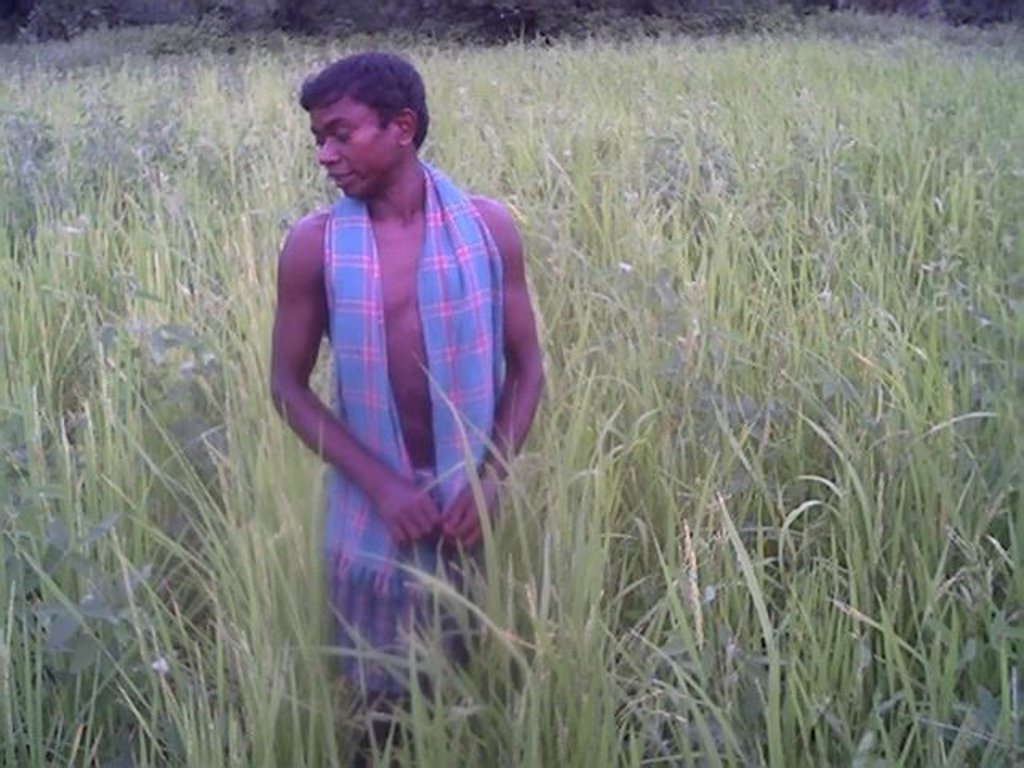
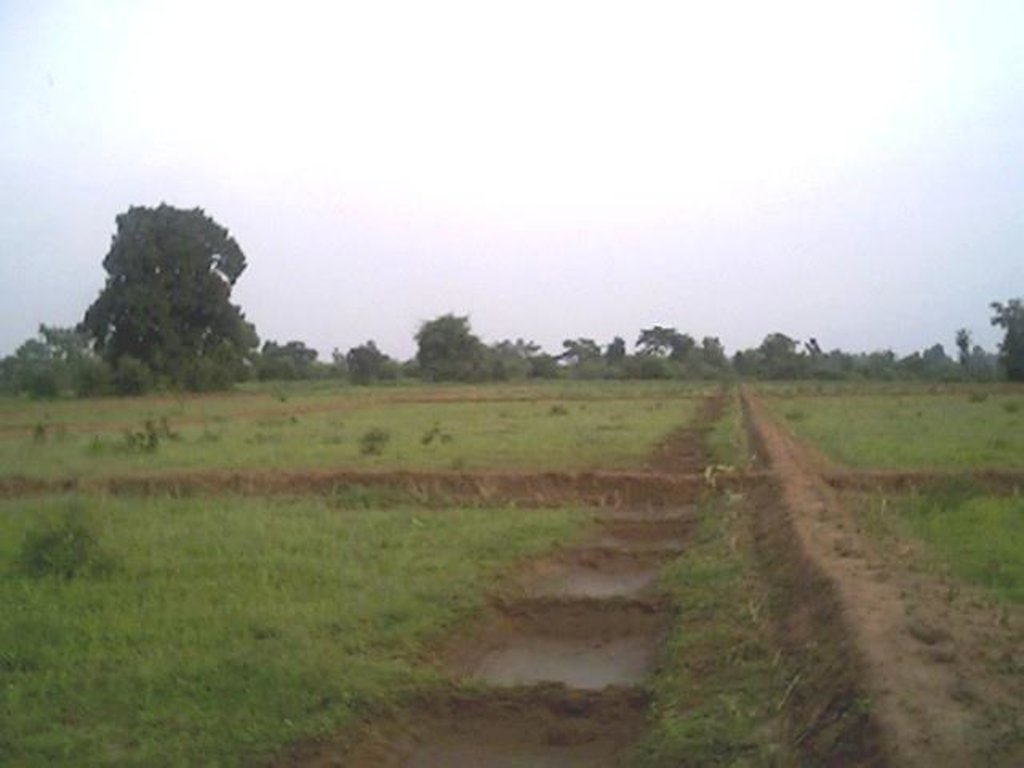
Dug-out sunken pond cum countour bund [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Buda Gata with Adibandha
technologies_1086 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Mohanty Rajib Kumar
印度
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
17/12/2004
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Community based sustainable livelihoods [印度]
Sustainable livelihoods enhanced through people's organisations by linking with other resource organisations prticularly for resource poor.
- 编制者: Unknown User
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
It can be defined as combination of structural & vegetative measures where contour bunds are constructed from the excavated sandy loam soil of cultivated wastelands in semi-arid climatic(?) zone with moderate slope in medium soil depth conditions in order to link with self-subsistance & market oriented production systems from private lands.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The area is located at the foot-slopes & hill slopes area where run-off is at peaks very often at the time of rainy season. Therefore, sand casting came as a first order priorities by the farmers of this patch. At the outset, a livelihood focused micro-plan had been prepared by the villagers stating the details of the base-line data along with problems & alternative solutions. The patch was identified to be the worst affected, concentraton of poor people (defined by villagers), people of this patch ready to contibute at least 20% of the cost. In the mean time project sent the PIA to BAIF, Bangalore to study the linking of farm ponds & its relevance in this context of our situation. As a demonstration, PIA & other technical team facilitated the villagers. One water harvesting structure was constructed by line deptt of soil conservation just at the down hills to harvest rain water & protect the lands below from sand casting. But there were no alternatives for the land users of that patch about the optimum utilisation recharged water. The surrounding area was totally unbunded with sandy loam soil. Therefore, land users are of opinion to go fo field bunding. Earlier the practice was to dig a trench at upper gadient & put a bund below it out of the excavated soil from trench. But the requirement of land users was to get some water in each farmers land to protect the Kharif & some early rabi crop.(june-dec). By which the lands where, farmers take up only minor millets for their subsistance, that too less production & land So the main purpose of this technology was to convert the land into bunded lands along with to fetch some water at the time of dry spell in between the monsoon period. A four days in field training was conducted by the project to community link workers(SWC), particularly on patch treatment, use of levelling instruments like A-frame, proper planning, design, lay-out of different type of structure in a map & ground. After many rounds of discussion with the land users, one of them ( rich farmers with more land) was ready to do it in his own land. But, the SWC specialist did a detail transact along with land users, although results of first round tansact was mentioned in the micro-plan. The main pupose was to looking at problems & demarkating on the map. After that