Conservation tillage [匈牙利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Ádám Kertész
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
talajkímélö földmüvelés (Hungarian)
technologies_1080 - 匈牙利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Csepinszky Béla
00361-3092686
Geographical Research Institute, Hungarian Academy of Sciences
H-1112 Budapest Budaörsi út 45.
匈牙利
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Geographical Research Institute, Hungarian Academy of Sciences (MTA CSFK) - 匈牙利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
18/10/2004
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Conservation tillage [匈牙利]
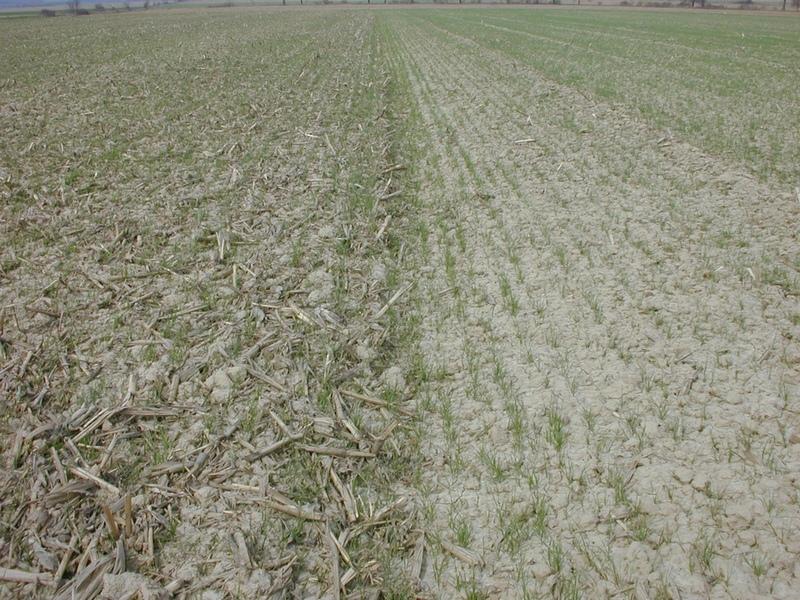
Non inversion, conservation (soil and water protective) tillage.
- 编制者: Adam Kertesz
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Non inversion, conservation (soil and water protective) tillage.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
According to our understanding conventional agriculture is based on tillage and it is highly mechanised. Conventional agriculture causes severe land degradation problems including soil erosion and pollution as well as other environmental damages like biodiversity and wildlife reduction, low energy efficiency and a contribution to global warming. Conservation Agriculture is a holistic approach to crop production, which encompasses "Conservation Tillage", and also seeks to preserve biodiversity in terms of both flora and fauna. Activities such as Integrated Crop, Weed, and Pest Management form part of Conservation Agriculture. The concept of "As little as possible, as much as is needed" will be the guiding principles for SOWAP in crop production, when it comes to chemical usage.
Purpose of the Technology: inding and Demonstrating Ways of Better Managing the Land. SOWAP (SOil and WAter Protection - supported by the EU LIFE Programme and by Syngenta) aims to assess the viability of a more "conservation-oriented" agriculture, where fewer tillage practices replace the numerous cultivations carried out under more "conventional" arable farming systems. The use of appropriate chemicals is tested, and their potential for off-site contamination assessed, to ensure that any suggested approaches are environmentally sound.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The SOWAP project started on study sites in Belgium, Czech Republik, Hungary and United Kingdom. I Hungary 3 sites were selected near Lake Balaton. One of them is Dióskál (2). There are 4 conservation and 4 conventional tilled plots, each between 3-5 Ha in size. The project has benn started in 2003.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
匈牙利
区域/州/省:
Zala county
有关地点的进一步说明:
Zala county, Zala-hills, Zala
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The technology came from England, nevetheless it is known among the Hungarian SWC specialists before.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
major cash crop: Maize
major food crop: Wheat
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Fine loess soil with significant soil degradation, soil compaction due to inconvenient land use
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): EU and government rules, problems of the subsidy system, sales and marketing concerns
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: maize, winter wheat, maize…
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 185; Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.2012 km2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: relay cropping, mulching, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, minimum tillage, contour tillage, breaking compacted subsoil
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Cp:土壤污染

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Cp: soil pollution
