Drainage Ditches in Steep Sloping Cropland [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Erik Bühlmann
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
technologies_1016 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - 吉尔吉斯斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
19/07/2005
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Drainage ditches are dug in steep cropland areas to reduce soil erosion by diverting excess rain water away.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
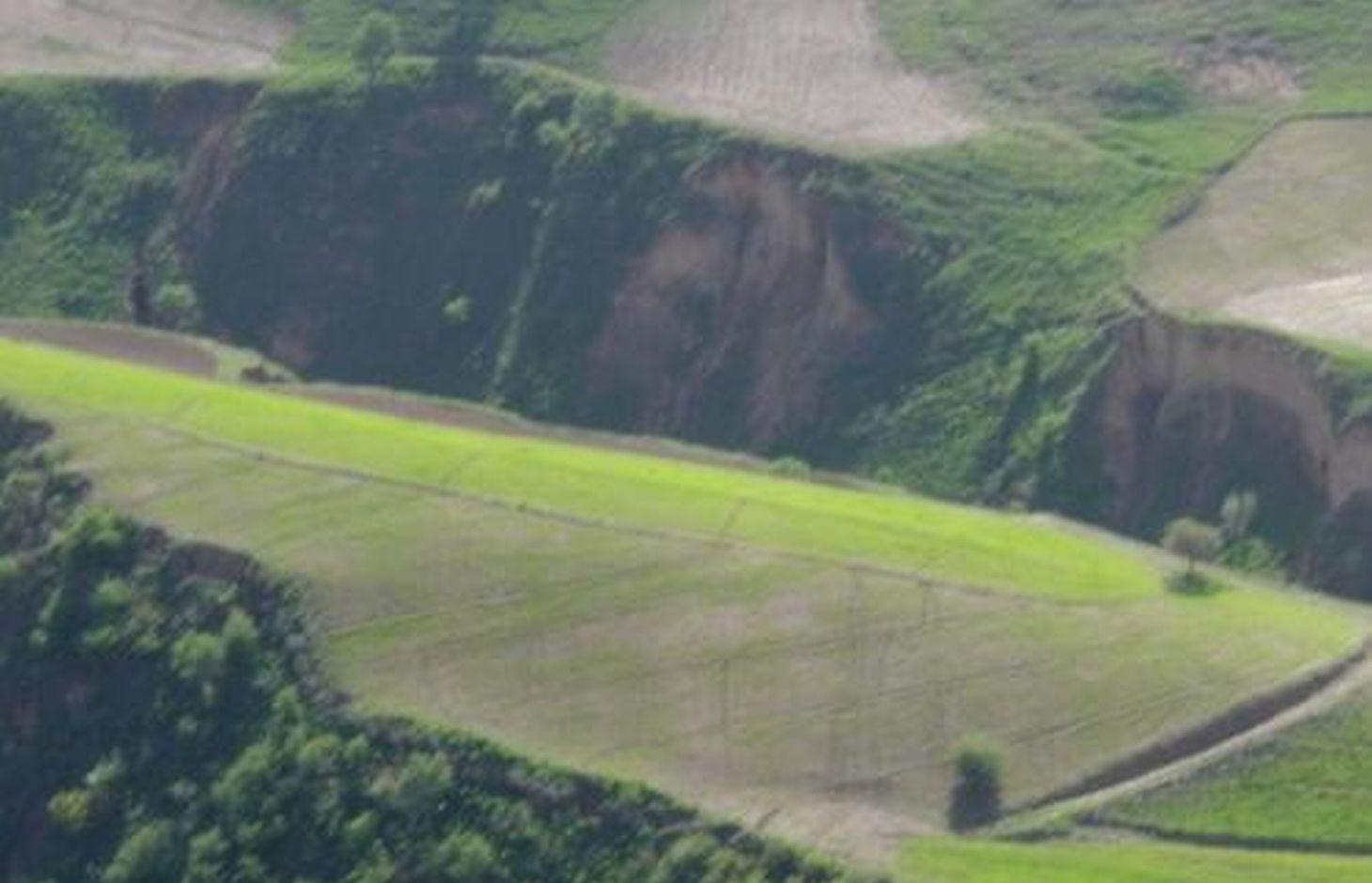
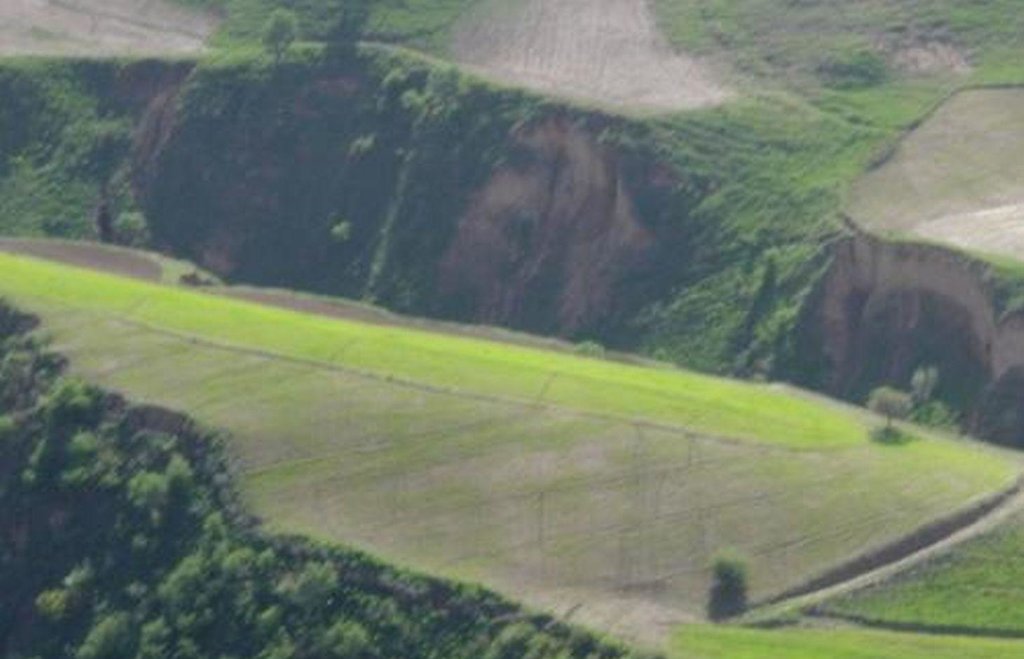
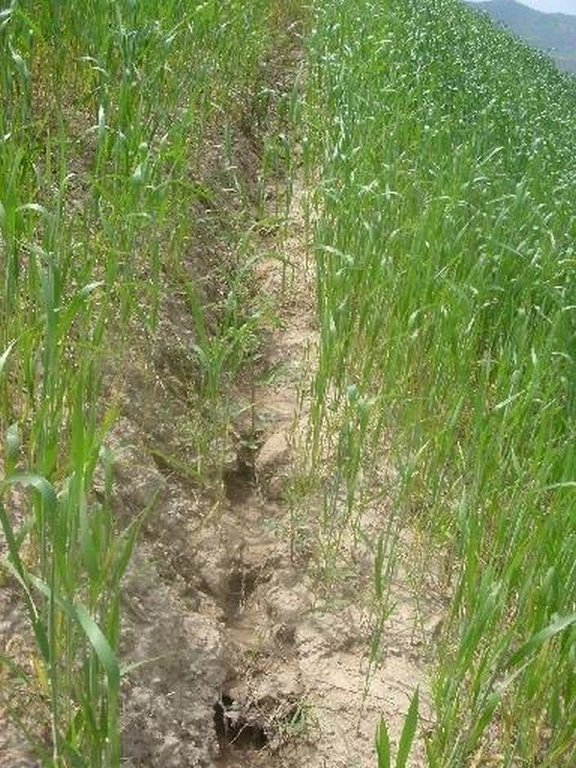
In steep wheat fields drainage ditches are dug at 5-10m intervals to help reduce soil erosion. The ditches are on average 15cm deep and 30cm wide, and are dug with a gradient of 10-20%, to facilitate the draining of excessive rain water. At the top of the field a 50x50cm cut-off drain prevents run-on onto the field.
