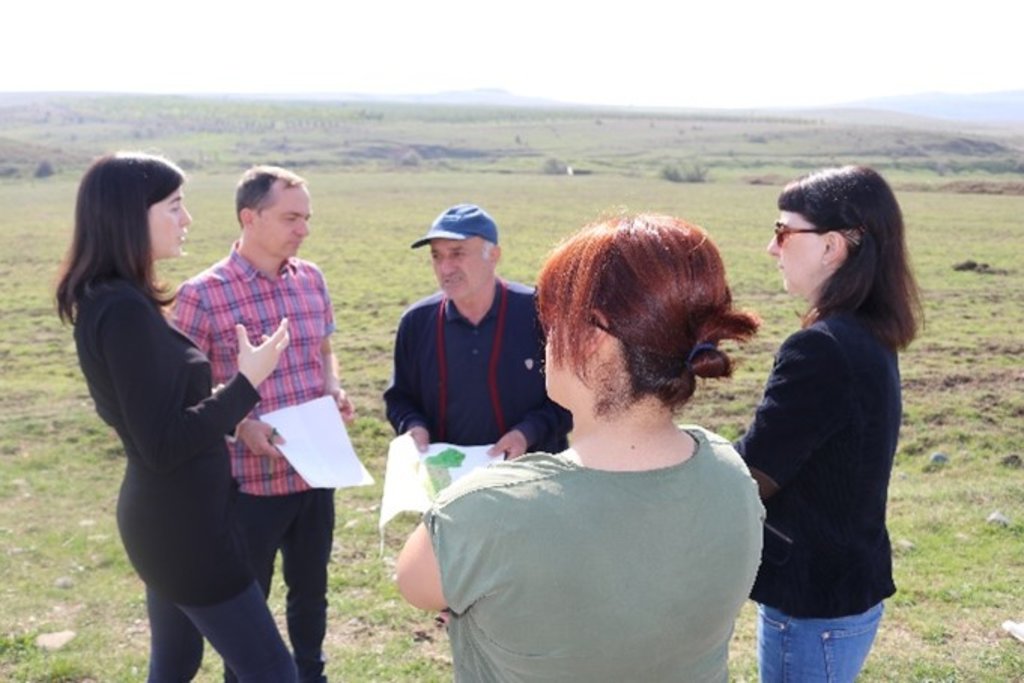
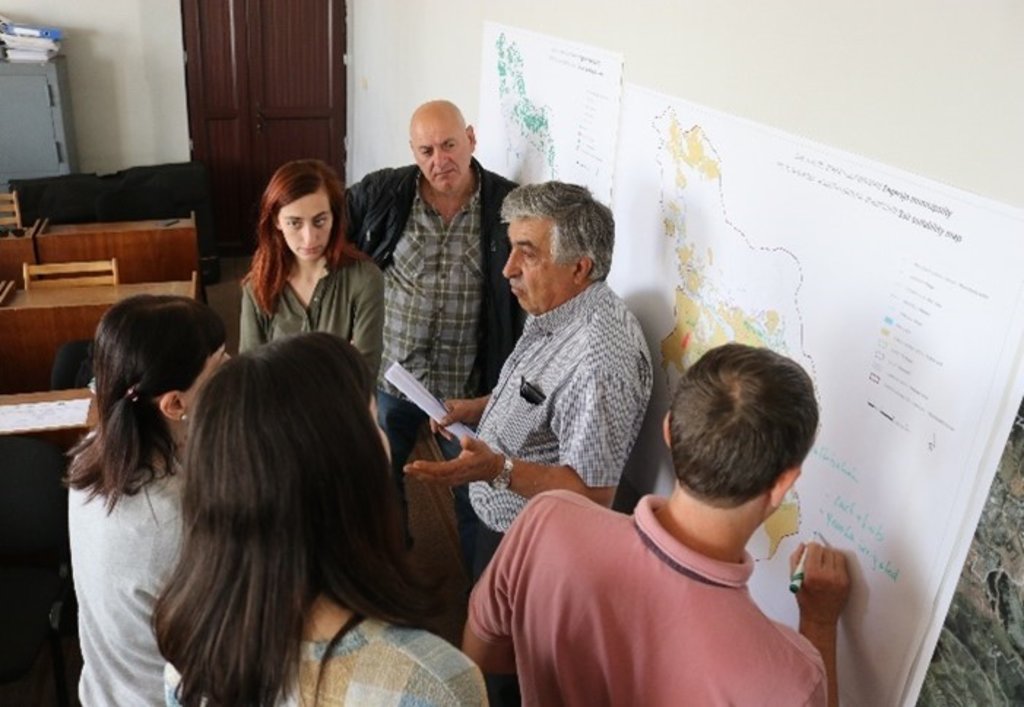
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乔治亚
区域/州/省:
Shida Kartli and Kakheti
有关地点的进一步说明:
Gori, Kareli, Kvareli, Sagarejo
注释:
The points are located within the four municipalities of Gori, Kareli, Kvareli and Sagarejo. The land use plan was prepared for the entire territory of the four municipalities.
