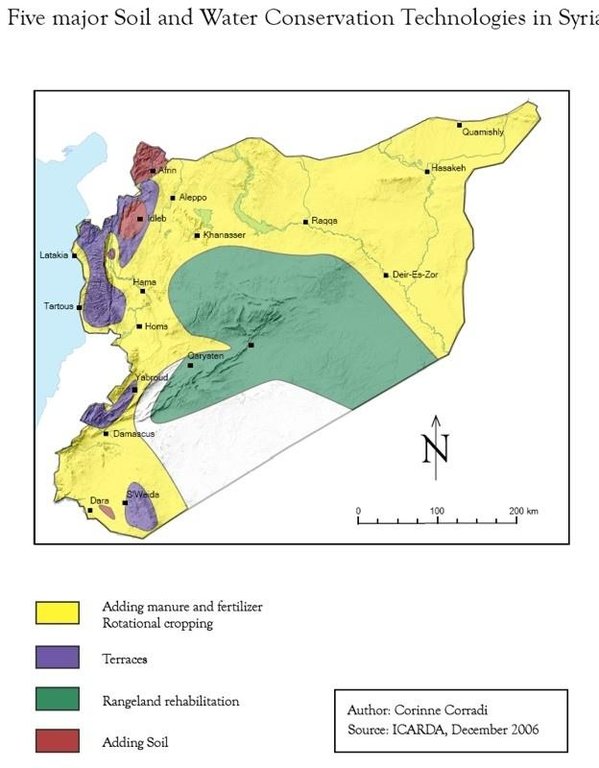
Adding Soil [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Liesbeth Colen
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Taghir al Turbe (arabic), akhelete (kurdish)
technologies_1004 - 阿拉伯叙利亚共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/12/2006
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Adding soil [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
没有可用的描述。
- 编制者: Liesbeth Colen
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
