Water-conservation technology at cultivation of the cotton in south. K [哈萨克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
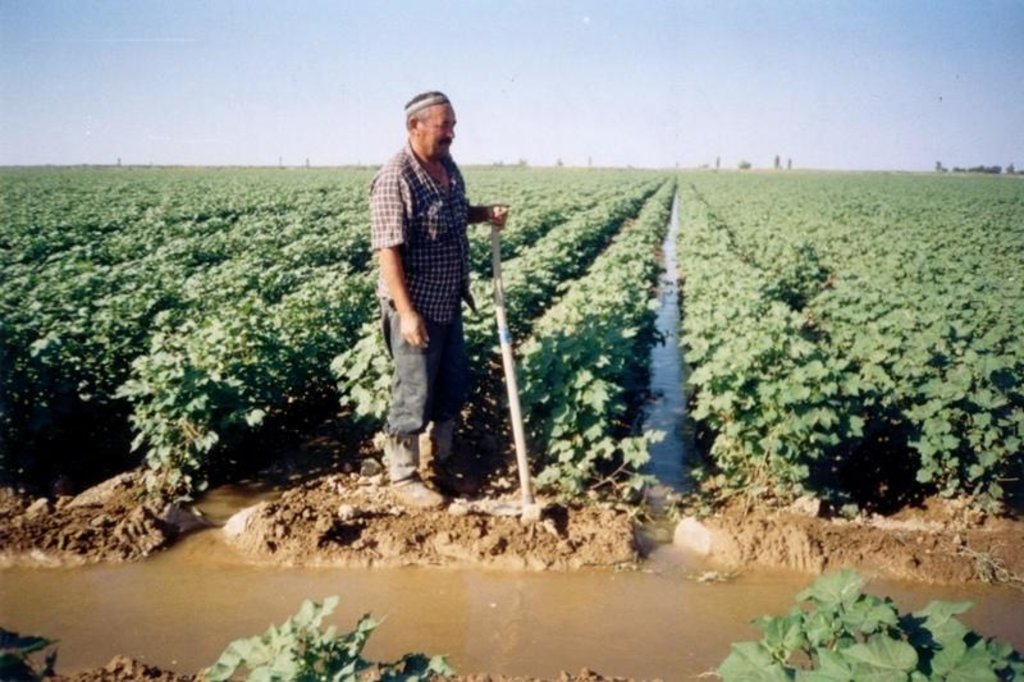
Watering through furrow
technologies_1091 - 哈萨克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Vyshepolsky Frank
哈萨克斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Khe Tatyana
kniv@nursat.kz
Taraz city
哈萨克斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Mukhamedzhanov Khamit
Scientific Production Center for Water management
12 Koigeldy str
哈萨克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of Agriculture of Kazakhstan (MoA) - 厄立特里亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
30/09/2003
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The technology of watering through furrow reduces the settlement (recommended) sizes of irrigating norms up to 30% keeps soil fertility
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
It is applied for watering on furrow at ploughed cultures.
It is intended for decrease in irrigating norms and preservation of fertility of soils.
The technology of watering through furrow
-Does not result in change of zone system of agriculture
-Provides pass of soil-cultivating technique on dry furrow therefore are reduced the rates of soil condensation
-Reduces technological losses of irrigating water to filtration shed from the irrigated grounds evaporation
-Reduces the sizes of irrigating norms (recommended) up to 30%
-Reduces loading to drainage system up to 30%
-Slows down the rates of development of erosive processes and keeps soil fertility
-Raises productivity of cultivated cultures at deficiency of water
-Improves ecological conditions due to reduction of drainage shed of water for limits of irrigated files
-Does not demand additional expenses for its introduction
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
哈萨克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Southern Kazakhstan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Basin of Syrdarya
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
Caused (provocative) waterings for reception of shoots at drying up of soil in a zone of an arrangement of seeds.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- Reduce amount of irrigation water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
major cash crop: Cotton

牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water resources management. Reduction of technological losses of irrigating water at its transportation from water-fence up to fields of an irrigation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Technologies of the water-conservation, reduction of norms of entering of mineral fertilizers, increase in soil fertility. Normalization of water-submission on cultures and soil-meliorative conditions.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 40 km2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A4:地表下处理

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), breaking compacted topsoil, pits, deep tillage / double digging
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: phospho-gypsum
Remarks: 4t/hec
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: tillage through grooves
Pits
Remarks: breaking compacted soil
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: by cultivator
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.50
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 650.0 | 650.0 | |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Polyethylene film | ha | 1.0 | 55.0 | 55.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 745.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage | 农业学的 | between / weekly |
| 2. | entering of phospho-gypsum | 农业学的 | watering / once a year in the autumn |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果可能,按下表分解技术维护费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出维护该技术的总成本估算。:
3.0
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Tillage and appliyng phospho-gypsum | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Polyethylene film | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 125.0 | |||||
注释:
For arrangement of 1 ha width of furrow makes 100 meters, quantity of furrow makes 50
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Arrangement of furrows its cutting and reinforcing of the bottom of furrow
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
235.00
农业气候带
- 干旱
Growing pirriod 4-5 months
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Valley of the Syrdarya river . Foothill plains of a ridge of the Karatau
Slopes on average: Flat for valley landforms for foothill plains
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium (Alluvial gray soils) - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium for alluvial meadow soils and poor for light gray soils
Soil water storage capacity is low for alluvial meadow soils and very low for light gray soils
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are rich and own 50% of the land.
19% of the land users are average wealthy and own 39% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 1% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Due to pasturable live stock and cultivation of gourds
Market orientation of production system:Mixed for grain-crops, grasses and commercial orientation for cotton
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for ploughing, chasing and harvesting and mechanised for tillage interrow cultivation
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 租赁
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
收入和成本
农业收入
其它社会经济效应
expenses on water
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
其它生态影响
soil fertility
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
The area of flooding at the end of a field is reduced 3-4 times
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Dump of drainage waters is reduced up to 2 times
norms of entering of mineral fertilizers
注释/具体说明:
due to decrease of washing out nutrients
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 10-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
850 households in an area of 40km2 (10-50 persons per km2)
注释:
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
850 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The existing system of water-subdivision does not provide for water consume on demand of farmers within the limits of allocated limit but establishes sequence of watering. At present water-subdivision the farmers who watering on furrows an create, additional stocks of a moisture and so the watering technology through furrows has not received universal application
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improves working conditions of labours and work of soil-cultivating technics |
| Reduces the sizes of irrigating norms |
| Raises productivity of agriculture at deficiency of wate |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Reduces technological losses of irrigating water to filtration, evaporations, shed from fields of on irrigation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Till progressive method od an irrigation drop, rain |
| Reduces intensity of soil condensation and development of denitrify processes |
| Reduces loading to drainage system and rates of pollution of water sources |
| Prevents degradation of the irrigated soils |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Increase in expenses for interrow processing | Application of soil cultivating technics |
| Increase in quantity of watering | Reinforcing furrows by pipes |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Reduction of the interwatering period | By increase in volume of use of subsoil waters to subirrigation |
| Increase in interrow processing | Regime of subsoil water management |
| Increase in cost the current expenses at watering and interrow processing | Increase in productivity of cultivated cultures |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Reports: Technology of an irrigation on the farm site in zone of Arys-Turkestan channal. 2000-2002 year.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SPC for Water management
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Recommendations on stabilization of agriculture in a zone of Arys-Turkestan channal
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块