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (natural soil compaction)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Relay cropping
Material/ species: wheat, maize
Mulching
Material/ species: stem remains
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: NPK
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat/maize
Other type of management: change of cultivation method( (non inversion), changing the depth of cultivation
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Hungarian Forint HUF
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
195.8
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
25.50
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing (yearly) | 管理 | autumn |
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Minimum tillage | 农业学的 | spring and autumn / after harvest |
| 2. | non inversion, minimum tillage, shallow tillage | 管理 | autumn / 1x -2x |
| 3. | if needed loosening | 管理 | early autumn / only if needed |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
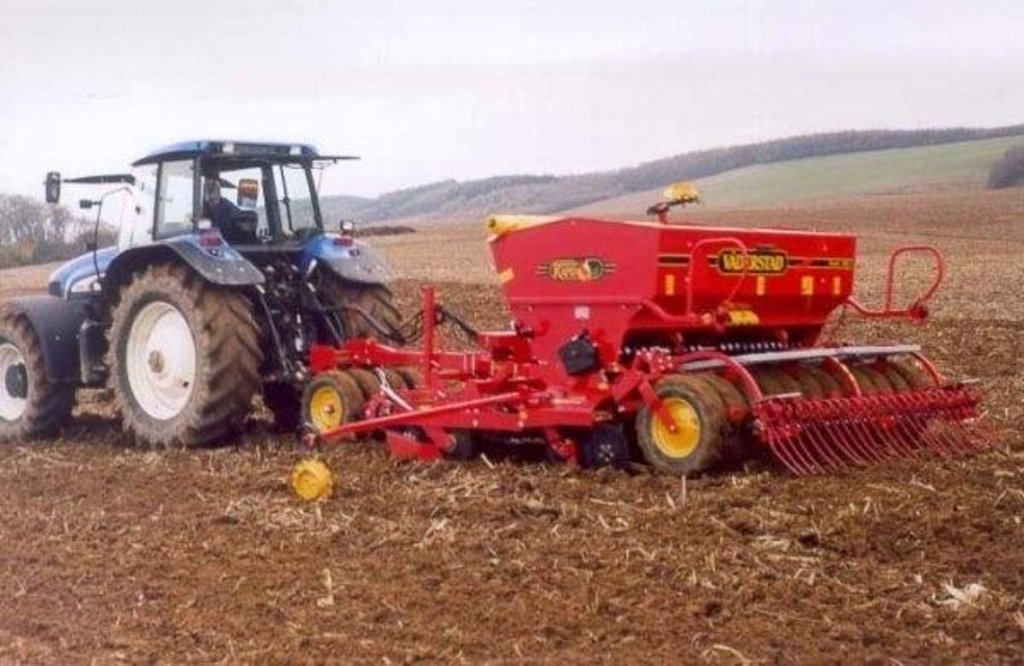
Machinery/ tools: powerful tractor, disk, direct drill, harvester, sprayer, cultivator
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
wet weather>get weedy; compacted soil surface>(loosening) chiselling
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
650.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: ~ 200 m
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium and sometimes high
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: They have no off-farm incomes.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Also 100-500 ha, 500-1,000 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
收入和成本
农业收入
其它社会经济效应
input contstraints
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
0.2
SLM之后的数量:
0
土壤有机物/地下C
其它生态影响
biodiversity
soil fertility
soil structure
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1 household
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| future subsidy expectations and better chance for competition |
| soil loss reduction |
| economicalness |
| environmental consciousness agriculture |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| soil loss reduction |
| biodiversity enhancement |
| spreading of environmental conscious agriculture |
| soil and water protection |
| economicalness |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| reduced production (yield) | |
| expensive machines |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Too many tools are required. Expensive machines. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
BIRKÁS, M., JOLÁNKAI, M., GYURICZA, CS., PERCZE, A. (2004): Tillage effects on compaction, earthworms and other soil quality indicators in Hungary.. 2004.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Soil & Tillage Research, Vol. 78. No. 2., pp. 185-196.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
HOLLAND, J.M. (2004): The environmental consequences of adopting conservation tillage in Europe: reviewing the evidence.. 2004.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, Vol. 103. No. 1., pp. 1-25.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
MANNINGER, G. A. (1957): A talaj sekély művelése.. 1957.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Mezőgazdasági Kiadó, Budapest, 135 p.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
BIRKÁS, M. (2002): Környezetkímélő és energiatakarékos talajművelés.. 2002.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SZIE, Mezőgazdasági és Környezettudományi Kar, Gödöllő, 345 p.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Talajkímélő művelés és környezetvédelem. 2003.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Gyakorlati Agrofórum Extra 3.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Conservation tillage [匈牙利]
Non inversion, conservation (soil and water protective) tillage.
- 编制者: Adam Kertesz
模块
无模块