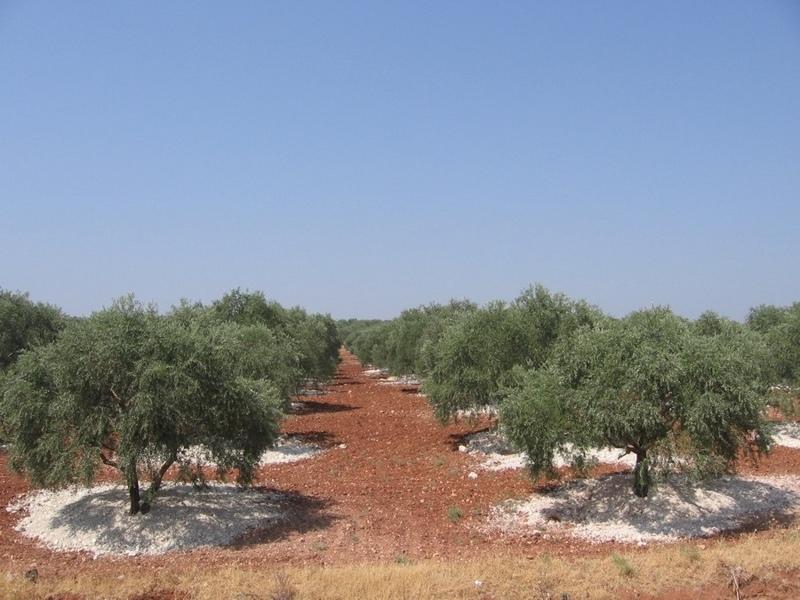
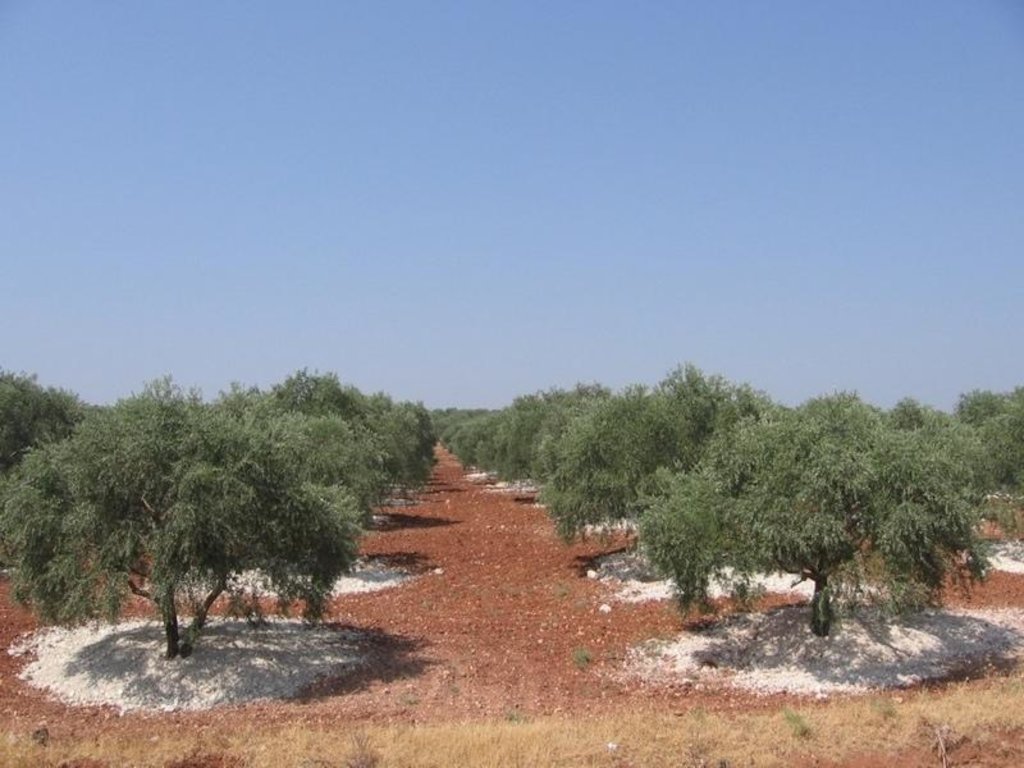
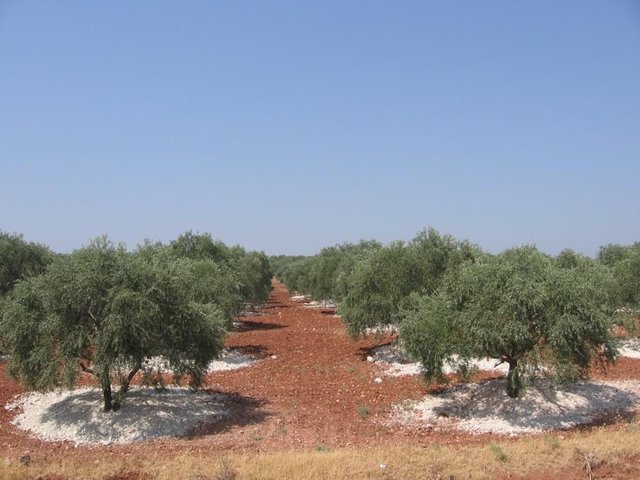
To add red (fertile, nutrient rich) valley soil to degraded white soil on slopes (in olive orchards)
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
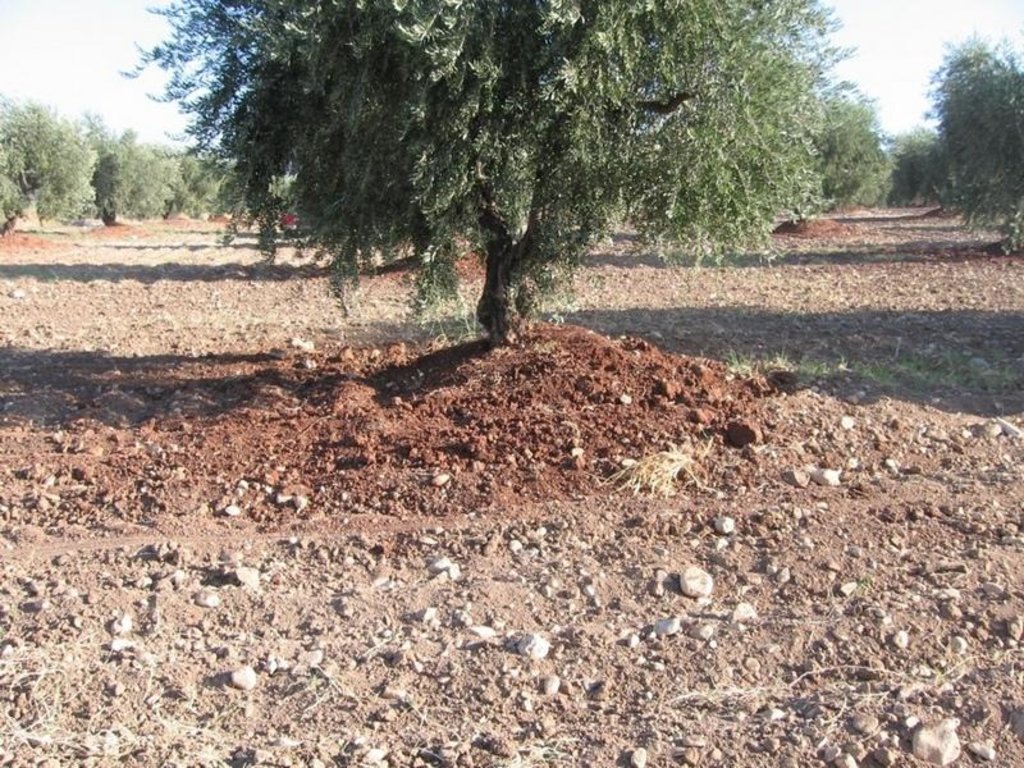
Red soil is taken from valley fields, mines and consruction work, transported to the slopes and added around the stem of each tree, ca. 2 m^3 per tree. Not done in the rainy season and only when there is soil available and spare time.
