Agro-forestry [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Kaadu, Vilai, Thottam (Tamil)
technologies_1083 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
27/02/2003
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Development of degraded lands through plantation of productive tree species for long term benefit (conservation and economic) and cultivation of intercrop for short term benefit.
2.2 技术的详细说明
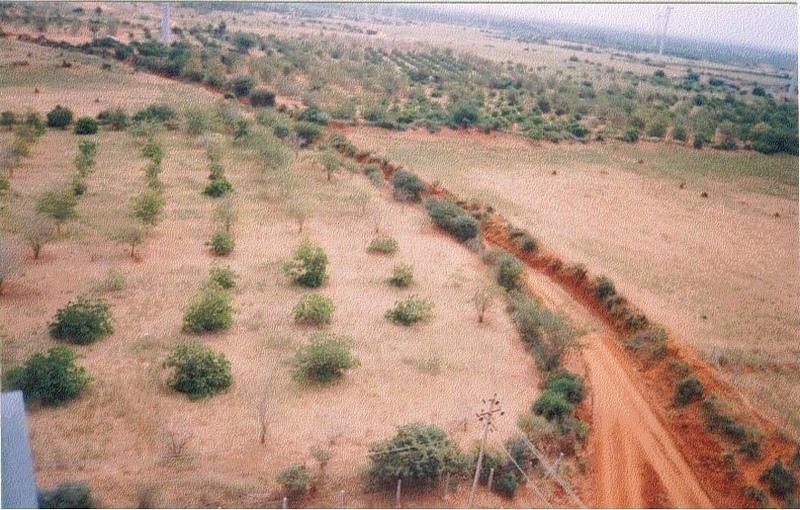
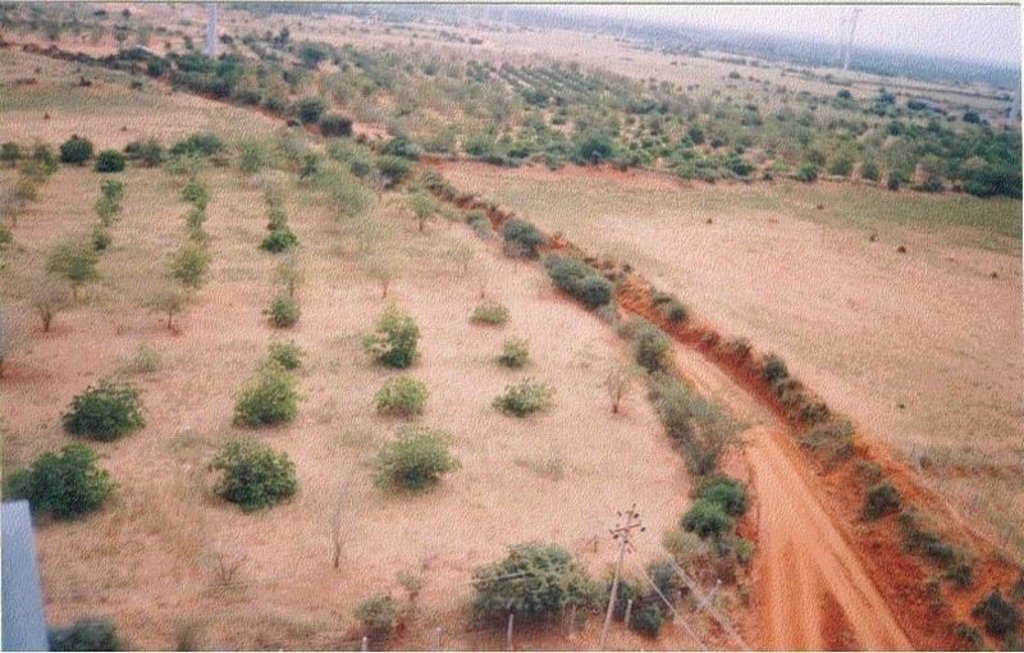
说明:
The technology can be described as a combination of tree cultivation ( mainly horticulture species) along with intercrop of pulse crops on degraded private lands, supported by in-situ measures for soil and water conservation. The supportive technology required is provision of water for protective irrigation during establishment phase.
Purpose of the Technology: the technology serves the folowing purposes 1. Short and long term economic benefits to land owners 2. Employment generation leading to reduced migration 3. Conservation of soil and water through vegetative and mechanical measures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: 1. Community organisation, formation of Village Development Association, Identification and training of beneficiaries 2. Delineation of micro-watersheds and plantation blocks. 3. Establishment of farmers's nurseries 4. Land preparation, sinking bore-well, plantation and inter-cropping 5. Watch and ward.
