Riverbed reclamation & silt trapping for sugarcane [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Kithinji Mutunga
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
Kyanda (Kikamab)
technologies_1096 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Ngati Mbuvi
MOARD
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Mwendwa Linus
MOARD
肯尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - 意大利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
17/04/2000
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Silt harvesting on riverbeds to maximise sugarcane growing in semi arid area
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
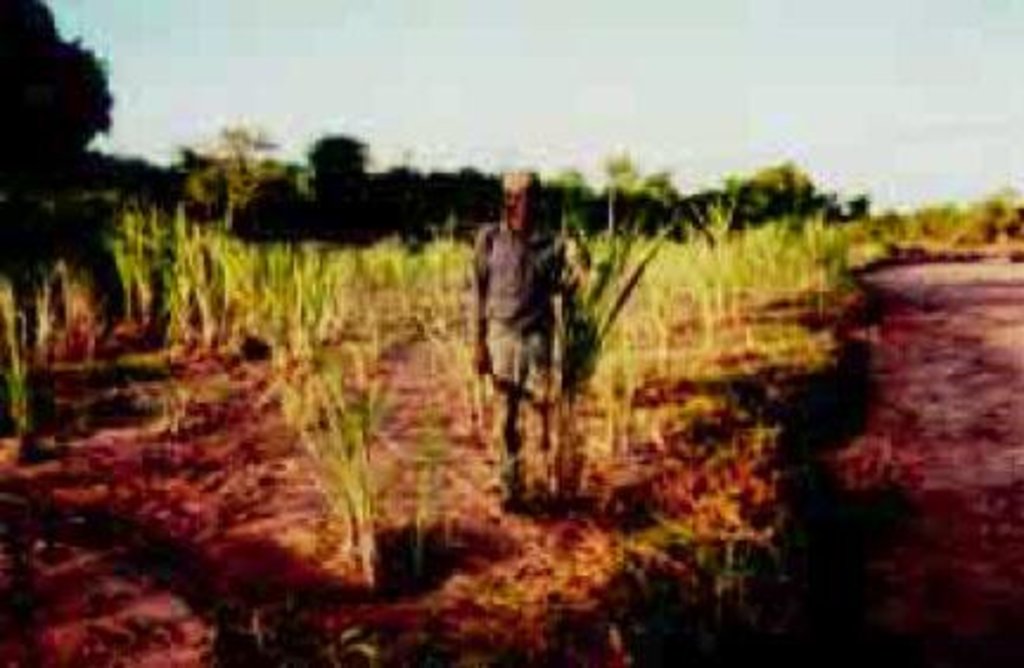
The technology first involves fencing off part of a riverbed with cut thorn scrub in order to keep livestock away. The enclosed area is then mulched with brushwood and herbaceous materials in places. Sugar cane is planted and harvested piecemeal when mature. Kamuti plants a perennial grass (Cynodon dactylon) between the canes to help bind the sand. This exercise has been done, incrementally, over a series of seasons, enclosing an increasingly large area. When the rains return and the river flows, floodwater passes through and over the sugar cane and silt is deposited as the flow is slowed.
Purpose of the Technology: This initiative is categorized as an agronomic/vegetative measure, for reclamation of land. Its purpose is to increase water stored in the soil and to increase fertility by sediment harvesting, as a way of making land productive, while simultaneously addressing riverbed erosion. Farm income increase from the sale of sugar cane is the main production/ socio-economic benefit, while the ecological benefits include sediment accumulation, soil (ie riverbed and bank) loss reduction, soil cover improvement, increase in soil moisture and increase in soil fertility.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The action involves cutting tree branches, trimming pegs about 1m long, and hammering these pegs into the bed of the sand river, parallel to the bank, enclosing a long narrow strip. This initial strip may be 10 metres wide in a riverbed of 100 meters wide. The tree branches and trimmings are used to form a brushwood-netting barrier, which protects the area from livestock, and simultaneously slows the river flow and traps sediments. To further strengthen the barrier, star grass (Cynodon dactylon) is planted along the line of the fence. Inside the fenced-off area, sugar cane cuttings are buried at a depth of 0.4 m, and the same grass planted between the canes. The area is mulched with brushwood, which rots down to increase organic matter in the soil. These cuttings sprout and an intercrop of grass and sugar cane is the result. Maintenance comprises repairing the fence and cutting grass for mulching. No special tools are required. To be effective, the technology requires mulching every season, as the old mulch is covered by the silt load during the rainy period. The perimeter fence is maintained seasonally and requires considerable material. Occasionally when the rainfall is heavy, the sugar cane is swept away by floods and needs replacing.
Natural / human environment: The farm on which this technology is applied is in the arid far-north of Mwingi District. During the rainy season the farm can be inaccessible. The farmer, who is over 60 years of age, lives with his wives and children in what effectively forms a mini-village. The annual average rainfall in this area is barely 500 mm, and famine years are common. Temperatures are consistently high. The farm borders a dry sand riverbed.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Eastern Province
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
Farmer own intiative
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Extensive grazing of animals/unit area, uncontrolled felling and burning of tree in land preparation, low soil fertility due to continous cultivation without conservation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low yields hence opening of large areas for cultivation. Difficult soils, hence ploughing during the rains. Infertile soils.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 75 Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - May Second longest growing period in days: 60 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Dec
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
- 集水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 m2.