Purpose of the Technology: increase the soil depth and add nutrients in response to erosion and nutrient mining.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: every five to ten years depending on rainfall and slope.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿拉伯叙利亚共和国
区域/州/省:
Aleppo
有关地点的进一步说明:
Idleb, Affrin
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
Idleb (region around Harem), 70 km from Aleppo, West
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop tree and shrub cropping: Olives
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water erosion on hill slopes, poor soil quality (vulnerable to erosion and lack of nutrients), exageratet tillage in olive orchards
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): loss of top soil due to water erosion, poor soil quality, difficult to do contour tillage because of steep slopes
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.04 m2.
Idleb no information available, probably 1.5 times more than Affrin
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in soil fertility, adding new soil
Secondary technical functions: sediment harvesting
Mulching
Material/ species: red soil
Remarks: depends on point of view, protection for "old"soil from the newly added soil
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: red soil
Quantity/ density: 2m^3/tree
Remarks: new soil mixed with the old one increases nutrient
Structural measure: add
Spacing between structures (m): 6 -10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Construction material (earth): red soil
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0 - 25%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
syrian pounds
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
50.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging soil | 结构性的 | dry season |
| 2. | transport soil | 结构性的 | dry season |
| 3. | distributing soil | 结构性的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Transport | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 300.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging soil | 农业学的 | dry season / once |
| 2. | transport soil | 农业学的 | dry season / once |
| 3. | distributing soil | 农业学的 | once |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: trolley for transport, machine for digging
for one farmer
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour, distance, transport, probably in the future also value of soil
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Very low (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: High
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
25% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
25% of the land users are poor.
Level of mechanization: Mechanised (ranked 1, tillage) and manual work (ranked 2, harvesting)
Market orientation of production system: export (seasonal)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
20-50% (red on white:63%, white on red: 38%)
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Young roots are encouraged to grow in the new added pile, but there they are more susceptible for damage (ploughin/frost/heat/diseases)
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
In case soil is taken from good valley fields
收入和成本
经济差异
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
For white on red soil, increased sand content may result in better infiltration and reduces cracks of topsoil, increased moisture in subsoil reported by farmers
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Adding white soil adds high active CaCO3, which might decrease availabilty of cation nutrients
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Spreading of soil-borne diseases. Especially Vertcillium Wilt, also Verticillium Dahliae
其它生态影响
Topsoil temperature
注释/具体说明:
Adding white soil on red soil might reduce the temerature (less absorption of sunlight) and therefore the evaporation and also repell insects, but this has not been measured
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
Downfields will benefit if erosion is not stopped
地下水/河流污染
风力搬运沉积物
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: exponential adaption, probably related to the recent (from 2003/2005) increase for olive oil prices and increased construction work
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| fast increase in yield |
| reverse the effects of erosion |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
reverse the effects of erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? combine with other conservation technologies (stone bands etc.) |
|
soil that otherwise wouldn't be used can be used in this way How can they be sustained / enhanced? offer free transport of soil by government or other organisation |
| don't have to apply to the entire field, possibility to keep investment down |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| expensive for the entire field | not |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| it is not sustainable | combine with conservation strategies like terraces, bands, less tillage |
| soil born disease spreading | soil analysis before adding and if positive either apply quarantine and solarization or leave it |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil transfers in olive orchards of NS Syria, a bio-physical and socio-economic analysis of a local innovation. June 2007.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICD Bern
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Adding soil [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
没有可用的描述。
- 编制者: Liesbeth Colen
模块
无模块