Natural / human environment: The environment is semi-arid, drought prone and subject to wind erosion. Soil depth is good.
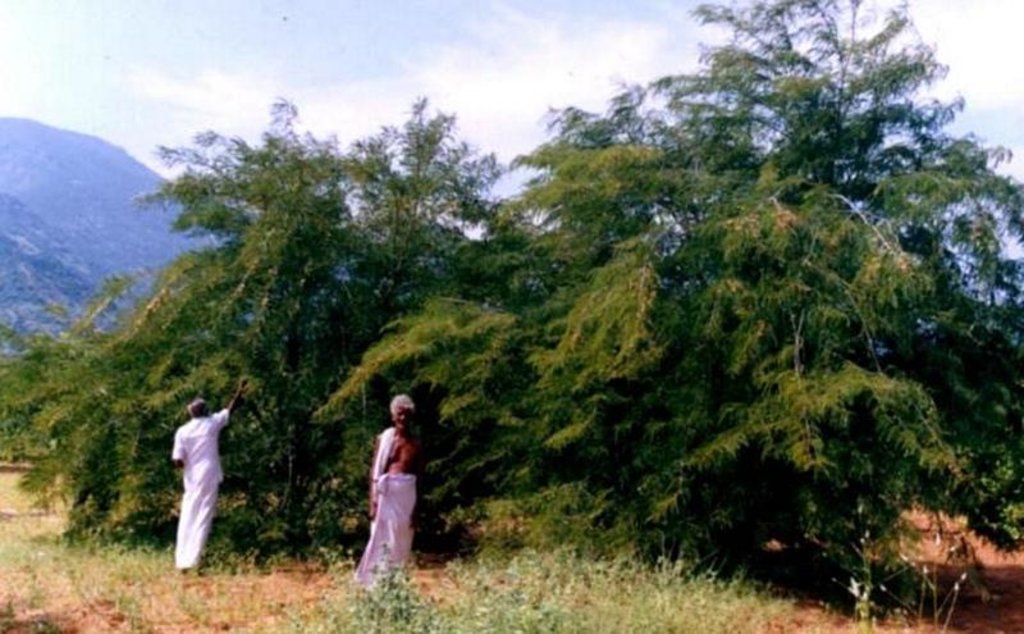
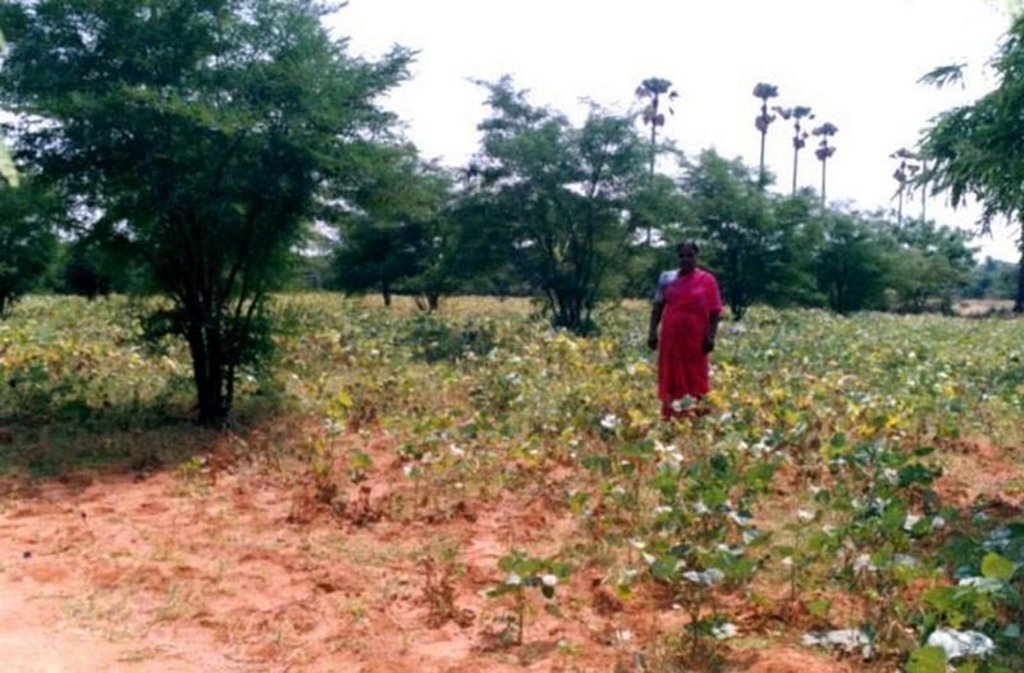
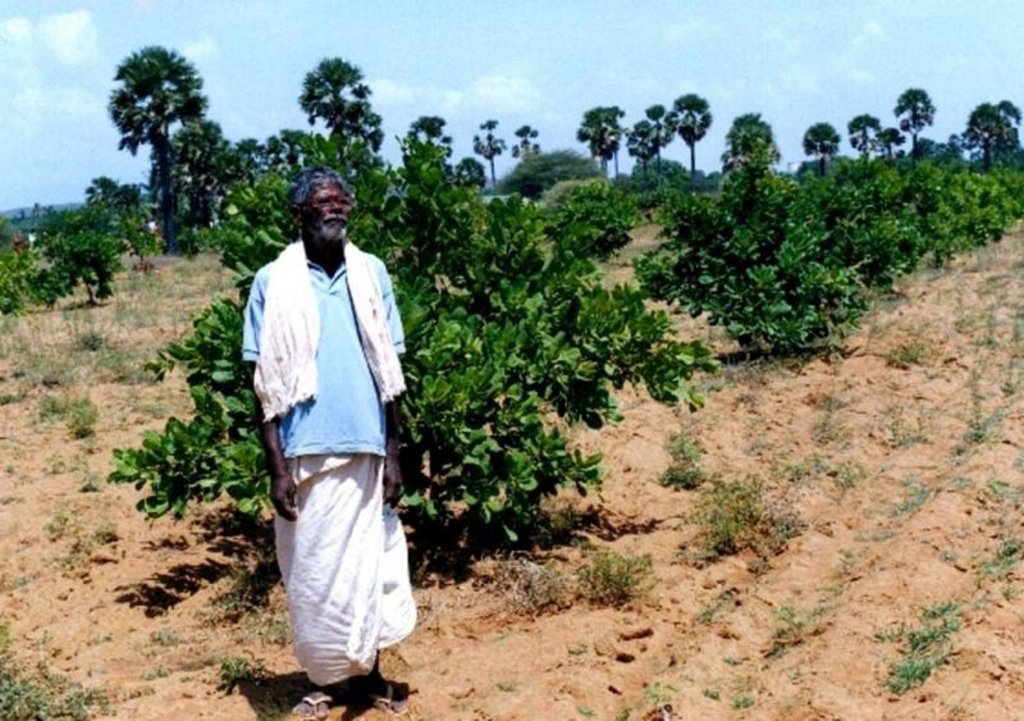
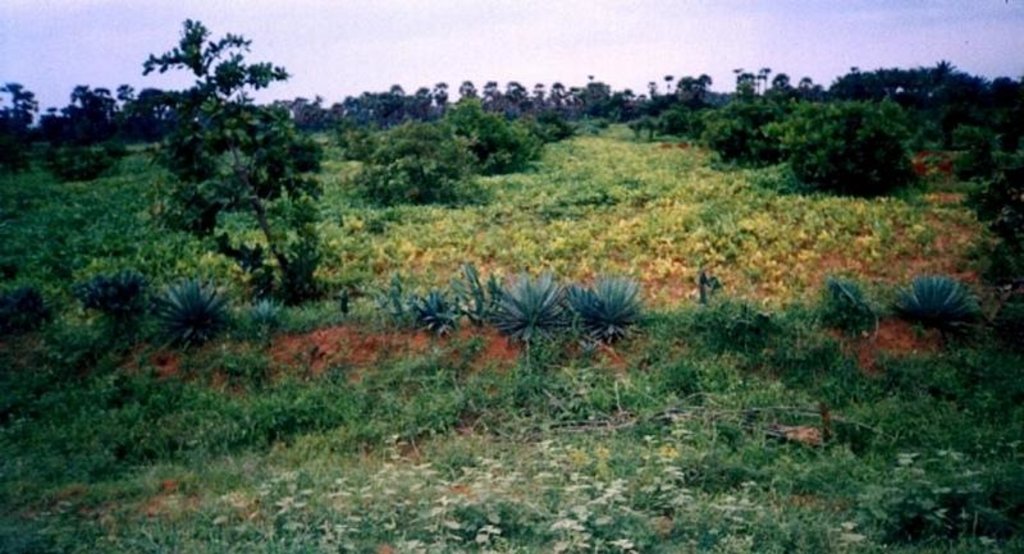
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Tamilnadu
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology evolved out farmers suggestions and project experiences while implementing the shelter programme to combat wind erosion.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林业
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Uncontrolled grazing on un-cultivated lands, abandonment of fields by poor farmers due to recurrent crop failure as a result of drought.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop lands are not economocal to cultivate due to recurrent crop failure as a result of drought. This has lead to abandonment of fields and increase in numbers of small livestock which are left free to graze.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The area is single cropped and hence only one food crop is taken per year.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 100 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jan
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3.83 km2.