This technology is along a riverbed and it is not adapted by other farmers
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A6:其它

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
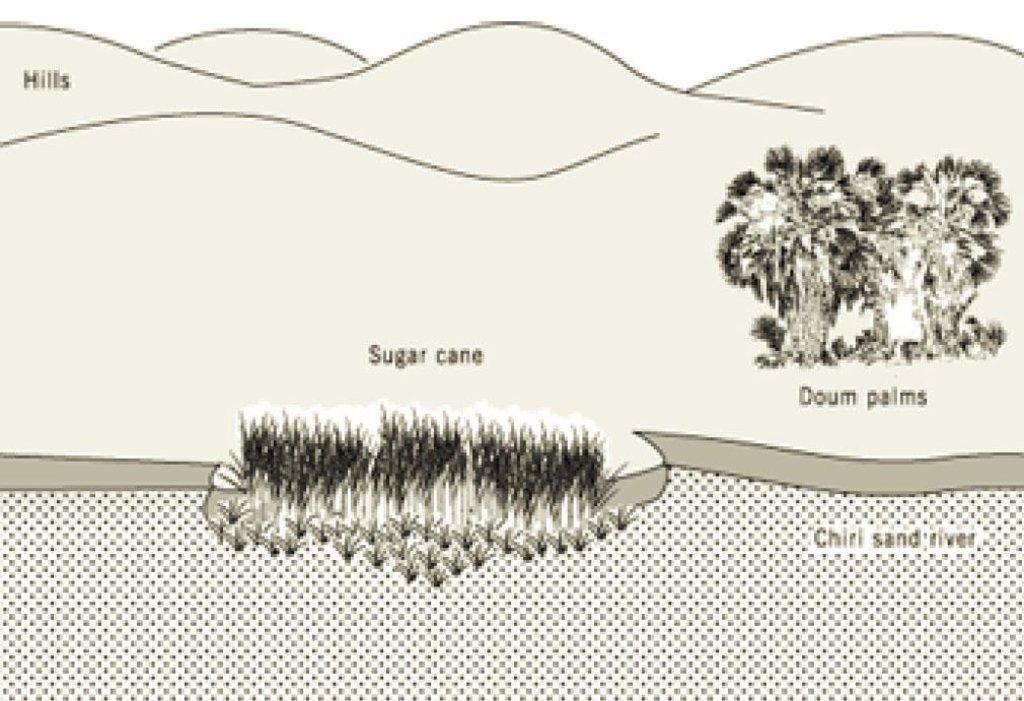
Reclaiming part of sand river bed with Sugar cane
Kenya
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: grasses
Quantity/ density: 2
Remarks: grass scattered
Grass species: stargrass
Change of land use type: fencing off portion of river bed
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kenya shilling
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
70.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.50
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | fencing | 植物性的 | after rains |
| 2. | mulching with bushes | 植物性的 | before rains |
| 3. | planting of sugarcane | 植物性的 | dry season |
| 4. | cuting grass for mulch | 植物性的 | rainy season |
| 5. | fencing riverbed to keep off animals | 管理 | after rain |
| 6. | planting grass | 管理 | after rain |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | fencing | 农业学的 | dry season / when height goes down |
| 2. | mulching with trash | 农业学的 | dry '' / after clearing |
| 3. | grass planting | 农业学的 | dry / before rains |
| 4. | sugarcane planting | 农业学的 | wet / end of rain |
| 5. | collection of mulch | 农业学的 | dry / biannual |
| 6. | fencing | 植物性的 | after rain /biannual |
| 7. | cutting grass for mulch | 植物性的 | rainy /biannual |
| 8. | scatterin thorn bushes | 植物性的 | during rain /biannual |
| 9. | fencing | 管理 | after rain / each cropping season |
| 10. | spreading brushwood | 管理 | after / annual |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: oxen plough, 2 pangas , 2 hoes
the above cost were calculated in terms of purchase of tools,material and manday used.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour affects cost as it is required in large quantities
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
- 干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Topsoil organic matter: Becomes medium after the technology
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is very low - medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 33% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 25% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 12% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 8% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 21% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: most of harvest are low and hence dependent on off farm income.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction is used for assembling the thorny bushes and for marking farrows
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Sugar cane
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Sugar cane
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
60
SLM之后的数量:
20
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
12
SLM之后的数量:
5
养分循环/补给
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
30 households (1% of the area stated)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: after farmer tour organised by the PFI most are attempting. At least five farmers had adopted the innovation by the beginning of 1999 (exact figures not available). This is a particularly site-specific system, and thus wide replication is simply not possible. It is only relevant to those who have farms bordering sand rivers with wide beds.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| This innovation demonstrates how productive use can be made of sub-surface moisture in sand rivers in arid areas while simultaneously protecting the riverbed and bank from erosion |
| Farm income increase through land reclamation |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
|
Planting within a riverbed is, strictly speaking, against regulations. |
Such technologies should not be attempted without consulting the local agricultural office. |
| The fence is constructed with thorn bush cuttings which have to be constantly replenished |
A live fence is recommended as an alternative to constantly having to replenish the fence with cut thorn bush. The fence is required to avoid grazing of the cane by domestic livestock. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Farm management Guidelines. 1989.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
MOA, Nairobi
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kithinji M., Critchley W. 2001. Farmers' initiatives in land husbandry: Promising technologies for the drier areas of East Africa. RELMA Technical Report series no. 27
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块