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2019
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2021
注释:
ILUPs as basic planning documents were finished in June 2021. However, there is a next phase needed in order to include local stakeholders, national experts and farmers more intensively for implementation on plot level.
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The objective of the ILUPs is to provide strategic guidelines for decision makers and authorities for the spatial development of sustainable agriculture in the four municipalities for the period from 2021 to 2030 at the landscape level. It takes into consideration the balance of nature and human needs and integrates different sectors and perspectives in the plan. This is to create synergies on the one hand and to avoid conflicting goals on the other.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 启动
basically, awareness of the necessity to use the land in a sustainable manner exists
- 阻碍
historically conditioned reservation
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 启动
a few international financing tools are existing (GEF, GCF, etc)
- 阻碍
holistic, transsectoral, and adaptive financing mechanisms restricted
机构设置
- 启动
agricultural experts at the local level
- 阻碍
lack of education possibilities
参与者的的协作/协调
- 启动
- permanent working groups existing (LDN working groups, ministerial working groups etc.)
- active actors in the region
- 阻碍
continuing lack of cooperation
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
legal framework has been established recently
- 阻碍
lack of land registration
政策
- 启动
abundant framework documents existing
- 阻碍
implementation of the policies is the challenge
土地治理(决策、实施和执行)
- 启动
recently re-structured administrative entities (is a potential in the long run)
- 阻碍
recently re-structured administrative entities (phase of change)
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 启动
national service provider existing
- 阻碍
lack of knowldege and capacity
市场(购买投入,销售产品)和价格
- 启动
adjacent urban areas
- 阻碍
- high economic pressure on the world market
- low income level in the regions
工作量、人力资源可用性
- 阻碍
demographic change
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
various farmers
visits to the fields with the local farmers, discussions about the type of cultivation, specific needs and ideas
- 研究人员
Tbilisi State University
Scientific expertise on land use and soil productivity
- NGO
REC Caucasus
Supervisors, consultants, GIS analyses, participation in the LDN Working Group Meeting
- 地方政府
- Executive Office of the Gori Municipal Council
- City Hall (formerly Municipal Administration“Gamgeoba”), Municipality of Gori
- City Hall (formerly Municipal Administration“Gamgeoba”), Municipality of Kareli
- City Hall (formerly Municipal Administration“Gamgeoba”), Municipality of Kvareli
- City Hall (formerly Municipal Administration“Gamgeoba”), Municipality of Sagarejo
Participation in the LDN Working Group Meeting
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- Ministry of Environmental Protection and Agriculture of Georgia (MEPA)
- Agricultural and Rural Development Agency (ARDA)
Participation in the LDN Working Group Meeting, process steering and embedment into national policies
- 国际组织
UNEP
Steering of the whole GEF project (with the ILUPs as one component of it)
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 无 | |
| 计划 | 被动 | Local land users were consulted to gain experience and insight into the situation of agriculture in the different areas. The interviews were then incorporated into the preparation of the maps and land use plans. |
| 实施 | 互动 | - during the inception mission - in the course of the interactive ILUP workshops |
| 监测/评估 | 外部支持 | - supervision and critical reflection by experts and the client - presentation and reflection at the GEF project steering commitee meeting (about 30 persons - decision makers from different policy levels, national and international experts, project manager etc.) |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
The ILUP provides several options to use SLM technologies: the final decision will take place in a next step. Some specific technologies and actions (no-tillage, windbreaks..) are currently implemented.
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
否
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
否
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,适度
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
说明机构、角色和职责、成员等。:
Representatives of the municipalities - regional expertise, practical implementation, embedded into local policies.
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
提供进一步细节:
Discussions and workshops to contribute to a better common understanding and transsectoral learning from each other.
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
否
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
否
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 10,000-100,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Global Environmental Facility (GEF), in the frame of the project: Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
如果是,请具体说明支持的类型、条件和提供者:
Different sources and options of support are recommended in the ILUPS, but needs to be decided.
