Arboriculture in interdunal depression [塞内加尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Julie Zähringer
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Verger (français)
technologies_1168 - 塞内加尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CSE (CSE) - 塞内加尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
12/10/2013
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
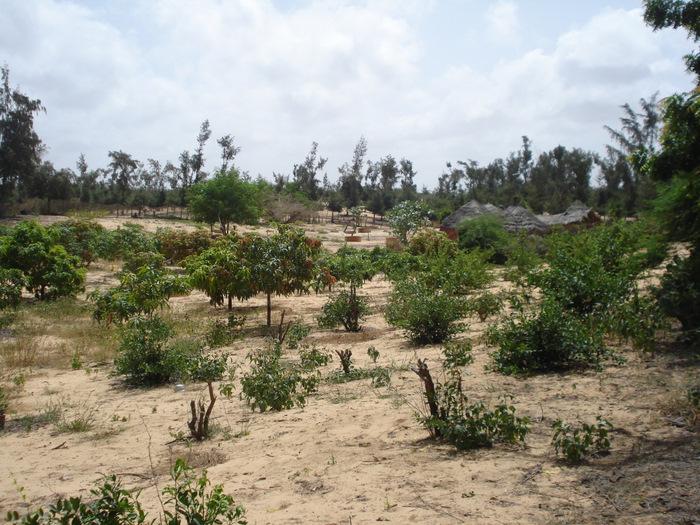
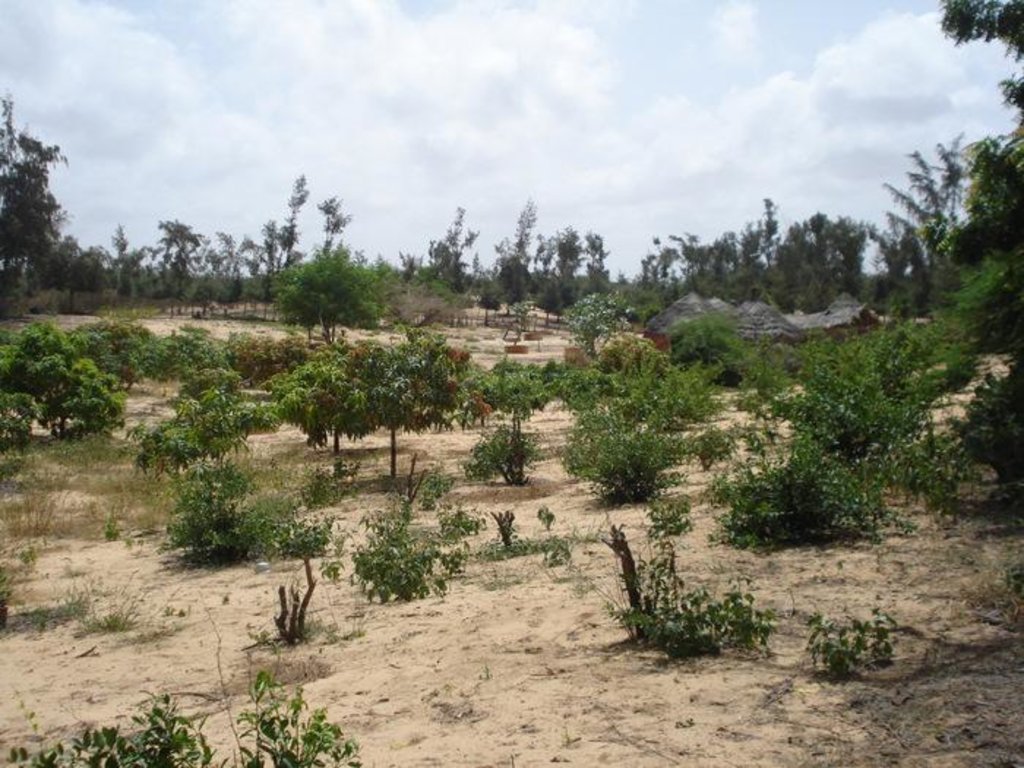
A small fruit orchard in between fixed wandering dunes mainly with Citrus lemon and Mangifera indica trees
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
This fruit orchard, mainly containing Mango (Mangifera indica) and Citrus (Citrus lemon) trees, is located in the hamlet of Thioukoun which is part of the village of Lompoul-sur-mer. The surface accounts for about 0.46 ha. Long before the establishment of the orchard, land cover consisted of denuded or sparsely covered white wandering sand dunes threatening agricultural production and villages alike. For some years vegetable production took place on this piece of land and later the orchard was established. Fruits are aimed at sale on the local market but production is insufficient for commercial purposes due to a pest and senescence of fruit trees. Citrus fruits are used by the cultivator and his family for pharmaceutical purposes. Inorganic fertilizers and organic manure are both used in order to improve soil fertility. Irrigation with water from one of the 8-9 m deep wells is practiced for a few Cocos nucifera plants but not for the other species. Labor is done by employees with whom the assigned caretaker of the orchard shares the little revenues from selling fruits on the market. The orchard is protected by a hedge made of dead Balanites aegyptiaca and Acacia raddiana branches and contains a small number of living individuals of other species.
Natural / human environment: The Niayes, located between Dakar and St. Louis, constitute a territory of 5-30 km width covering a surface of 4’200 km2. The region profits from a cool, humid climate, caused by the northern maritime winds (alizés) during the the dry season, while the rest of Senegal experiences the dry and hot Harmattan winds from the East. This results in favorable conditions for vegetable production during the dry season. Sand dunes cover the entire territory being categorized as white or wandering dunes, yellow semi-fixed dunes and as a system of continental fixed red dunes. The continental sand dunes support a shrub savanna which has been used as grazing ground by Fulbe pastoralists for centuries. The near-surface groundwater is the key that allows for cultivation of the zone, however considering the decline in rainfall during the last 60 years, the future of this water source remains uncertain. Lack of rainfall was one of the causes that led to the retreat of natural vegetation which therefore was not sufficient to stabilize the dunes any longer. Migration of sand dunes could now attain up to 10-12 m a year. However, deforestation at the beginning of the 19th century as well as overgrazing were important factors causing gradual desertification in this system.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塞内加尔
区域/州/省:
Department of Kébémer
有关地点的进一步说明:
Thioukun
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major casch crop: Mango, lemon
Major food crop: Mango, lemon
Other crops: Cocos
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): wind erosion
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul-Sept
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: retaining more vegetation cover, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (topography, dunes)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: trees
Quantity/ density: 340 / ha
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: cattle manure
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: fertilizer 10-10-20
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
300 mm, dry season 9 months with occasional showers
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Footslopes (sanddunes)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Relic species from guinean ecozone present
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Market orientation: Mixed (commercialisation difficult because of loss of production due to pest)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
The mango fly
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
风力搬运沉积物
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increased fruit availability |
| Maintenance of property rights of this piece of land (would be lost if uncultivated) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increased vegetation cover How can they be sustained / enhanced? renew senescing stand of mango and lemon trees |
|
Soil stabilization How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintain vegetation cover |
|
Increased product diversification How can they be sustained / enhanced? plant more different fruit trees, e.g. Ziziphus mauritiana, Neocarya macrophylla |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Pest | Subsidies for fertilizers |
| Lacking soil fertility and humidity |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Problems with infestation of mangos - "mouche blanche" | Pest management |
| Senescense of fruit tree stands | Renewal of fruit tree stands |
| Lacking soil fertility and humidity | Use improved compost and manure, leave land for fallow, increase vegetation cover |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块