Agroforestry with Acacia senegal [塞内加尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Julie Zähringer
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1119 - 塞内加尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CSE (CSE) - 塞内加尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
26/07/2009
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
An agroforestry system, dominated by Acacia senegal, developed through protection of all naturally regenerating trees with improvement of soil properties through presence of trees, application of manure and a fallow rotation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
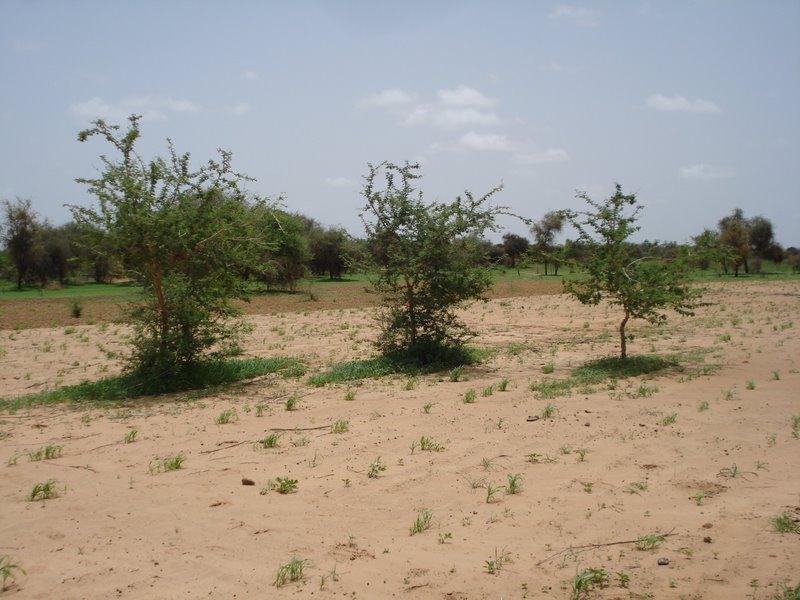
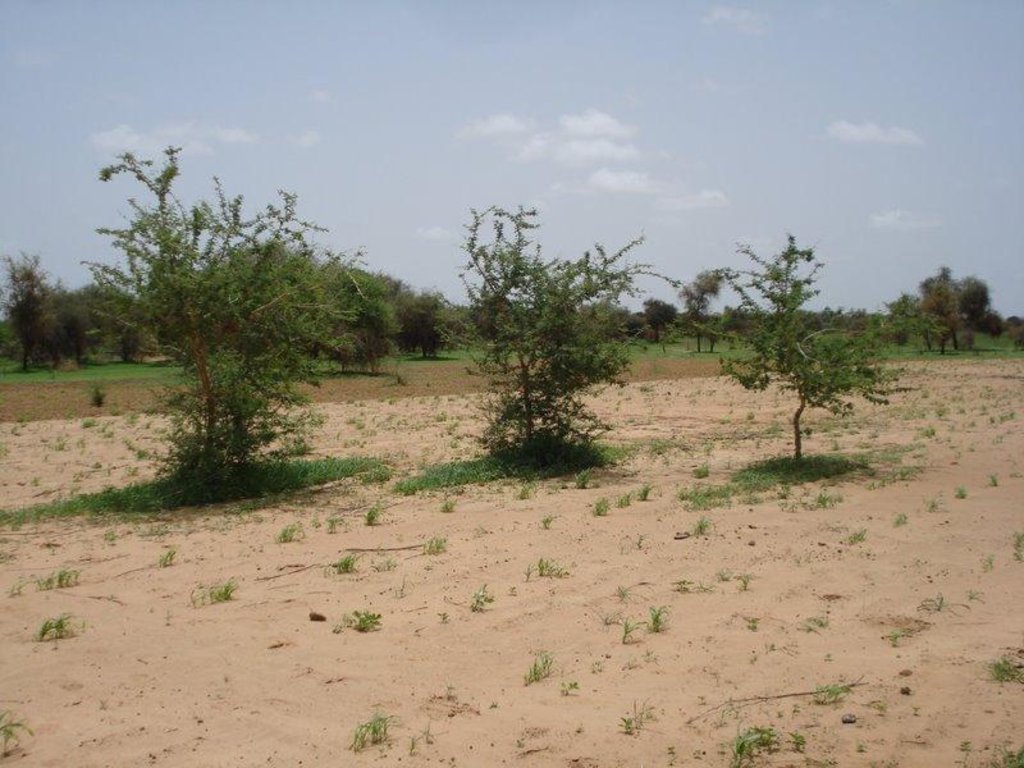
说明:
Acacia senegal is the dominating woody species in this agroforestry system. To improve soil properties and crop production, organic manure is applied and a fallow system practiced. One part of the field is being cultivated with either millet (Pennisetum typhoides), cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) or maïz (Zea mais] whereas the other part is left fallow for two years before rotation.