The area is predominantly degraded land affected by wind erosion. The annual rainfall is <600 mm, however distribution is erratic resulting in drought conditions. People are mostly small farmers engaged in rainfed agriculture, however large areas have been abandoned due to frequent crop failure. The technology has been applied in a gross area of over 300 sq.km.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
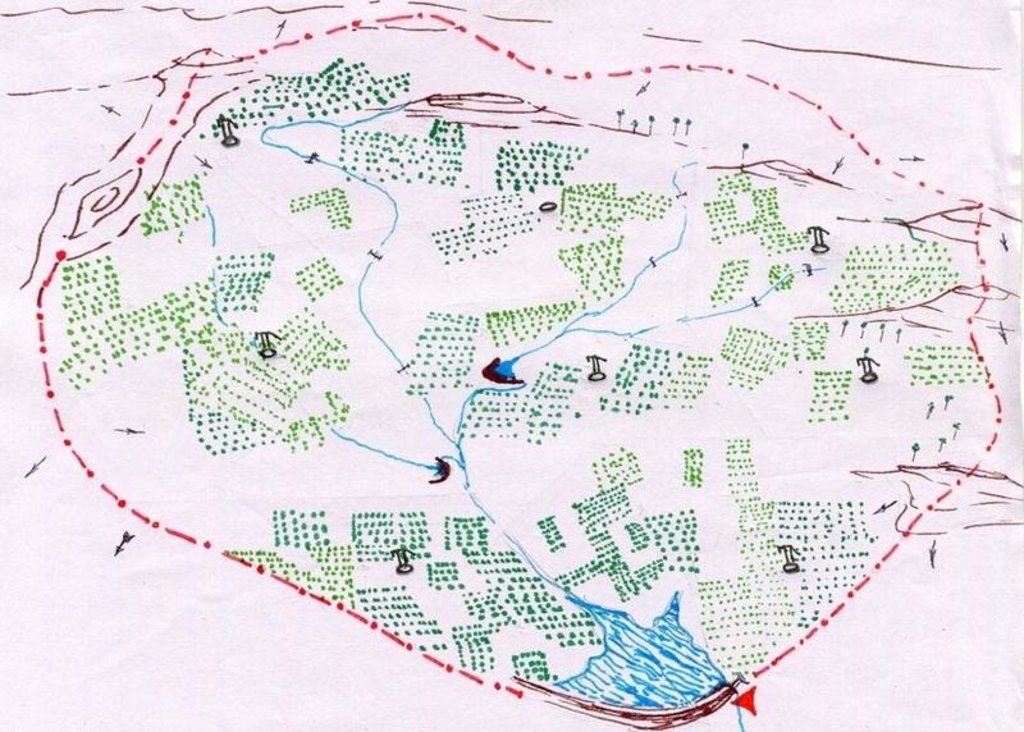
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical Drawing Agro-forestry
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction in wind speed
Better crop cover
Material/ species: trees + legume crops
Quantity/ density: 125 trees/
Remarks: Block plantation/ intercorp
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: trees + legume crops
Quantity/ density: 125 trees/
Remarks: Block plantation/ intercorp
Mulching
Material/ species: soil mulch
Quantity/ density: 125 basins
Remarks: 1 m. diameter basin per tree
Agronomic measure: vegetative hedges
Material/ species: agace, euphorbia sp.
Quantity/ density: 15 cm. Spa
Remarks: Along field boundries
Pits
Remarks: 125 pits/ha., 9 m. spacing. 45*45*45 cm for local species & 60*60*60 cm for grafts.
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: disc ploughing before pitting in first year, tiller ploughing annually at sowing of intercorp..
Trees/ shrubs species: Azadirachta indica, Albizia lebeck
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Anacardium occidentale, Tamarandus indicus, Emblica officianalis, Mangifera incica
Other species: Phaseolus mungo, Arachis hypogea
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
Change of land use type: open grazing, cropping to agro-forestry
Change of land use practices / intensity level: open access to protected
Layout change according to natural and human environment: borewell blocks formed as per human environment but within watershed boundary.