estimate was prepared & lay-out of key contour was done by SWC specialist with the help of community link workers & land users. The work was implemented by by the labourers with the supervision of the respective User's group leade & monitoring was done by the SWC specialist. The prioty ranking by the land users vegetaive measures like vertiver & Sabai (grass plantation on the bund along the side of the bund. For that, the necessary requirement like nursery, seedling collection was done by agriculture specialist. Training was conducted on the probable alternatives of agronomic measures like taking of crop which is of little longer duration, intercrops & cash crops etc. The vegetaive & structructural measures are subsidised by the project & the agronomic measures was taken up on loan basis. The development fund was also generated out of contribution from the land users which was deposited in a separate account for future maintainance cost.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Orissa
有关地点的进一步说明:
Khaparakhol
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
A group of SWC proffessionals were sent to BAIF Karnatka to study the replication of ' Linking of farm ponds models. After a detail study we concluded that the climate in particular & rainfall in general of our area is not fit for that technolgy. When SWC specialist share their experience to land users, some of the farmers agreed to have a experimentation of the technology. Therefore, modification has been done by the SWC specialists as per the suitability & requirement of the land users.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: Ground nut
Major food crop: Paddy/minormillets
Major other crop: Cotton

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农牧业
- 农林牧业
主要产品/服务:
Major cash crop: Fruit like mango/Custard apple
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): This patch of the land is poor in the nutrient status in comparison to other lands of the village, with high concentration of marginal farmer. Heavy top soil erosion over the years yields to decreasing of productivity of land. The main requirement of water is in the dry spell in between the monsoon period.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Run-off was severe at the time of rainy season which causes heavy soil erosion. 2. Sand casting on down below lands . 3. Long duration crops is not possible, ex- Ground nut, paddy, cotton etc. 3. Lands was not levelled for smoothening of ploughing operation. 4. The uncultivated wasteland(according the record of rights) was distributed to some landless persons who are unable to take up any productive cultivation in these lands.
Ranching: Although technolgy is not directly applied, but indirect effect is there on grazing.
Grazingland comments: The major cause of loss in livestock is that there is no option for the villagers for stall feeding. Example- in summer no availability of green fodder or less availabity.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Minor Millets/ Paddy(june-Sept)- Black gram or pulses(Sep-Dec) or cotton as the sole crop for nine months.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - SepSecond longest growing period in days: 75Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Dec
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 集水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 km2.