Purpose of the Technology: Initially, the main objective of the land user applying the technology was to improve soil properties and crop production in his fields by maintaining any tree and protecting natural regeneration when preparing his land for cultivation. With the start of exploiting Acacia senegal for the exudates, gum arabic, the potential of revenue increase through gum exploitation became evident and the objective shifted from soil protection to gum exploitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Because of knowledge his father passed on to him, the land user applying this agroforestry practice believes that any tree in his fields is useful and should be protected.Through the technique of assisted natural regeneration, trees naturally growing in the field are protected to reach mature age instead of being cut to clear area for cultivation. The only inputs related to this technology are those for seeds for crop cultivation. During the 3-4 months of gum Arabic exploitation, the land user is obliged to survey his fields day and night, as intruders try to tap the Acacia senegal trees illegally. However, this task is fulfilled by the landuser himself and does not involve expenses for payed manpower.
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology site is located in the sylvopastoral region of the Ferlo in the north of Sénégal. The agro-climatic zone is classified as semi-arid with mean annual precipitation of 300-400 mm. The main land use type in the area is extensive pastoralism followed by rainfed agriculture. Pastoralism is primarily practiced by transhumant Fula (Peulh) herders and further by Mauritanian Moor herders with herds of dromedaries. Vegetation cover in the area has been largely degraded due to cutting for domestic uses and cattle feeding, bushfires and overgrazing. The soil is exposed to wind erosion which carries away nutrients in the topsoil and therefore declines soil fertility. During intense rains in the rainy season, surface runoff is accelerated and leads to the formation of gullies and ravines.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塞内加尔
区域/州/省:
Louga
有关地点的进一步说明:
Barkédji
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
family tradition: the father taught the sons not to cut any trees in their fields, as they have beneficial properties
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林业
主要产品/服务:
Major cash crop: Acacia senegal
Major food crop: Millet, groundnut, cowpea
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): degradation of vegetation cover, wind erosion, increased surface runoff, formation of gullies and ravines, management of natural water sources (people doing laundry and personal hygiene in temporal ponds used as sources of drinking water)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): wind erosion, water erosion, reduction of vegetation cover
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: July to October
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.35 km2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (absence of inorganic fertilizers, reduction of fallow period), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (domestic uses), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (oversized herds of cattle and dromadaires), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (during rainy season), population pressure (need for pasture and cultivable land), poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: organic manure (untreated)
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Get all the seeds | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物材料 | Seeds for millet | ha | 1.0 | 1.68 | 1.68 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds for groundnut | ha | 1.0 | 5.25 | 5.25 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds for cowpeas | ha | 1.0 | 7.85 | 7.85 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 14.78 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing of crops | 农业学的 | beginning of growing season once a year |
| 2. | Application of manure | 农业学的 | several times during growing season |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
The landuser has to spend 90-120 person days for surveillance of his Acacia senegal trees every year during the exploitation of gum arabic. No costs incur to the landuser because of this activity, as he or somebody from his family is undertaking the task.The protection of natural regeneration in the fields does not have any costs, as the young trees are not enclosured.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
seeds for crop planting
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
300.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
During one rainy season (july-september), dry period from october-mai
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics, in the sylvopastoral zone of the Ferlo
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: High (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, ranked 1, groundwater from borehole during dry season) and for agricultural use only (irrigation, ranked 2, water from temporary ponds during the rainy season)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Compared to the sudano-guinean zones of the country, this zone is not very species rich
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: women do not have the right to ask for land to cultivate, it can only been attributed to them by their husbands
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
22% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: no off-farm income (if income generated through gum exploitation is seen as farm income)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1) and Mixed (ranked 2, only gum from Acacia senegal is sold)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
The single landuser applying the technology exploits cropland of about 35 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
As the land user can count on income from gum exploitation he is less vulnerable to crop failure
产品多样性
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Applies especially for fallow part, cultivation might be entirely given up
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Income from gum arabic exploitation
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
冲突缓解
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Biological N-fixation (A.senegal), but amount questionable
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Through plant litterfall, application of manure
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Mainly applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part only little
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Applies for the cultivated part only
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Birds building nests in trees on fields
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
注释/具体说明:
Applies for the part left fallow, in the cultivated part negligible
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 未知 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
the landuser is expecting a rise in income through increased gum production
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
increase of crop production How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintain or increase number of trees in fields |
|
increase of income How can they be sustained / enhanced? assist natural regeneration of Acacia senegal |
|
provision of shade for cattle and increased availability of manure as consequence How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintain or increase number of trees in fields |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
increase of soil fertility increase of soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase the number of trees with positive impact on soil fertility improve manure application and increase number of trees in cultivated part |
|
reduction of wind erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase tree abundance |
| maintenance of woody species diversity |
|
improvement of soil cover How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase tree abundance |
| little to no costs of establishment |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| surveillance of Acacia senegal trees during exploitation season required | establish a fence |
| crop damaging birds find a habitat to build nests in trees | put scarecrows |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| tendency towards a monoculture of Acacia senegal (in the part of the field left fallow) | encourage natural regeneration of other local species as well |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块