Control / change of species composition: scrub clearance followed by plantation of agro-horticulture species.
Other type of management: VDA established - to manage all activities at village level
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Indian Rupee
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
48.85
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery raising | 植物性的 | May - Nov |
| 2. | Planting in pits | 植物性的 | Oct -Dec, onset of monsoon |
| 3. | Life watering | 植物性的 | immediately after plantation |
| 4. | Planting of vegetative hedges | 植物性的 | Oct - Dec |
| 5. | Sowing of intercrop (broadcasting, dibbling) | 植物性的 | Premonsoon-groundnut, monsoon-legumes |
| 6. | Application of FYM to intercrop | 植物性的 | September during tiller ploughing |
| 7. | Selection of village as per criteria | 管理 | Mar/Apr, dry season |
| 8. | Rapport building, awareness generation | 管理 | |
| 9. | VDA formation | 管理 | April / May |
| 10. | Development of watershed plan including agroforestry | 管理 | May / June |
| 11. | Trainings for VDA, farmers, nursery etc. | 管理 | Jun - Aug |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | scrub clearance | 农业学的 | Sept/Oct,dry season / once before planting |
| 2. | deep ploughing | 农业学的 | Oct/Nov,onset of monsoon / once before planting |
| 3. | pitting | 农业学的 | Oct/Nov / once before planting |
| 4. | manuring | 农业学的 | Oct/Nov / once before planting |
| 5. | filling pits, planting, forming basins | 农业学的 | Nov / once before planting |
| 6. | life watering | 农业学的 | Nov / after planting |
| 7. | tiller ploughing & sowing | 农业学的 | Oct/Nov / annually after onset of monsoon |
| 8. | maintenance of tree basins | 农业学的 | Oct / after annual tiller ploughing |
| 9. | Periodical watering | 植物性的 | dry months 1st year /weekly |
| 10. | Weed removal | 植物性的 | Nov / Dec /once during annual crop |
| 11. | Application of pesticides | 植物性的 | Dec - Feb /as necessary |
| 12. | Pruning | 植物性的 | Nov /annually |
| 13. | Casualty replacement | 植物性的 | Nov /One year after plantation |
| 14. | Monitoring by VDA | 管理 | - / monthly |
| 15. | Hand pump maintenance | 管理 | / as required |
| 16. | Protection against animals | 管理 | Year one / full time |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
- The costs were calculated for establishment of one block (average area 12.5 ha.) of horticulture plantation with project support. The agriculture component was implemented by farmer with project support for seeds during first monsoon and tiller ploughing during second monsoon.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
- Establishment of the technology requires high labor input, specially for watering and watch & ward, which adds significantly to the cost. - Presence of hard pan necessiates deep ploughing with machinery. - Horticulture tree species were selected over forest species.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
680 mm, however the rainfall over the past few years has been < 500 mm.
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Since past few years arid conditions prevail in the area
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Plateau/plains (level lands lying between hill slopes of Western mountain range & East coast of south India.)
Slopes on average: Flat (level land with some gullies passing through (originating in upper hilly area))
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2, patches of deep soil)
Soil texture: Medium (sandy loam)
Soil fertility: Medium (loss of top soil due to erosion)
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (originally low before agro-forestry)
Soil drainage/infiltration level: Medium (presence of hardpan below six inch depth. However, no waterlogging is observed due to runoff.)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (has improved due to deep ploughing post treatment)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
11% of the land users are rich and own 18% of the land (large holdings > 2 ha.).
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 56% of the land (holdings of 1 to 2 ha.).
39% of the land users are poor and own 26% of the land (holdings < 1 ha.).
Off-farm income specification: Off farm sources are; poor - rolling beedis (locally made cigarettes), daily wage labor in fields and brick kilns. Average / rich; Business, livestock.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour (ranked 1, pitting, planting, watering, cultivating, watch and ward), mechanised (ranked 2, deep ploughing, tiller ploughing, drilling borewell) and animal traction (ranked 3, ploughing)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
99% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
284 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers are purchasing seedlings for plantation on their fields in small patches around existing water sources - Farmers who did not participate initially are now expressing a desire to treat their lands under the project.
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Review reports.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Chief Engineer, Agriculture Engineering Department, Anna Salai-439, Nandanam, Chennai-600035
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Project Implementation Plan. 2001.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Programme Coordinator, WDCU, 11/1 Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi-110016.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Participatory Impact Evaluation. 2001.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块