The concerned watershed is a subsidiary system of the Suktel river drainage sytem. The area of operation is micro watershed , i.e. 500 hac as a unit of the tributary of the Suktel river.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡
- Wo:场外劣化效应
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Suitable alternatives which will yield more benefit with less investments.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Knowledge sustainable livelihoods framework)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Maintainance & responsibility sharing for protection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Particularly vegetation which yields non-timber forest produce.), overgrazing (Uncontrolled & free grazing at the period Dec-June restricts the land users to go for second crop.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Frequent drought occurs in every alternative 3rd year.), poverty / wealth (Initiation of any activities for sustainance of livelihoods need some capital)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Better crop cover
Material/ species: paddy, minor millets, groundnut, vegetables
Quantity/ density: Average
Relay cropping
Material/ species: pulses after minor millets or short duration paddy
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Ground nut, green gram & fibre crop(Jute)
Remarks: Line sowing- 5 lines of green gram with one line of green gram & jute on the fence of the land.
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Cotton as a demonstation practice.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: The silt deposits in the sunken pond is used in the nearby land.
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: After paddy the land is used for pulse
Minimum tillage
Remarks: Previously unbunded, now bunded upland rquires minimum tillage.
Pits
Remarks: Thecontour bunds & field bunds constructed out the excavated soil from the pits.
Agronomic measure: Soil moisture condition
Remarks: It is enhanced due to the technology
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15-20 ft
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 1250
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 inches
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 inches
Trees/ shrubs species: Teak
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, Custard Apple
Grass species: Vertiver & Sabai
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Spacing between structures (m): 50 ft
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6 ft
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25 ft
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25 ft
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 ft
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 ft
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50ft
Construction material (earth): The earth from the dug-out sunken pond is used for the construction of contour bunding
Construction material (stone): Stone is used at the weak point for stabilisation
Change of land use type: Minor millets, long duration upland paddy, Grount nut, pulses after paddy/millets or cotton etc.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: After harvest of first crop like minor millets/ paddy, next crop is taken up by land users along with some vegetables(Horticulture crop).