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
5.5 其它激励或手段
是否有其他激励措施或工具用于促进SLM技术的实施?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否有助于当地土地使用者,提高利益相关者的参与度?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
- integration of local decision maker was core part of the planning procedure - more empowerment of land users planned for the detailed planning phase
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The ILUP is designed to be the fundamental basis for any kind of SLM technologies
该方法是否提高了SLM的协调性和成本效益?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The whole plan is dedicated to coordinate approaches and implementations
该方法是否提高了土地使用者实施土地管理的知识和能力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Little in the process of elaboration, but will improve significantly in the course of implementation
该方法是否提高了其他利益相关者的知识和能力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Little in the process of elaboration, but will improve significantly in the course of implementation
该方法是否缓解了冲突?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The whole plan is designed to mitigate land use conflicts
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
A large proportion of the approach is dedicated to small farmers
该方法是否改善了性别平等并赋予女性权力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The gender aspect is integrated into the plan, but needs implementation
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The approach underlined the necessity of land registration
The plan is designed to improve food security
The plan is designed to improve the development of new markets resp. the access of existing markets
该方法是否带来了更可持续的能源使用?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Some components are dealing with energy topics.
该方法是否提高了土地使用者适应气候变化/极端情况和减轻气候相关灾害的能力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Little in the process of elaboration, but will improve significantly in the course of implementation
该方法是否会带来就业、收入机会?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Little in the process of elaboration, but should improve significantly in the course of implementation
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加生产
- 增加利润(能力),提高成本效益比
- 减少土地退化
- 降低灾害风险
- 环境意识
- 提高SLM知识和技能
- 冲突缓解
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 否
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
The approach needs embedding into local governance structures
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| clear overview of land suitability |
| diversification options |
| set of proposed measures and actions |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| fundamental for strategic and coordinated development, practical framework for implementation |
| stringent target system, compiled at different levels |
| integrated development approach, combining all dimensions of sustainability |
| core tool to adapt to and mitigate climate change |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| plan might raise expectations and an "atmosphere of departure", that cannot be fullfilled in due time |
- consistent and timely implementation of proposed measures - acquisition of financial resources - strengthening local structures and participation |
| plan will not enter next phases, thus implementation might get stuck and/or will not meet the needs on plot level fully | Consistent and timely implementation of the proposed next steps (review process, detailed planning, embedding into municipal land use planning system) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Risk that further planning process gets stuck and/or lacks participation |
- intensive land user involvement - cross-sectoral participation - detailed (process) planning (at plot level) |
| Risk of weak implementation because of lack of framework conditions |
- further land registration needed - detailed planning needed (next phase) - according financing mechanisms needed - embedding into communal planning environment |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
4 local workshops
- 与土地使用者的访谈
about 5 interviews
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
- one scientific expert
- several representatives from the steering commitee of the project
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
About 50 reports and documents
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Zollner, D., Zumbulidze, M., Kirchmeir, H., Fuchs, A. und Huber, M. 2021: Gori Integrated Land Use Plan (ILUP Gori) for sustainable agriculture and rural development with special emphasis on SLM, CSA and LDN. Part A – ILUP Gori. Version 2.0. Klagenfurt, Tbilisi, Gori. 80 p. + documentation volume/ annex.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
REC Caucasus, E.C.O- Institute of Ecology
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Zollner, D., Zumbulidze, M., Kirchmeir, H., Fuchs, A. und Huber, M. 2021: Kareli Integrated Land Use Plan (ILUP Gori) for sustainable agriculture and rural development with special emphasis on SLM, CSA and LDN. Part A – ILUP Gori. Version 2.0. Klagenfurt, Tbilisi, Gori. 80 p. + documentation volume/ annex.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
REC Caucasus, E.C.O- Institute of Ecology
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Zollner, D., Zumbulidze, M., Kirchmeir, H., Fuchs, A. und Huber, M. 2021: Kvareli Integrated Land Use Plan (ILUP Gori) for sustainable agriculture and rural development with special emphasis on SLM, CSA and LDN. Part A – ILUP Gori. Version 2.0. Klagenfurt, Tbilisi, Gori. 80 p. + documentation volume/ annex.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
REC Caucasus, E.C.O- Institute of Ecology
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Zollner, D., Zumbulidze, M., Kirchmeir, H., Fuchs, A. und Huber, M. 2021: Sagarejo Integrated Land Use Plan (ILUP Gori) for sustainable agriculture and rural development with special emphasis on SLM, CSA and LDN. Part A – ILUP Gori. Version 2.0. Klagenfurt, Tbilisi, Gori. 80 p. + documentation volume/ annex.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
REC Caucasus, E.C.O- Institute of Ecology
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块