The small drainage ditches in the field are dug each year after tillage and sowing activities. The earth removed from the diches is piled up below the ditch to decrease the risk them breaching. The cut-off drain at the top was established 5 years ago and is cleared regularly from washed in soil. Most farmers in Faizabad Rayon dig 1-3 drainage ditches in their sloping cropland. Drainage ditches and cut-off drains are often not constructed deep enough and are not well maintained. Construction of the technology is not time consuming or costly, however, drainage ditches and cut-off drains are completely ineffective if not maintained on a regular basis.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Labour input for this work does not exceed three person days per hectare.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
RRS
有关地点的进一步说明:
Faizabad Rayon
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
major cash crop: vegetables
major food crop: wheat
other: chickpeas, flax
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): severe water erosion (gullies and rills) and subsequent fertility decline on cropland and overgrazed pastures
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): fertility decline, soil erosion and downslope washing of seeds before sprouting
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Winter wheat (and sometimes chickpeas) are sown in the autumn, all other crops are cultivated in the spring. Harvesting takes place in July and August.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: March - August
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 引水和排水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 10-100 平方千米
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
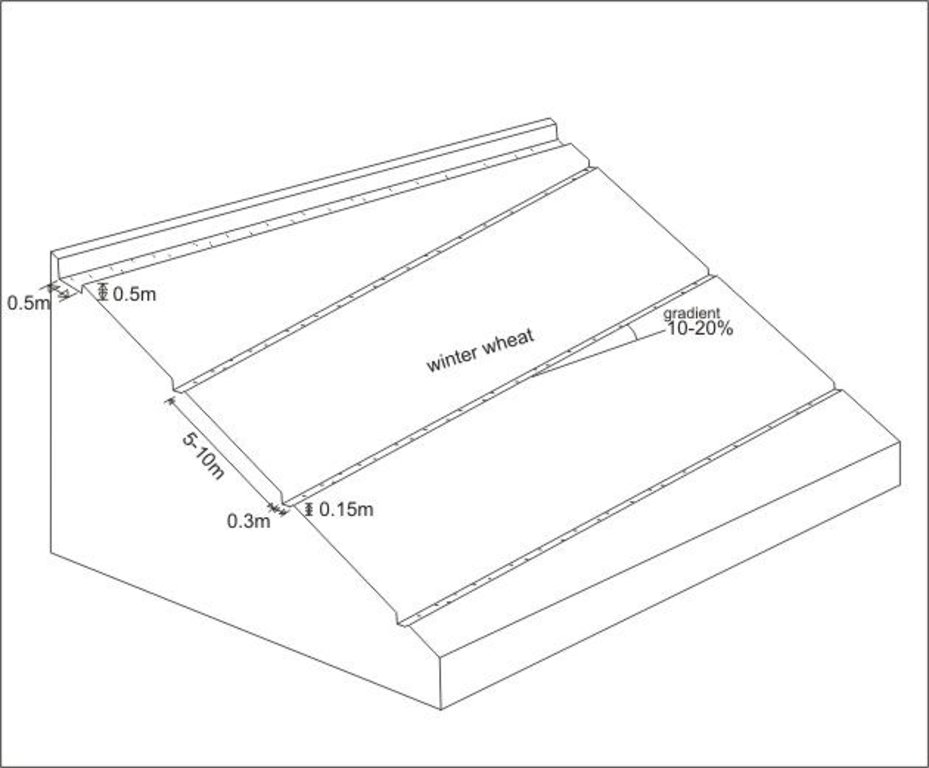
Graded drainage ditches in steep sloping cropland, cut-off drain at top of field to prevent runon
Location: Chinoro. Faizabad Rayon, RRS
Date: 10.07.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Agronomic measure: drainage ditches
Remarks: depth: 0.15m, width: 0.3m, intervals: 5-10m, gradient: 10-20%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Construction material (earth): earth with spade removed
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 40%
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging of cut-off drain | 结构性的 | spring |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | digging of cut-off drain | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 8.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging of drainage ditches | 农业学的 | after sowing of crops / annually |
| 2. | deepening and clearing | 农业学的 | rainy season / after every rainfall event |
| 3. | clearing of cut-off drain from washed in soil | 结构性的 | rainy season/after heavy rainfall events |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | digging of drainage ditches | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | deepening and clearing | ha | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 21.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: tool: spade
Per hectare of cropland; maintainance activities for drainage ditches and cut-off drain after every heavy rainfall (twice a week over 3 months, based on an average of one hour of work per time)
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
growing period between 180-210 days
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: Also 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Also mountain slopes
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: low - high
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium - good
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
5% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In general, all farmers (including those applying SWC technologies) are highly dependent on off-farm income which in most cases is earned in Russia either by themselves or by their relatives.
Level of mechanization: ploughing is carried out by tractor whenever possible an therefore mechanized/ motorized is also existent in this area.
Market orientation of production system subsistence (self-supply): Subsistence, only surplus crops are sold
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology aslo: 0.5-1 ha
Furthermore: Households are depending on available working force, labour is limiting factor
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 租赁
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产区域
土地管理
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤流失
其它生态影响
soil fertility
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
NA
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Increasingly, farmers have to cope with fertility decline of their cropland; one of the first measures they take is the establishment of drainage ditches. However, most farmers implement only a few drainage ditches without maintaining them in an appropriate way.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| reduces soil erosion |
| reduces fertility decline |
| low cost |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Require only a small cost for establishment and maintainance. |
| effectively prevents development of large rills and therefore reduces soil erosion |
| Has the potential to reduce the deline in fertility of the soil |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| requires regular checking | |
| cause a lot of damage, if they collapse |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| technology ineffective if not maintained on a regular basis | deepening and clearing after every rainfall event |
| does not prevent development of small rills and hence does not stop all erosion | small intervalls between drainage ditches reduce soil erosion more effectively. Combining this technology with other measures (grass strips, agroforestry etc.) is advisable |
| if the drainage ditches collapse, they cause a lot of damage to the cropland | appropriate management reduces the risk of braking |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块