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Grazing was restricted in these areas & land was optimally used, like bund cultivation.
Major change in timing of activities: Tthese lands were last option for the land users.But now the activities like summer plough has changed the time.
Control / change of species composition: Earlier sole crop, like only minor millets/Upland paddy. But now land users have started intercropping systems.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rupee
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
50.0
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey & alignment of key Contour & lay-out of tanks | 植物性的 | Beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Digging of pits for grass, fruit plants & timber | 植物性的 | June |
| 3. | Collection of Vertiver & Sabai grass from external source | 植物性的 | july |
| 4. | Collection of seedling of Trees/Plants | 植物性的 | July |
| 5. | Survey & contour demarkation | 结构性的 | April-May |
| 6. | Demarkation on map | 结构性的 | April-May |
| 7. | Estimate & lay-Out | 结构性的 | April-May |
| 8. | Implementation of work | 结构性的 | June |
| 9. | Survey & Key Contour line demarkation at 75 ft interval | 管理 | June |
| 10. | Digging of Sunken ponds | 管理 | July |
| 11. | Top level dressing of bund | 管理 | July |
| 12. | Water-way with connection Dug-out sunken ponds | 管理 | August |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 20.0 |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 20.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 120.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing | 农业学的 | April-May / annual |
| 2. | Intercultural operation with manure application | 农业学的 | June / annual |
| 3. | Sowing | 农业学的 | July & sep for two crops / each cropping season |
| 4. | weeding & intercultural operation, if required. | 农业学的 | July / annual |
| 5. | Harvesting of paddy or minor millets or ground nut | 农业学的 | Aug-sep / annual |
| 6. | Sowing of pulses as relay crop | 农业学的 | Aug-sep / each cropping season |
| 7. | Harvesting of pulses | 农业学的 | Nov-Dec / each cropping season |
| 8. | Collapsing of bunds may damage th evegetation | 植物性的 | Rainy Season /annual |
| 9. | Checking against free grazing | 植物性的 | Jan-June / |
| 10. | Watering to plants | 植物性的 | Dec-May /annual |
| 11. | Management of surplus water | 结构性的 | Rainy Season/Once in Year |
| 12. | Collapsing of bund | 结构性的 | |
| 13. | Tanks must be desilted | 结构性的 | Dry season/Once in Year |
| 14. | Control of surplus water-flow | 管理 | Rainy season / once a year |
| 15. | Stabilisation of bund at weak points | 管理 | August / once a year |
| 16. | Desiltation of ponds | 管理 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: in a typical area of 5 hac, around 30,000 has been spent in which 20% of the establishment cost is borned by the land users.
There are two types of dug-out sunken pits of specifications. The sunken pit was dug & the earth from the sunken pit was put on a contour bund. So the earth-work was calculated as per cubic ft. The seedlings were bought from nursery & planted with 20% contribution of labour.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Soil depth is very less, hard soil with slope variation because of undulating lands. The labour was also not sufficiently available at the time of establishment, because the work was implemented at time of main growing season. At that time land users are busy in their own field because of cultivation work.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
1000-1500 mm: Ranked 1, Avg rainfall from liz kiff report. The study of 20 years of rainfall data shows that, drought comes in every alternative 3 years. The rainfall varies from a minimum of 715.6 mm to maximum of 1863 mm
500-750 mm: Ranked 2
1500-2000 mm: Ranked 3
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (as per the record in the topo-sheet No-64 P/1 with scale1:50,000)
Slopes on average: Gentle (As the stretch of land is at the hill slopes. The slope firstly from 5-8% where as the land where dug-out sunken ponds were dug is of slope 2-5%, ranked 1) and moderate (ranked 2)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, due to continuos soil erosion the topsoil eroded completely which resulted into varied soil depth where only deep rooted crops & plants are possible) and moderately deep
Soil texture: Coarse/light (Ranked 1, the soil is basically reddish in colour with sandy loam texture) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1, the soil fertility of uplands is very low where the said technology is established. But the lands near to it some what medium land with medium soil fertility) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (the watershed map from the topo-sheet shows that there only one drainage line where two contributaries are there. That is the perinneal stream where water from the lands drain out to main drainage lei, ranked 1) and poor (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (the soil texture being the sandy loam category, the storage capacity is very low. Therefore, after monsoon rainfall the soil is unable to maintain the water requirement at the dry spell to high percol, ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
20% of the land users are very rich (1-2 farmers having more than 10-15 acre of land).
30% of the land users are average wealthy (land users having upto 5 acres(Little less in comparison to first categ).
50% of the land users are poor (land users having only0-2 acres(more in No. in this patch)).
Off-farm income specification: Others have also activities like NTFP collection, keeping small ruminants like goats, chicks etc.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, wooden plough) and manual labour (ranked 2)
Market orientation cropland: subsistence (self-supply, minor millets/paddy/pulses, ranked 1) and mixed (ground nut & vegetables, ranked 2)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (micro-plan)
Grazing land: 0.5-1 ha (130 Households with 25 hac of grazing lands)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Per hac production/economic cost.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Vertiver as fodder on bund.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Vertiver as fodder on bund.
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Teak plants has been planted this year. The yeild is yet to come.
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Land users believe that some land is wastage due the structure.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Ploughing operation.
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Resource rich & resource poor land users accrued double benefit by changing the crop.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Farm employment at lean period. Income through labour
其它社会经济效应
Field Demonstration- living institution
注释/具体说明:
Alternatives to mitigate drought.
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Contribution labour from land users because of convincing benefit from the technology. The women also contributed in plantation activities.
国家机构
注释/具体说明:
Members from other areas of district also learnt the technology through exposure visit.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Some of the land users of other patch of the village decided to take up similar activity.
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Transparency: The details of activity is shared amongst all the villagers.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Land users having land below 1 hac are getting more benefit out this technology.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
10
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Earthen hume pipes.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
This condition help the land users to take up second crop.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Particularly top-soil.
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
30
SLM之后的数量:
20
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
Production/ Economic benefit becomes double.
Water availability in dry spell
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
19
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
19 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Many farmers & SWC specialists visited the spot for the learning purpose. All we cannot say that it is a spontaneous adoption, but they have started taking up this technology in their own area.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Maintainance is very less How can they be sustained / enhanced? Only timely care is needed. |
|
Land users can have water in their field other than rain water to be used for different purpose. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Some demos agriculture was done in this patch which has to be repeated for the second year for confidence building of the land users. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Water availability in the dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the land users will desilt the pond timely & care to plants grass on the bund. |
|
The land where only one crop is possible, vegetable & pulse crop can be taken up as second crop How can they be sustained / enhanced? Some methodology is to be applied to keep water in the pond for longer duration. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Ploughing operation will be difficult. | This is although difficult but th benefit is more, therefore land users will compromise with this type of difficulty. |
| Water availability in dry period & desiltaion process. | This can be overcomed by planting vertiver on the sides of the pond & low cost polythene can be used for prolonging percolation rate of water in sandy loam soil. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The farmers started taking up cotton & paddy in stead of minor millets | Improved variety of minor millets is supplied to farmers for better yield in comparison to country variety. |
| Diversion of surplus water | The land users have to dig atleast one more feet & earthen pipes will be used for the diversion of surplus water. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Community based sustainable livelihoods [印度]
Sustainable livelihoods enhanced through people's organisations by linking with other resource organisations prticularly for resource poor.
- 编制者: Unknown User
模块
无模块